Dissolution of partnership means partnership coming to an end while the firm still stands. Various reasons for the dissolution of partnership could be: Admission of a partner Death of a partner Retirement of a partner Dissolution of firm In the event of the above cases, the existing partnership is dRead more
Dissolution of partnership means partnership coming to an end while the firm still stands. Various reasons for the dissolution of partnership could be:
- Admission of a partner
- Death of a partner
- Retirement of a partner
- Dissolution of firm
In the event of the above cases, the existing partnership is dissolved and a new partnership is created with the new partners without affecting the firm.
A new partnership deed is created, in case there is a partnership deed agreed among partners and new profit-sharing ratios among the partners are decided, while the assets and liabilities of the firm remain the same.
Dissolution of a firm means the firm no longer exists. Various reasons for the dissolution of a partnership firm could be:
- Mutual decision of partners
- By the court of law
A partnership firm is dissolved by a court of law when there has been a non-compliance of law, the firm is engaged in illegal practices, or that the court’s opinion is that it is in the public interest for the firm to be dissolved.
The partnership is also dissolved with the dissolution of the firm but the converse need not be true.
When a firm is dissolved, there is a sequence that is followed to pay creditors and partners.
- First, outside creditors like banks, third party creditors are paid firstly with the cash available with the firm and then by selling the assets.
- Second, partners who have lent money in the form of a loan to the firm are paid.
- Lastly, if there is any surplus, partners are paid with the amount of their capital. In case of loss, partners are required to pay from their personal assets.
Dissolution of the firm can be done by the partners themselves and they could also appoint a third person to do so on the payment of fees, charges, the proportion of surplus, or any contract that has been agreed to.
To summarize, we can a draw a difference table as follows:
| Dissolution of Partnership | Dissolution of Partnership Firm |
| The partnership ends but the firm still stands. | A partnership firm no longer exists. |
| A new partnership deed is created by the mutual agreement of partners. | A new partnership firm is created if the partners decide. |
| Reasons:
· Admission · Retirement · Death |
Reasons:
· By court · Mutual decision of partners |



You must have knowledge of what depreciation is. Depreciation is the process of allocating the value of an asset over its useful life. It reduces the carrying value of the asset year by year till it is scraped. It is an expense (expense of using the asset for business purposes) and it is charged toRead more
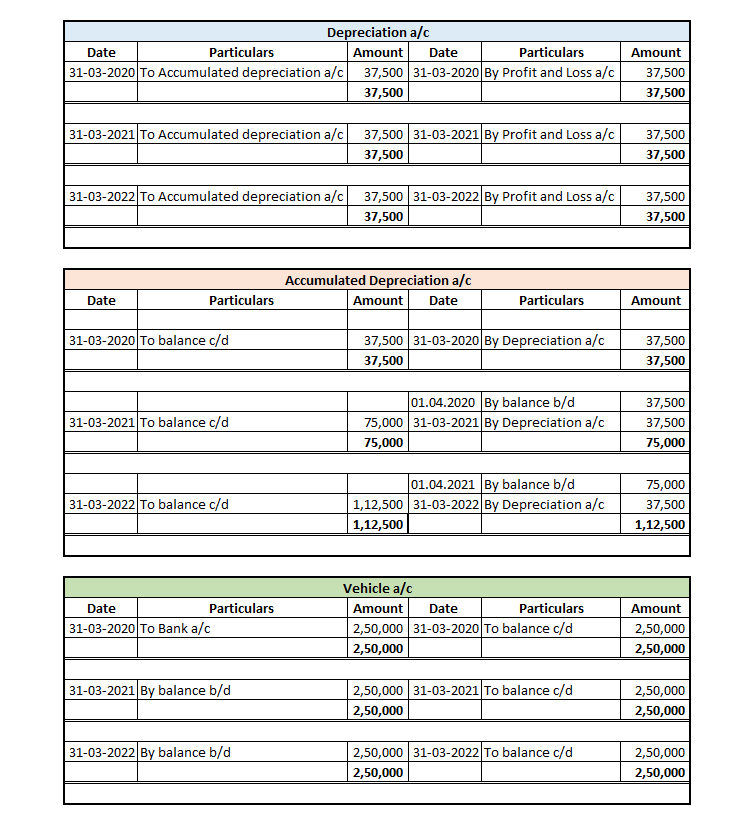
You must have knowledge of what depreciation is. Depreciation is the process of allocating the value of an asset over its useful life. It reduces the carrying value of the asset year by year till it is scraped.
It is an expense (expense of using the asset for business purposes) and it is charged to profit and loss account.
Depreciation can be reported in the financial statement in two ways:
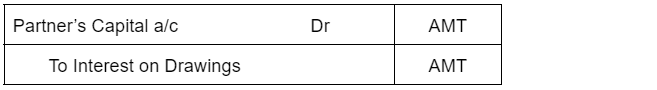
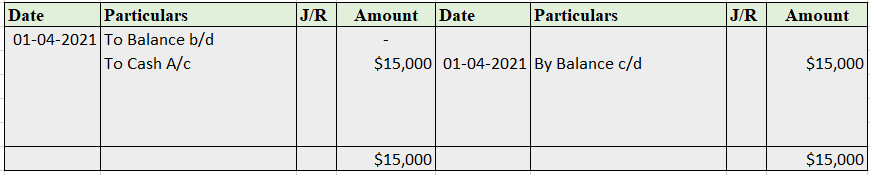
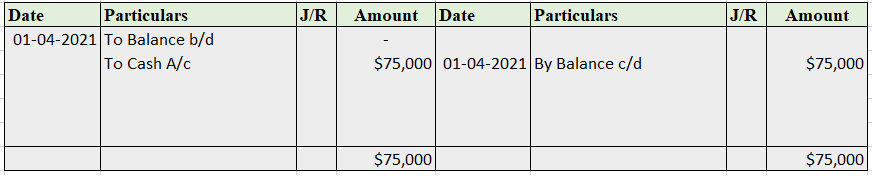
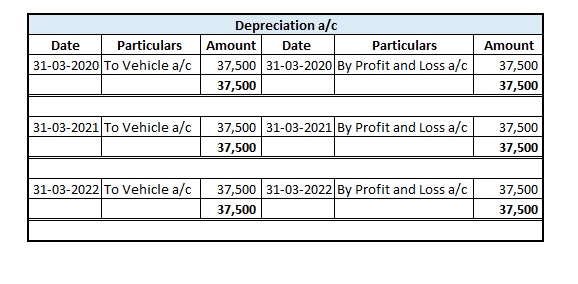
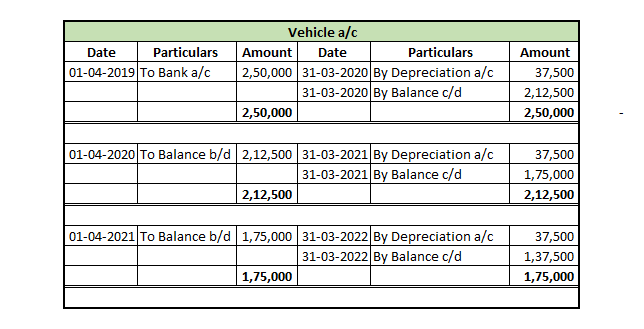
Provision for depreciation account represents the collection of total depreciation till date on an asset. That’s why it is also called accumulated depreciation account. When an asset is sold, its accumulated depreciation is credited to the asset account. See the journal entry below:
It is shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet. It is a nominal account because it is shown as an expense in the statement of profit or loss.
In case provision for depreciation account is not maintained then the balance sheet looks like this:

See less