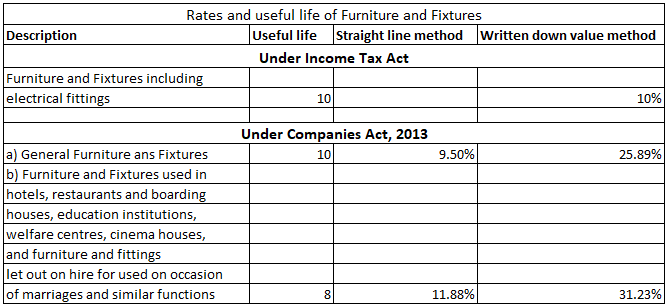
The Furniture and Fixture is depreciated @10% according to the income tax act and as per the companies act, 2013 @9.50% under Straight line method and @25.89% under written down value method. Furniture and fixture form a major part to furnish an office. For Example, the chair, table, bookshelves, etRead more
The Furniture and Fixture is depreciated @10% according to the income tax act and as per the companies act, 2013 @9.50% under Straight line method and @25.89% under written down value method.
Furniture and fixture form a major part to furnish an office. For Example, the chair, table, bookshelves, etc. all comes under Furniture and Fixture. The useful life of Furniture and Fixtures is estimated as 5-10 years depending upon the kind of furniture.
Rate of depreciation in reference to days
- If Furniture is bought and put to use for more than 180 days, then the full rate of depreciation will be charged.
- If the furniture is bought and put to use for less than 180 days, then half the rate of depreciation will be charged.
- If the furniture is bought but is not put to use, then no depreciation will be charged.

To begin with, lets us understand what the Companies Act 2013 tells about calls-in-advance, so basically as per section 50 of the companies act 2013 "A company may if so authorized by its articles, accepts from any members the whole or part of amount remaining unpaid on any share held by him, even iRead more
To begin with, lets us understand what the Companies Act 2013 tells about calls-in-advance, so basically as per section 50 of the companies act 2013 “A company may if so authorized by its articles, accepts from any members the whole or part of amount remaining unpaid on any share held by him, even if no amount has been called up”.
To be more precise whenever excess money is received by the company than, what has been called up is known as calls-in-advance.
Accounting Treatment
Well, it is to be noted that calls-in-advance is never a part of share capital. A company when authorized by its article can accept those advance amounts and directly credit the amount received to the calls-in-advance account.
As these advance amounts are a liability for the company these are shown under the head current liability of the balance sheet until calls are made and are paid to the shareholders.
Since this is the liability of the company, it is liable to pay the interest amount on such call money from the date of receipt until the payment is done to the shareholders. The rate of interest is mentioned in the articles of association. If the article is silent regarding the rate on which interest is paid then it is assumed to be @6%.
Accounting Entry
Bonnie let us understand the entries with help of an example
ADIDAS LTD issued 25,000 equity shares of Rs 10 each payable as follows:
ON APPLICATION Rs 5
ON ALLOTMENT Rs 3
ON FINAL CALL Rs 2
Application on 30,000 shares was received. excess money received on the application was refunded immediately. Mr. X who was allotted 1,000 shares paid the call money at the time of allotment and all amounts were duly received assume interest rate @6% for 3 months, so the relevant accounting entry goes as follows:
Important Points to be noted under calls-in-advance as per the companies act 2013
- The shareholder is not entitled to any voting rights on money paid until the said money is called for.
- No dividends are payable on advance money.
- Board may pay interest on advance not exceeding 12%.
- The shareholders are entitled to claim the interest amount as mentioned in the article, if there are no profits, then it must be paid out of capital because shareholders become the creditors of the company.
See less