The correct option is option A. Journal is the book of original entry. It is from the journal, the postings in the ledgers are made. As it is the journal first to record the transactions, it is called the book of original entry. It is from the journal, the postings in the ledgers are made. Ledgers aRead more
The correct option is option A.
Journal is the book of original entry. It is from the journal, the postings in the ledgers are made. As it is the journal first to record the transactions, it is called the book of original entry.
It is from the journal, the postings in the ledgers are made. Ledgers are called the books of principal book of entry.
Option B Duplicate is wrong as there is no such thing as the book of duplicate entry in financial accounting. Journal entries are the first-hand record of business transactions. Hence, it cannot be the book of duplicate entries.
Option C Personal is wrong. This classification of ‘personal’ is a type of account as per traditional rules of accounting, not books of accounts
Option D Nominal is wrong. It is also a type of account as per the traditional rules of accounting.
See less
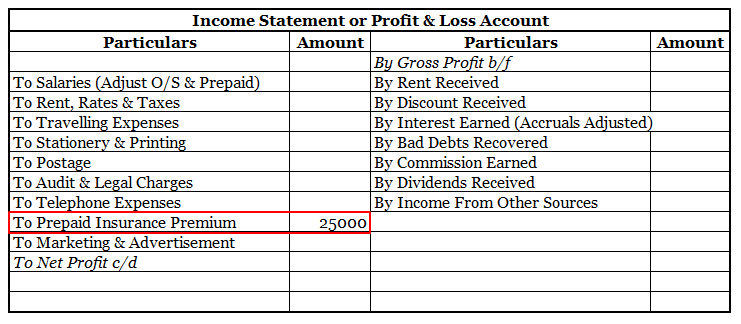
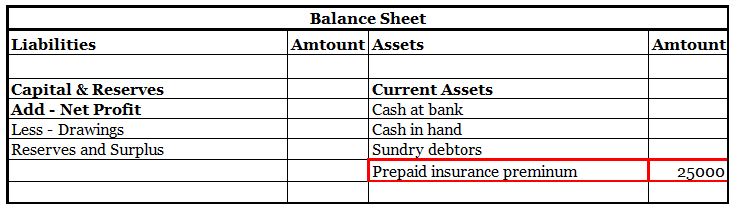
Definition Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable. Bad debts will be treated in the following ways : On the debit side of the profit and loss account. In the curreRead more
Definition
Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable.
Bad debts will be treated in the following ways :
On the debit side of the profit and loss account.
In the current assets side of the balance sheet, these are deducted from sundry debtors.
For example loans from banks are declared as bad debt, sales made on credit and amounts not received from customers, etc.
Now I will show you an extract of the profit and loss account and balance sheet
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or the rendering of services in the ordinary course of business.
For example, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Current liabilities are defined as liabilities that are payable normally within 12 months from the end of the accounting period or in other words which fall due for payment in a relatively short period.
For example bills payable, short-term loans, etc.
Accounting treatment
Now let me try to explain to you the accounting treatment for bad debts which is as follows :
Reasons for bad debts
There are several reasons why businesses may have bad debts some of them are as follows:-
Accounting methods
There are two methods for accounting for bad debts which are mentioned below:-
Related terms
So there are a few related terms whose meanings you should know
See less