The accounting equation for a non-profit organisation is almost the same as in the case of the profit-oriented organisation. Let's first briefly understand what accounting equation and non-profit organisation are: Accounting Equation Accounting equation is an equation that depicts the relationship bRead more
The accounting equation for a non-profit organisation is almost the same as in the case of the profit-oriented organisation. Let’s first briefly understand what accounting equation and non-profit organisation are:
Accounting Equation
Accounting equation is an equation that depicts the relationship between assets, liabilities and capital of an entity.
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
As per this equation, the total assets of an entity are equal to the sum of its total liabilities and total capital. This equation holds good in every situation.
Non-Profit Organisation
A Non-Profit Organisation is an entity which exists for purposes other than for profit. Such organizations exist and operate for charitable purposes, promotion of culture and sports and welfare of society. The accounting for Non-profit organisation is slightly different from For-profit organisations. In the case of a non-profit organisation, the capital account is known as the capital fund.
Accounting Equation for non-profit organisations
The Accounting equation for a non-profit organisation is as follows:
Assets = Liabilities + Capital fund.
The difference is only in name. In the case of non-profit organizations, the capital is known as a capital fund. Rest everything is the same. The accounting equation will be prepared as normally prepared for business concerns.
See less
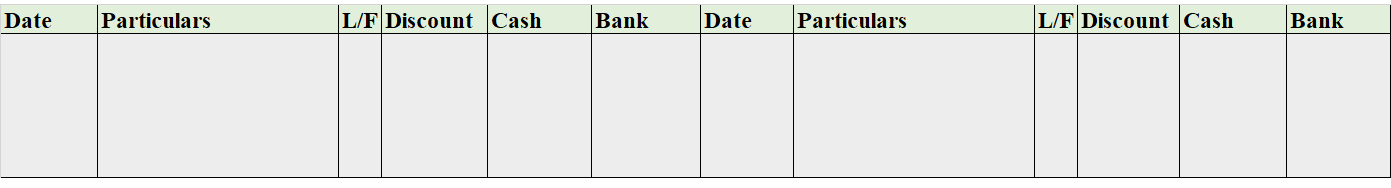
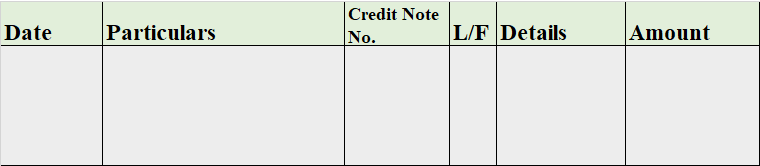
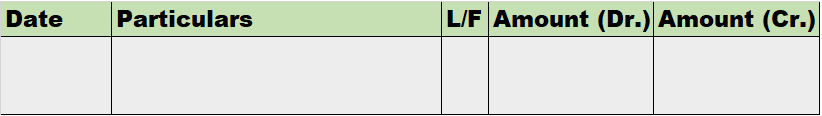
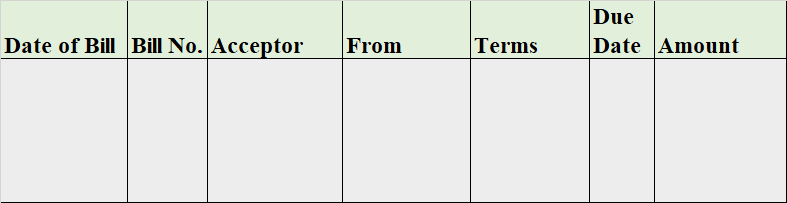
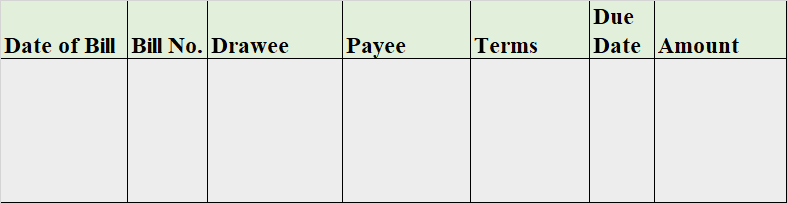
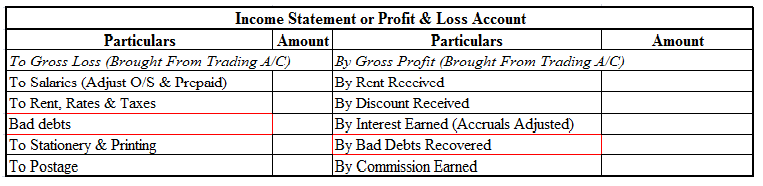
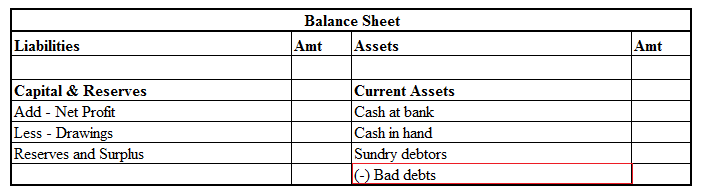
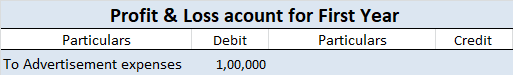
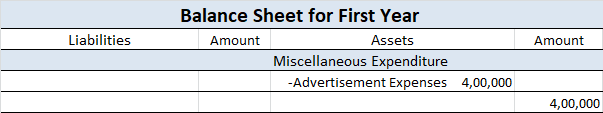
When it is said that furniture is purchased for office use, it means it is an asset for the business and the journal entry for this event will be the following: Furniture A/c Dr. Amt To Cash/Bank / Vendor A/c Cr. Amt (Being furniture purchased for office use) Explanation of the journal as per the goRead more
When it is said that furniture is purchased for office use, it means it is an asset for the business and the journal entry for this event will be the following:
Explanation of the journal as per the golden rules of accounting
The furniture account is a real account because it represents a material asset and the golden rule for real accounts is “Debit what comes in, credit what goes out”. Hence, the furniture account is debited as it is increased. The cash and bank are also real accounts and they are debited because there is an outflow from cash or bank.
If the furniture is purchased on credit then the vendor account is credited. A vendor account represents a person and the golden rule for personal accounts is, “Debit the receiver, credit the giver”. It is credited as the furniture is given by the vendor.
Explanation of journal as per modern rules of accounting
The furniture account is an asset account hence it is debited as asset accounts are debited on increase. Cash and bank accounts are also assets accounts and they are credited as they are decreased on the purchase of furniture.
A vendor account is a liability account as there is an obligation to pay the vendor. It is credited as it is increased. Liability accounts are credited on the increase and vice versa.
When furniture is purchased for personal use
If the furniture is purchased for personal use and the payment is made or is to be made out of business, then the asset will not be recognised as an asset for the business and it will be recorded as a drawing. It will be deducted out of capital. The journal entry will be the following:
See less