A. Normal wear and tear B. Foreseen obsolescence C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence D. Unforeseen obsolescence
Capital Expenditure Capital expenditure refers to the money a business spends to buy, maintain, or improve the quality of its assets. Capital expenditures are the expenses incurred by an organization for long-term benefits, i.e on the long-term assets which help in improving the efficiency or capaciRead more
Capital Expenditure
Capital expenditure refers to the money a business spends to buy, maintain, or improve the quality of its assets. Capital expenditures are the expenses incurred by an organization for long-term benefits, i.e on the long-term assets which help in improving the efficiency or capacity of the company. These expenses are borne by the company to boost its earning capacity.
The investment done by the companies on assets is capital in nature and through capital expenditure, the company may use it for acquiring new assets or may use it in the maintenance of previous ones. These expenditures are added to the asset side of the balance sheet.
Example: Purchase of machinery, patents, copyrights, installation of equipment, etc.
Revenue Expenditure
Revenue expenditure refers to the routine expenditures incurred by the business to manage day-to-day expenses. They are incurred for a shorter duration and are mostly limited to an accounting year. These expenses are borne by a company to sustain its profitability. These expenditures are shown in the income statement.
These expenditures do not increase the revenue but stay maintained. These expenses are not capitalized.
They are divided into two sub-categories:
- Expenditures for generating revenue for a business- Those expenditures essential for meeting the operational cost of the business are further classified as operating expenses.
- Expenditures for maintaining revenue-generating assets- Those expenses incurred by the business for repairing and maintenance of the assets of an organization to keep them in a working state.
Example: Wages, salary, insurance, rent, electricity, taxes, etc.
See less
Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence. Normal wear & tear refers to the damage caused to an asset due to its continuous usage. Even when the asset is properly maintained, wear and tear occurs. Hence, it is considered to be inevitableRead more
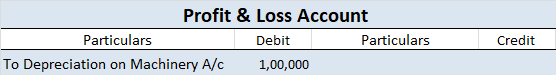
Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence.
Normal wear & tear refers to the damage caused to an asset due to its continuous usage. Even when the asset is properly maintained, wear and tear occurs. Hence, it is considered to be inevitable and natural.
For example, Kumar has purchased a car for 25,00,000. After five years he wishes to sell his car. Now the market price of his used car is 12,00,000. This reduction in the value of the car from 25,00,000 to 12,00,000 is because of its usage. This fall in the value of the asset due to usage is known as normal wear & tear.
In generic terms, obsolescence means something that has become outdated or is no longer being used. Foreseen obsolescence is nothing but obsolescence that is expected.
In the context of business, whenever the value of an asset falls because it has become outdated or is replaced by a superior version, we call it obsolescence. The fall in the value of the asset due to obsolescence expected by the purchaser of the asset is known as foreseen obsolescence.
When an asset becomes obsolete it doesn’t mean it is not in working condition. Even when an asset is in good working condition it can become obsolete due to the following reasons:
For example, before the invention of computers, people used typewriters for getting their paperwork done. With the invention of computers, laptops, etc. it is easier to type as well as save our documents, spreadsheets, etc. Thus typewriters became obsolete with the invention of computers. It has become a technology of the past.
Here is a summarised version of wear & tear and obsolescence:

See less