Meaning We know that an account in ledger format has two amount columns i.e. debit and credit amount columns. Now, most of the time, the total of debit and credit sides do not match. The difference between their totals is called the balance of the account and it is posted on the shorter side. ThisRead more
Meaning
We know that an account in ledger format has two amount columns i.e. debit and credit amount columns. Now, most of the time, the total of debit and credit sides do not match. The difference between their totals is called the balance of the account and it is posted on the shorter side. This result in equalling the total of both sides, hence this act is called ‘balancing an account.
Types of balances
Balancing an account is a very usual practice so that the balance of an account can be known. An account can have two types of balances:
- Debit balance, where the debit side total is more than the credit side total.
- Credit balance, where the credit side is more than the debit side total.
The balance of an account is posted on the shorter side. It means:
- The debit balance will be shown on the credit side as the credit side total is shorter. (posted as ‘By Balance c/d’)
- The credit balance will be shown on the debit side as the debit side total is shorter (posted as ‘To Balance c/d’)
Example
The following is a cash account that is not balanced:
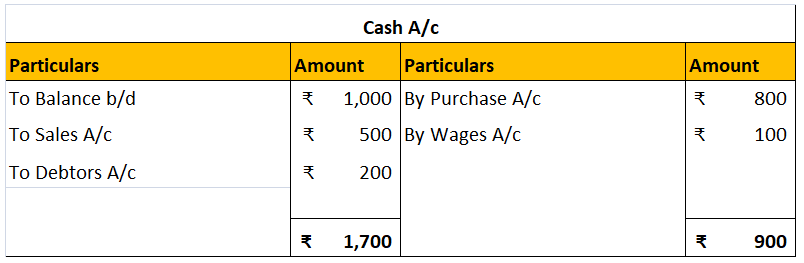
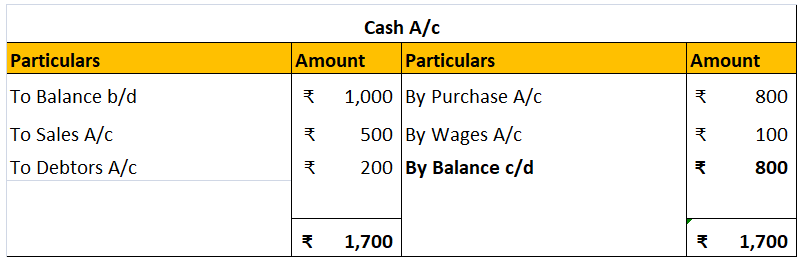
We can see the debit side is ₹800 more than the credit side. It means there is a debit balance. It will be posted on the credit side as ‘By balance c/d’ to balance the account.
Exceptions
Balance of the income and the expense accounts (nominal accounts)are not computed. Instead, they are closed to trading account or profit and loss account to balance their amount totals. For example, the salaries account and sales accounts
Only the balance of the following types of accounts are computed and carried forwarded to successive accounting years:
- Assets
- Liabilities
- Capital
The balance of these accounts is shown on the trial balance and balance sheet as well.
See less
Goods and services tax (GST) is an indirect tax that was introduced in place of other indirect taxes like value-added tax, service tax, purchase tax, etc. It was introduced to ensure that only one tax would be applicable all over India. Reverse Charge is a mechanism where the liability to pay tax onRead more
Goods and services tax (GST) is an indirect tax that was introduced in place of other indirect taxes like value-added tax, service tax, purchase tax, etc. It was introduced to ensure that only one tax would be applicable all over India. Reverse Charge is a mechanism where the liability to pay tax on goods and services lies on the recipient instead of the supplier.
APPLICABILITY
Reverse charge is applicable when:
TIME OF SUPPLY
As per reverse charge in the case of goods, the time of supply is the earliest of the three:
For example, If goods were received by the supplier on 15th June, and the date of the invoice was on 3rd July but the date of entry in the books of the receiver was 25th June, then the time of supply of goods would be on 15th June.
As per reverse charge in the case of services, the time of supply is the earliest of the two:
For example, if the date of payment of services provided was on 16th July, and the date of issue of the invoice was on 15th May ( 60 days from 15th May is 14th July), then the time of supply of services would be 14th July.
See less