Fictitious assets are not actually assets. They are expenses/losses not written off in the year in which they are incurred. They do not have any physical presence. Their expense is spread over more than one accounting period. A part of the expense is amortized/written off every year against the compRead more
Fictitious assets are not actually assets. They are expenses/losses not written off in the year in which they are incurred. They do not have any physical presence. Their expense is spread over more than one accounting period.
A part of the expense is amortized/written off every year against the company’s earnings. The remaining part (which is yet to be written off) is shown as an asset in the balance sheet. They are shown as assets because these expenses are expected to give returns to the company over a period of time.
Here are some examples of fictitious assets:
- Preliminary expenses.
- Promotional expenses.
- Loss incurred on the issue of debentures.
- Underwriting commission.
- Discount on issue of shares.
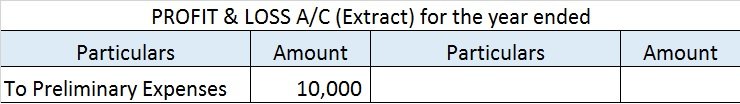
To make it simple I’ll explain the accounting treatment of preliminary expenses with an example.
The promoters of KL Ltd. paid 50,000 as consultation fees for incorporating the company. The consultation fee is a preliminary expense as they are incurred for the formation of the company. The company agreed to write off this expense over a period of 5 years.
At the end of every year, the company will write off 10,000 (50,000/5) as an expense in the Profit & Loss A/c.
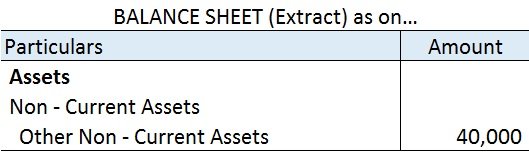
The remaining portion i.e. 40,000 (50,000 – 10,000) will be shown on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet under the head Non – Current Assets and sub-head Other Non – Current Assets.
Here are the financial statements of KL Ltd.,
Note: As per AS 26 preliminary expenses are fully written off in the year they are incurred. This is because such expenses do not meet the definition of assets and must be written off in the year of incurring.
Source: Some fictitious assets examples are from Accountingcapital.com & others from Wikipedia.
See less

Sales Return is shown on the debit side of the Trial Balance. Sales Return is also called Return Inward. Sales Return refers to those goods which are returned by the customer to the seller of the goods. The goods can be returned due to various reasons. For example, due to defects, quality differenceRead more
Sales Return is shown on the debit side of the Trial Balance.
Sales Return is also called Return Inward.
Sales Return refers to those goods which are returned by the customer to the seller of the goods. The goods can be returned due to various reasons. For example, due to defects, quality differences, damaged products, and so on.
In a business, sales is a form of income as it generates revenue. So, when the customer sends back those goods sold earlier, it reduces the income generated from sales and hence goes on the debit side of the trial balance as per the modern rule of accounting Debit the increases and Credit the decreases.
For Example, Mr. Sam sold goods to Mr. John for Rs 500. Mr. John found the goods damaged and returned those goods to Mr. Sam.
So, here Sam is the seller and John is the customer.
The journal entry for sales return in the books of Mr. Sam will be
Treatment in Trial Balance

See less