A Capital Account is an account that shows the owner's equity in the firm and a Partner's Capital Account is an account that shows the partner's equity in a partnership firm. Partner’s Capital Account includes transactions between the partners and the firm. Examples of such transactions are: CapitalRead more
A Capital Account is an account that shows the owner’s equity in the firm and a Partner’s Capital Account is an account that shows the partner’s equity in a partnership firm.
Partner’s Capital Account includes transactions between the partners and the firm. Examples of such transactions are:
- Capital introduced in the firm
- Capital withdrawn
- Interest on Capital
- Interest on Drawings
- Profit or loss in the financial year, etc.
When partners are given interest on their capital contribution in the firm, it is called on Interest on Capital.
In case the partnership firm does not have a Partnership Deed, the Partnership Act does not include a provision for Interest on Capital. However, if the partners want they can mutually decide the rate of Interest on Capital.
Interest on Capital is calculated on the opening capital of the partners and is only allowed when the firm makes a profit, that is, in case a firm incurs losses, it cannot allow Interest on Capital to its partners.
Example:
In a partnership firm, there are two partners A and B, and their capital contribution is Rs 10,000 and 20,000 respectively. Interest on capital is @ 10% p.a. The Interest on Capital for both the partners is:
Partner A- 10,000 * 10/100 = 1,000
Partner B- 20,000 * 10/100 = 2,000
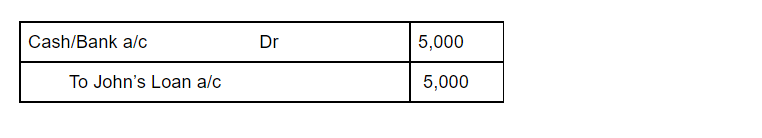
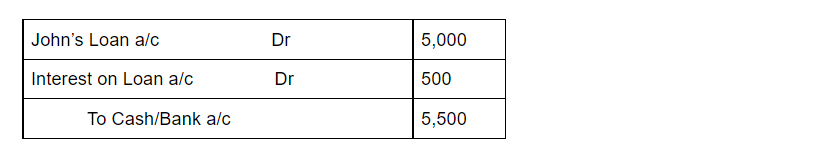
The journal entry for Interest on Capital is an adjusting entry and is shown as:
| Interest on Capital A/c Dr. | 3,000 | |
| To A’s Capital a/c | 1,000 | |
| To B’s Capital A/c | 2,000 |
- Partner’s Capital Account is credited because it is credit in nature and interest on capital is an addition to the account.
- Interest on Capital Account is debited because it is an expense account.
See less

A contra account is a general ledger account that is used to reduce the value of the account related to it. Basically, a contra account is the opposite of its associated account. If the associated account has a debit balance, then the contra account would have a credit balance. They are used to mainRead more
A contra account is a general ledger account that is used to reduce the value of the account related to it. Basically, a contra account is the opposite of its associated account. If the associated account has a debit balance, then the contra account would have a credit balance. They are used to maintain the historical value of the main account while all the deductions are recorded in the contra account, which when clubbed together show the net book value.
For example
if the cost of machinery was Rs. 50,000 and the company wants to preserve its original cost, then the accumulated depreciation of such machinery is recorded separately. Let’s say Rs 10,000 was the accumulated depreciation. Then such amount is recorded in the contra account named accumulated depreciation account. This makes the net value of the machinery Rs 40,000.
Types
There are various types of contra accounts such as contra asset, contra equity, contra revenue, and contra liability.
Accountants make use of contra accounts instead of reducing the value of the actual account to keep the financial statements clean.
See less