The term ‘bad debt’ and ‘write off’ are often used together in a sentence but they have different meanings. First, we will discuss them in brief to understand the differences between them. Bad debts We know, debtors for a business are their assets because the business has the right to receive moneyRead more
The term ‘bad debt’ and ‘write off’ are often used together in a sentence but they have different meanings. First, we will discuss them in brief to understand the differences between them.
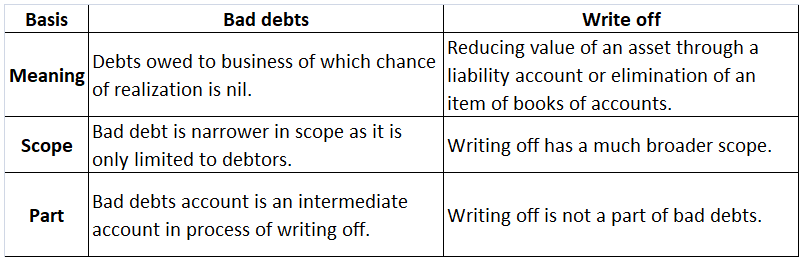
Bad debts
We know, debtors for a business are their assets because the business has the right to receive money from the debtors due to the goods supplied to them.
But if due to circumstances, there appears no probability that the amount due to one or more debtors will be realised to the business, then such debts are categorised as bad debts.
In short, bad debts refer to the amount of money that will not be received from some debtors of the business due to some circumstances like insolvency of debtor etc.
Bad debt is deducted from debtors account by the following journal entry:
| Bad debts A/c | Dr. | Amt |
| To Debtors A/c | Cr. | Amt |
| (Being bad debts written off from debtors) |
As bad debts are losses to a business, it is ultimately written off from the profit and loss account.
| Profit and loss A/c | Dr. | Amt |
| To Bad debts A/c | Cr. | Amt |
| (Being bad debts written off to profit and loss account) |
Write off
In layman terms, write off means to deduct something out from something. In accounting, write off means to deduct or reduce value of assets by crediting it to a liability account which is usually a reserve account or the profit and loss account.
It also refers to the elimination of an item from the books of accounts particularly losses and expenses.
Generally, writing off is associated with the following:
- Bad debts.
- Damaged Inventories.
- Loss on issue or redemption of debentures.
- Preliminary expenses.
- Bad loans and advances.
Write off can be done in one of the following methods:
- Direct write-off: The write off is directly done by crediting asset account or loss account and debiting the reserve or P/L account.
- Indirect write-off: Here, an intermediate account is involved between the asset account and liabilities account. A common example is writing off of bad debts where the bad debts account is the intermediate account.
Hence, the following differences can be observed between bad debts and write off or writing off:

Activity-based costing (ABC) is a system used to find production costs. It breaks down overhead costs between production-related activities and other activities. The ABC system assigns costs to each activity that goes into production, such as workers testing a product. ABC is based on the principleRead more
Activity-based costing (ABC) is a system used to find production costs.
It breaks down overhead costs between production-related activities and other activities.
The ABC system assigns costs to each activity that goes into production, such as workers testing a product. ABC is based on the principle that ‘products consume activities.’
Traditional cost systems allocate costs based on direct labor, material costs, revenue, or other simplistic methods. As a result, traditional systems tend to over-cost high volume products, services, and customers; and under-cost low volume.
Hence, Activity Based Costing was developed for determining the cost. The basic feature of ABC is its focus on activities. It uses activities as the basis for determining the costs of products or services.
Activity-Based Costing is mostly used in manufacturing industries, however, its application is not only limited to that. Various industries like, construction, health care, medical organizations also use this method of assigning costs. Industries where customized products are made also tend to use such methods as it is easier to charge appropriate overhead costs from the customer.
Objectives of Activity-Based Costing:
Companies adopt ABC to assign cost elements to the products, activities, or services so that it helps the management to decide:
Advantages of Activity Based Costing are:
Before implementing ABC, a company should consider the following:
Formula= Total Cost Pool / Cost Driver
For example:
For a company, the salary for workers is Rs 1,00,000 for a financial year, the number of labor hours worked is 50,00 hrs. The cost driver rate is calculated by dividing the workers’ salary by the labor hours worked, that is,
Salary of the workers / Number of labor hours
Rs 1,00,000 / 50,000 hrs = Rs 2 per labor hour.
In the above example, the salary of the workers is the total cost pool or the overhead cost for which we want to find the cost driver rate and labor hours is the cost driver, that is, on the basis of what we want to find the rate.
See less