When a partnership firm decides to admit a new partner into their firm, the old partners have to forego a part of their share for the new partner. Therefore, sacrificing Ratio is the proportion in which the existing partners of a company give up a part of their share for the new partner. The partnerRead more
When a partnership firm decides to admit a new partner into their firm, the old partners have to forego a part of their share for the new partner. Therefore, sacrificing Ratio is the proportion in which the existing partners of a company give up a part of their share for the new partner. The partners can choose to forego their shares equally or in an agreed proportion.
Before admission of the new partner, the existing partners would be sharing their profits in the old ratio. Upon admission, the profit-sharing ratio would change to accommodate the new partner. This would give rise to the new ratio. Hence Sacrificing ratio formula can be calculated as:
Sacrificing Ratio = Old Ratio – New Ratio
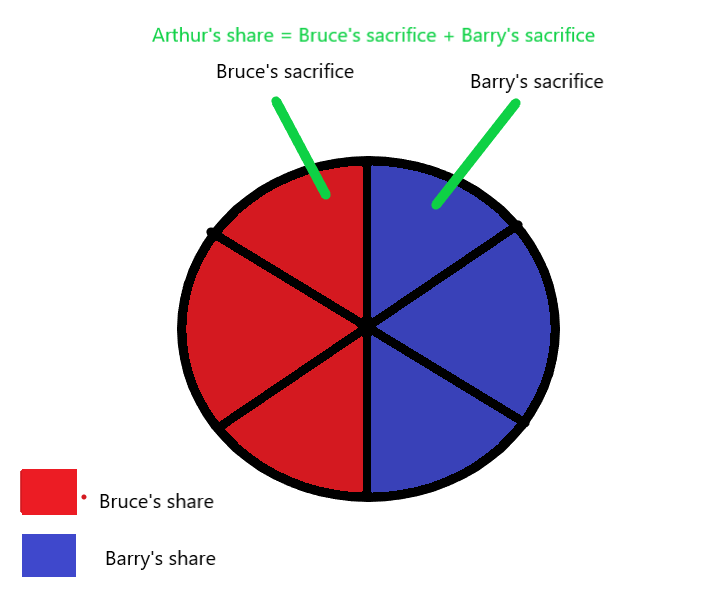
To further understand the formula, let’s say Bruce and Barry are sharing a pizza of 6 slices equally (3 slices each). They decide to share their pizza with Arthur such that they all get equal slices (2 slices each). Hence, we can use the formula to calculate their sacrifice as follows:
Bruce’s sacrifice = 3 – 2 = 1 slice
Barry’s sacrifice = 3 – 2 = 1 slice
Therefore, their sacrificing ratio = 1:1. In this same way, we can solve various problems to calculate the sacrifice of partners during a change in their profit sharing ratio.
For example, Joshua and Edwin are partners, sharing profits in the ratio 7:3. They admit Adam into their partnership such that the new profit-sharing ratio is 5:2:3. Therefore, their sacrificing ratio can be calculated as:
Joshua’s sacrifice = old share – new share = 7/10 – 5/10 = 2/10
Edwin’s sacrifice = old share – new share = 3/10 – 2/10 = 1/10
Hence, sacrificing ratio of Joshua and Edwin is 2:1. Once the denominators are equal, we ignore them and only consider numerators while showing sacrificing ratio.
See less
Accumulated profit is the amount of profit left after the payment of dividends to the shareholders. It is also known as retained earnings. It is the profit that is not distributed as dividends to shareholders, hence called retained earnings. This accumulated profit is an important source of internalRead more
Accumulated profit is the amount of profit left after the payment of dividends to the shareholders. It is also known as retained earnings. It is the profit that is not distributed as dividends to shareholders, hence called retained earnings. This accumulated profit is an important source of internal finance for a company. Accumulated profit or retained earnings can be ascertained using the following formula:
Accumulated profit = Opening balance of accumulated profit + Net Profit/Loss (loss being in the negative figure) – Dividend paid
Accumulated profit can be put to the following uses:
Accumulated profit and reserves are often considered the same. But in substance, they are not. The reserves are actually part of the accumulated profit, but the converse is not true. They are created by transferring amounts from the accumulated profit. While reserves are created for purpose of strengthening the financial foundation of a firm, the accumulated profit’s main purpose is to make reinvest in the business to increase its growth.
The amount of accumulated profits depends upon the retention ratio and dividend payout ratio of a company. The retention ratio is the opposite of the dividend payout ratio.
The formula of dividend pay-out ratio = Dividend payable/Net Income
And retention ratio = 1 – (Dividend payable/Net Income)
If the retention ratio is more than the dividend payout ratio, the accumulated profit remains positive.
See less