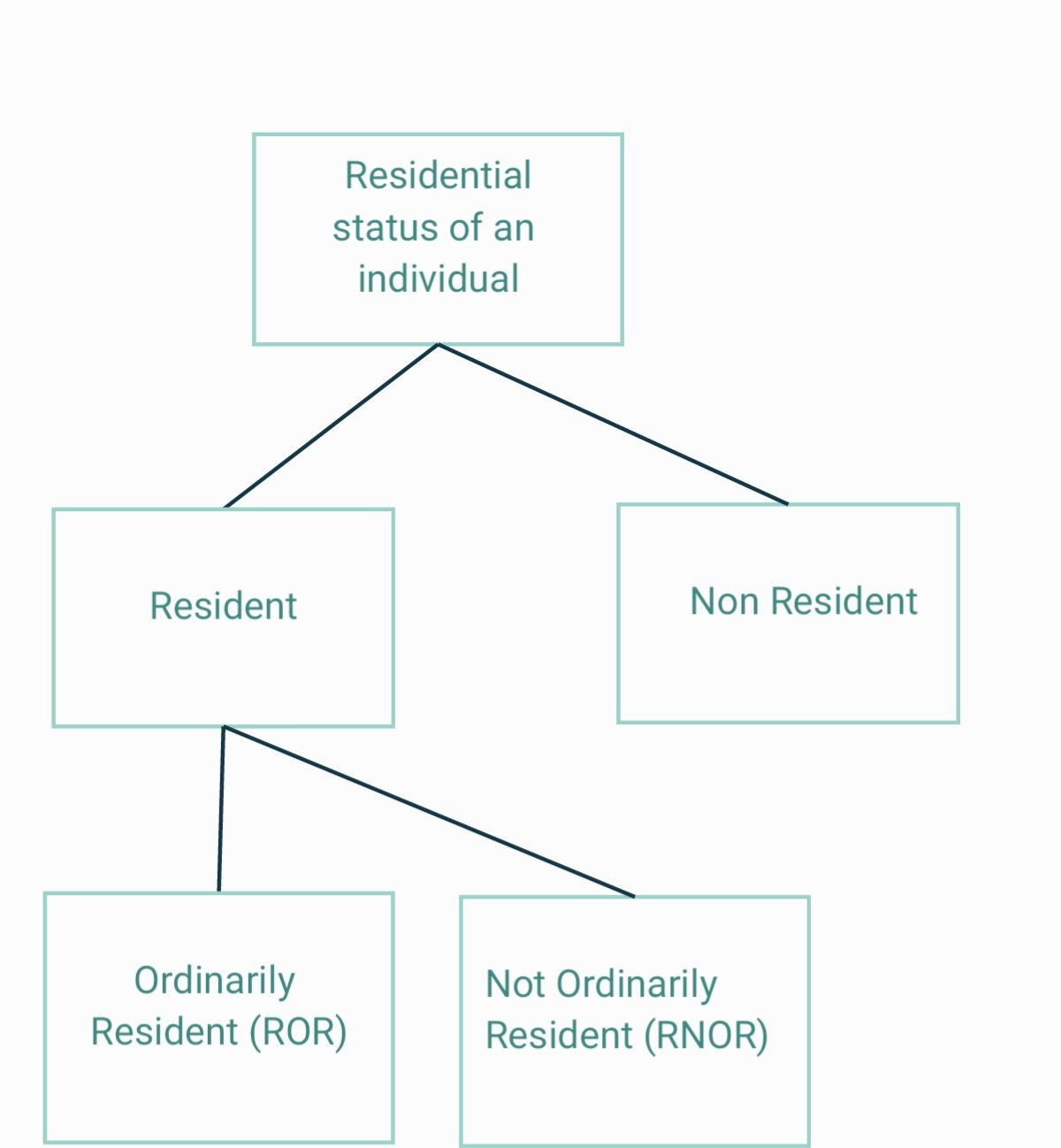
AS-11: The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates deal with the issues in the translation of foreign currency transactions and foreign operations. Foreign operations of a reporting enterprise mean its subsidiary, associate, joint venture or branch which is based or conducted in a country otherRead more
AS-11: The effects of changes in foreign exchange rates deal with the issues in the translation of foreign currency transactions and foreign operations.
Foreign operations of a reporting enterprise mean its subsidiary, associate, joint venture or branch which is based or conducted in a country other than the country of the reporting entity
For simple understanding let’s consider foreign operation as a branch of a business that is based in a foreign country.
Foreign Integral operations
So, integral foreign operations will be a dependent branch that works on the directions of the head office and it is like an extension of the business. The head office consigns goods to it and it sells them and remits cash and reports to the head office.
It is dependent on head office for receiving goods to sell and to cover its expenses.
Further, the difference in foreign exchange rate affects the present and future cash flows to the head office.
Foreign Non-Integral operations
A non-integral foreign operation will be like an independent branch that can operate without the aid of the head office. Apart from selling goods of the head office, it also buys goods from the local market and sells them.
Also, it covers its expenses on its own. It doesn’t remit the cash from sales regularly like a dependent branch. It is like acts an investment of the main business.
The difference in the foreign exchange rate has little or no effect on the present or future cash flows of the head office
See less
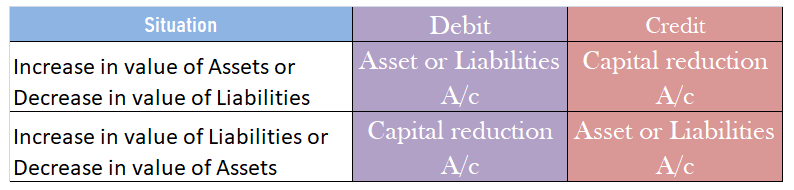

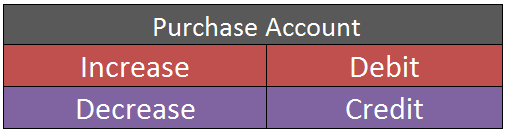
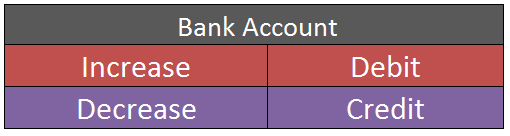
The journal entry for asset purchase is- Particulars Amount Amount Asset A/c Dr $$$ To Bank A/c $$$ According to the Modern Approach for Assets Account: When there is an increase in the Asset, it is ‘Debited’. When there is a decreaseRead more
The journal entry for asset purchase is-
According to the Modern Approach for Assets Account:
So the journal entry here is about the purchase of an asset and since there is an increase in Asset, the assets account will be debited as per the modern rule and due to the decrease of cash in the bank account, it will be credited.
For Example, Richard purchased furniture worth Rs 6,000 for his business.
I will try to explain it with the help of steps.
Step 1: To identify the account heads.
In this transaction, two accounts are involved, i.e. Furniture A/c and Bank A/c as Richard has acquired the furniture paying a certain amount.
Step 2: To Classify the account heads.
According to the modern approach: Furniture A/c is an Asset account and Bank A/c is also an Asset account.
According to the traditional approach: Furniture A/c is a Real account and Bank A/c is also a Real account.
Step 3: Application of Rules for Debit and Credit:
According to the modern approach: As asset increases because Furniture has been bought, ‘Furniture A/c’ will be debited. (Rule – increase in Asset is debited).
Bank account is also an Asset account. As the asset is in the form of cash decreases because the amount has been paid by cash or cheque, Bank account will be credited. (Rule – decrease in Asset is credited).
According to the traditional approach: Furniture A/c is a Real account and Bank is also a Real account, for which the rule to be applied is ‘Debit what comes in and Credit what goes out’. Furniture being asset comes in the business, so Furniture A/c will be debited and as cash goes out Bank A/c will be credited.
So from the above explanation, the Journal Entry will be-
See less