Meaning of Partnership Deed A Partnership Deed is a written agreement between partners who are willing to form a Partnership Firm. It is also called as a Partnership Agreement. Contents of a Partnership Deed A Partnership Deed shall mainly include the following contents: Name of the Partnership firmRead more
Meaning of Partnership Deed
A Partnership Deed is a written agreement between partners who are willing to form a Partnership Firm. It is also called as a Partnership Agreement.
Contents of a Partnership Deed
A Partnership Deed shall mainly include the following contents:
- Name of the Partnership firm
- Address of the Partnership firm
- Details of all the Partners
- Date of commencement of the Business
- The amount of capital contributed by each of the partners forming the Partnership firm
- The Profit sharing ratio (The Business profit shared among the partners on a ratio basis)
- The rate or amount of Interest on Capital & the rate or amount of Interest on drawings to each partner respectively.
- The salary payable to each of the partners of the firm.
- The rights, duties, and power of each partner of the firm.
- The duration of the existence of the firm
Importance of Partnership Deed
- Proper regulation of duties, liabilities, and rights of the partners are made in the partnership deed and hence there cannot be any issue during the course of the business.
- There can be no disputes between the partners upon Profit sharing, salary, commission, interest on capital, and interest on drawings.
- A partnership Deed acts as Legal proof for the conduct of the business and is used for many other registrations such as GST registration, and other related purposes.
Format of a Partnership Deed
The Partnership Deed shall originally be executed on an Indian Non-Judicial stamp paper.
The format of the Partnership deed is given below with an assumption that 4 partners are forming the Partnership.
PARTNERSHIP DEED
This deed of partnership is made on [Date, Month, Year] between:
1. [First Partner’s Name], [Son/Daughter] of [Mr. Father’s Name], residing at [Address Line 1, Address Line 2, City, State, Pin Code] hereinafter referred to as FIRST PARTNER.
2. [Second Partner’s Name], [Son/Daughter] of [Mr. Father’s Name], residing at [Address Line 1, Address Line 2, City, State, Pin Code] hereinafter referred to as SECOND PARTNER.
3. [Third Partner’s Name], [Son/Daughter] of [Mr. Father’s Name], residing at [Address Line 1, Address Line 2, City, State, Pin Code] hereinafter referred to as THIRD PARTNER.
4. [Fourth Partner’s Name], [Son/Daughter] of [Mr. Father’s Name], residing at [Address Line 1, Address Line 2, City, State, Pin Code] hereinafter referred to as FOURTH PARTNER.
Whereas, the parties hereto have agreed to commence business in partnership and it is expedient to have a written instrument of partnership. Now, this partnership deed witnesses as follows:
1. BUSINESS ACTIVITY
The parties hereto have mutually agreed to carry on the business of [Description of Business Activity Proposed].
2. PLACE OF BUSINESS
The principal place of the partnership business will be situated at [Address Line 1, Address Line 2, City, State, Pin Code]
3. DURATION OF PARTNERSHIP
The duration of the partnership will be at will.
4. CAPITAL OF THE FIRM
Initially, the capital of the firm shall be Rs. [Total Partners Contribution].
5. PROFIT SHARING RATIO
The profit or loss of the firm shall be shared equally among all the partners and transferred to the partner’s current account.
6. MANAGEMENT
The [First Partner] of the firm shall be Managing Partner and he will look after all the day-to-day transactions of the firm and any legal activities in the name of the firm and the remaining partners shall cooperate to do so.
7. OPERATION OF BANK ACCOUNTS
The firm shall open a current account in the name of [Partnership Firm Name] at any bank and such account shall be operated by [First Partner] and [Second Partner] jointly as declared from time to time to the Banks.
8. BORROWING
The written consent of all Partners will be required for the partnership to avail credit facilities from any financial institution.
9. ACCOUNTS
The firms shall regularly maintain in the ordinary course of business, true and correct accounts of all its transactions and also of all its assets and liabilities, the property books of account, which shall ordinarily be kept at the firm’s place of business. The accounting year shall be the financial year from 1st April onwards and the balance sheet shall be properly audited and the same shall be signed by all the Partners. Every Partner shall have access to the books and the right to verify their correctness.
10. RETIREMENT
If any partner shall at any time during the subsistence of the partnership, be desirous of retiring from the firm, it shall be competent from his to do so, provided he shall give at least one calendar month’s notice of his intention of doing so. The remaining partner shall pay the retiring partner or his legal representatives of the deceased partner, the purchase money of his share in the assets of the firm.
11. DEATH OF PARTNER
In the event of the death of any partners, one of the legal representatives of the deceased partner shall become the partner of the firm and in the event, the legal representative shows their denial to point the firm, they shall be paid part of the purchase amount calculated as on the date of the death of the partner.
12. ARBITRATION
Whenever there by any difference of opinion or any dispute between the partners shall refer the same to the arbitration of one person. The decision of the arbitration so nominated shall be final and binding on all partners, such arbitration proceedings shall be governed by Indian Arbitration Act, which is in force.
In witness whereof, this deed of partnership is signed sealed, and delivered this [Day, Month, Year] at [City, State]:
FIRST PARTNER SECOND PARTNER
[Address Line 1] [Address Line 1]
[Address Line 2] [Address Line 2]
[City, State, Pin Code] [City, State, Pin Code]
THIRD PARTNER FOURTH PARTNER
[Address Line 1] [Address Line 1]
[Address Line 2] [Address Line 2]
[City, State, Pin Code] [City, State, Pin Code]
WITNESS ONE WITNESS TWO
[Address Line 1] [Address Line 1]
[Address Line 2] [Address Line 2]
[City, State, Pin Code] [City, State, Pin Code]


Fixed Working Capital Permanent working capital is also known as fixed working capital. Working capital is the excess of the current assets over the current liability and further, it is classified on the basis of periodicity, into two categories, permanent working capital, and variable working capitRead more
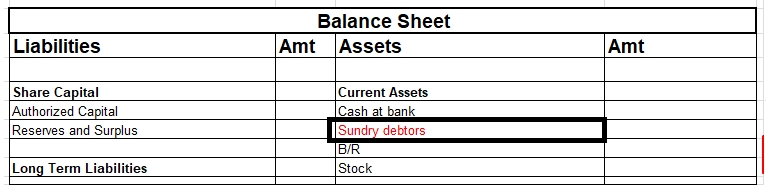
Fixed Working Capital
Permanent working capital is also known as fixed working capital.
Working capital is the excess of the current assets over the current liability and further, it is classified on the basis of periodicity, into two categories, permanent working capital, and variable working capital.
Permanent working capital means the part of working capital that is permanently locked up in current assets to carry business smoothly and effortlessly. Thus, it’s also known as fixed working capital.
The minimum amount of current assets which is required to conduct a business smoothly during the year is called permanent working capital. The amount of permanent working capital depends upon the nature, growth, and size of the business.
Fixed working capital can further be divided into two categories:
Whereas, on the other hand, variable working capital, also known as temporary working capital refers to the level of working capital that is temporary and keeps fluctuating.
See less