The rate of depreciation on a car as per the Income Tax Act depends upon the purpose for which it has been purchased and the year on which it was acquired. As per the Income Tax Act, cars come under the Plant and Machinery block of assets. The Act classifies cars into two categories, Group 1 - MotorRead more
The rate of depreciation on a car as per the Income Tax Act depends upon the purpose for which it has been purchased and the year on which it was acquired.
As per the Income Tax Act, cars come under the Plant and Machinery block of assets.
The Act classifies cars into two categories,
- Group 1 – Motor cars other than those used in the business of running them on hire.
- Group 2 – Motor taxis used in the business of running them on hire.
Group 1:
- If the motor car is acquired and put to use on or after 23rd August 2019 but before 1st April 2020, then the rate applicable is 30%.
- If the motor car is acquired and put to use on or after 1st April 1990, then the rate applicable is 15%. (All the cars which are not covered under the category (1) comes under this category.)
Group 2:
- If the motor taxi is acquired and put to use on or after 23rd August 2019 but before 1st April 2020, then the rate applicable is 45%.
- The rate applicable for motor taxis not covered under category (1) is 30%.
Here is a summarised version of the rates applicable to cars,
The rates can also be found on the Income Tax India website.
See less



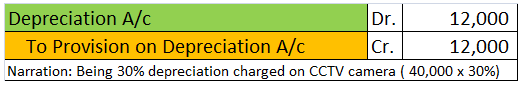
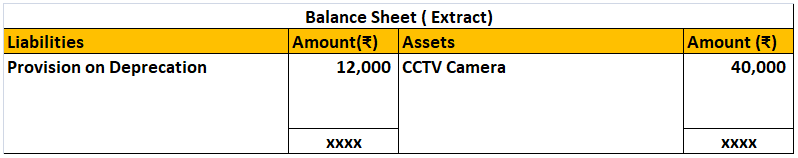
Journal Entry for Calls in Advance Calls in advance mean excess money received by the company than what has been called up. Calls in advance are treated as Current Liability and shown in the Balance Sheet on the liability side. Journal Entry will be : Here we will "Debit" Bank A/c as it will increaRead more
Journal Entry for Calls in Advance
Calls in advance mean excess money received by the company than what has been called up. Calls in advance are treated as Current Liability and shown in the Balance Sheet on the liability side.
Journal Entry will be :
Here we will “Debit” Bank A/c as it will increase assets of the company and “Credit” Calls in Advance A/c because it will increase the company’s current liabilties.
For Example:
Mr.Z shareholder of ABC Ltd was allotted 2,000 equity shares of Rs.10 each. He paid call money at the time of allotment.
Journal Entry is as follows:
Here, the company received an excess amount of Rs.6,000 (2,000*3) from a shareholder Mr.Z who paid the call money in advance. ABC Ltd will record this under Calls in Advance A/c. While passing journal entry ABC Ltd will debit its Bank A/c by Rs.6,000 and credit calls in advance account by Rs.6,000.
When share calls are called up, calls received in advance are adjusted. The company will hold only the required amount which will make allotted shares fully paid.
Once the amount is transferred to relevant call accounts, calls in advance account will be written off.
See less