To determine if a person is a resident in India as per the Income Tax Act 1961, he has to fulfil any of the 2 following conditions; Condition A Stay in India for 182 days or more in the previous year, or Stay in India for 60 days or more in the previous year and another 365 days or more in the 4 yeaRead more
To determine if a person is a resident in India as per the Income Tax Act 1961, he has to fulfil any of the 2 following conditions;
Condition A
- Stay in India for 182 days or more in the previous year, or
- Stay in India for 60 days or more in the previous year and another 365 days or more in the 4 years immediately preceding the previous year.
The second condition above is not applicable if he is an Indian citizen leaving India for the purpose of employment, or he is a member of the crew of an Indian ship, or he is only coming to India on a visit.
If he fails to fulfil either of the two conditions, then he is termed as a non-resident.
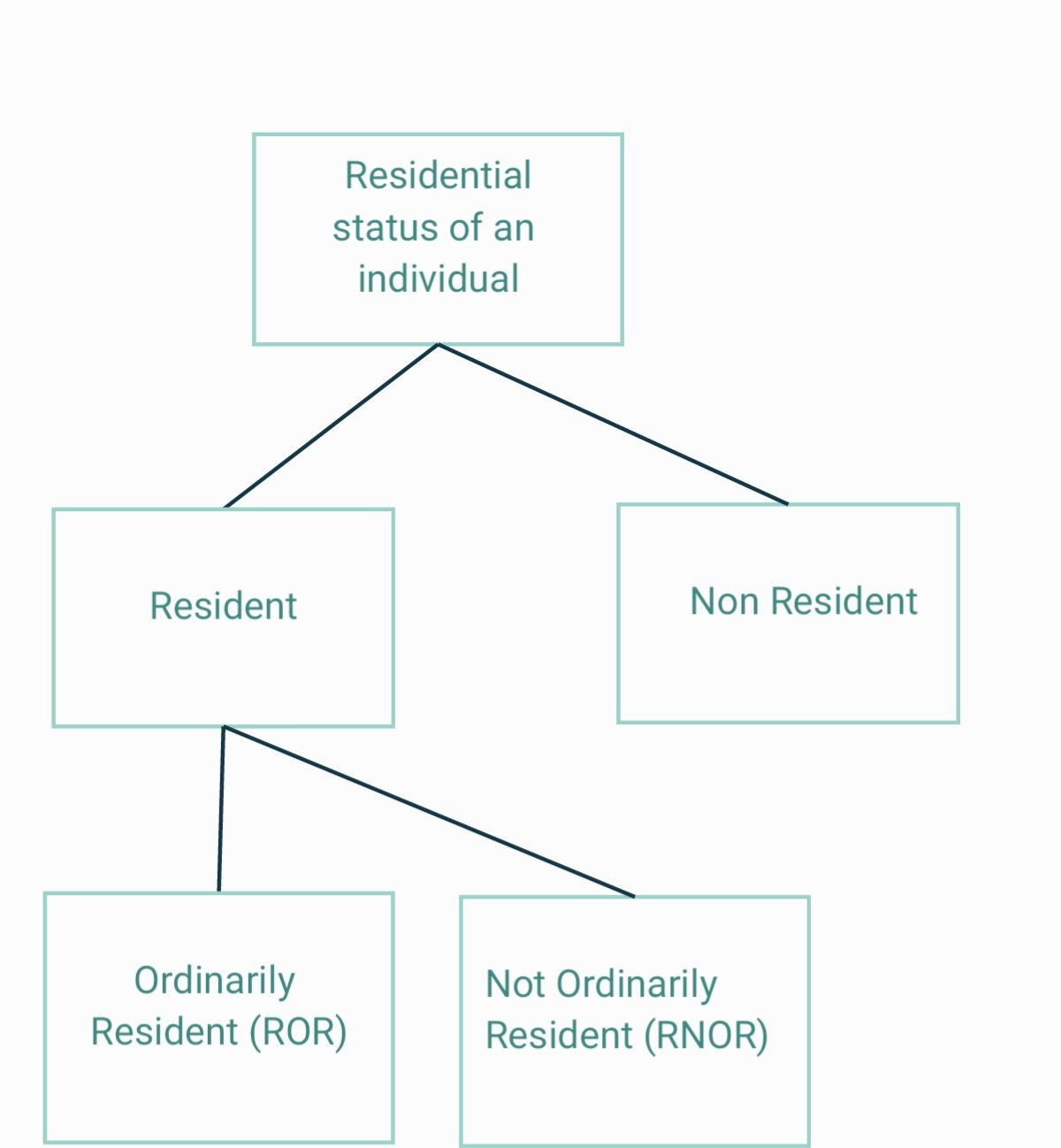
In India, a resident person can be classified into two:
- Resident and ordinarily resident
- Resident but not ordinarily resident
Condition B
A resident is a resident and ordinarily resident if (B):
- He has been a resident in India for at least 2 out of the previous 10 years immediately preceding the relevant previous year, and
- He has been in India for a period of 730 days or more during 7 years immediately preceding the relevant previous year.
If a person satisfies any one condition of (A) but does not follow all conditions of (B), then he is termed as a resident but not ordinarily resident.
EXAMPLE
If Nithin is living in India for 190 days in the previous year and was a resident for the previous two years only staying for 400 days in the previous 7 years, then he fulfils condition (A) but not both conditions of (B) and hence he is a resident but not ordinarily resident.

Brief Introduction Alternate Minimum Tax or AMT as the name suggests, is an alternate tax that an assessee has to pay, subject to certain conditions, instead of the income tax liability which is computed as per normal provisions of the Income-tax law. Alternate Minimum Tax is levied to impose higherRead more
Brief Introduction
Alternate Minimum Tax or AMT as the name suggests, is an alternate tax that an assessee has to pay, subject to certain conditions, instead of the income tax liability which is computed as per normal provisions of the Income-tax law.
Alternate Minimum Tax is levied to impose higher tax liability on non-corporate assessees who have claimed various profit-link deductions or investment-linked deductions in the relevant previous year.
My answer is based on the Indian Income law i.e. Income Tax Act, 1961.
The concept behind Alternate Minimum Tax
Let’s start our discussion with MAT i.e. Minimum Alternative Tax. It applies to corporate entities or companies.
Before MAT, it was seen that companies used to declare huge dividends to their shareholders. But when it came to filing income tax returns, they used to claim various profit linked and investment-linked deductions to report very low profits and even losses to arrive at negligible tax or nil tax whereas their financial statements would report huge profits.
It is true that the government provides such profit linked or investment linked deductions to encourage business and investments, but it also needs a sufficient and regular flow of revenue in the form of tax to fund its expenditure.
Hence, to prevent misuse of deductions to evade taxes by corporates, government introduce Minimum Alternate Tax to charge such assessees a minimum rate of tax.
Alternate Minimum Tax is the same as Minimum Alternate Tax in terms of concept. The provisions related to AMT are given under section 115JC of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Scope of AMT as per section 115JC
Alternate Minimum Tax applies to all non-corporate assessees who claimed have claimed
However, there is a threshold limit for certain non-corporates.
By non-corporate assessees we mean:
AMT is applicable to all except
If their total adjusted income does not exceed Rs 20,00,000 in the previous year.
Therefore, AMT is applicable to all other non-corporate assessees like LLP, firms and cooperative societies irrespective of their total adjusted income.
Calculation of Alternate Minimum Tax
The rate of AMT is 18.5% of the adjusted total income. This adjusted total income and the AMT on it is calculated in the following manner:
The higher of the following becomes the tax liability of the assessee:
Numerical example
Mr X is a businessman who has earned the following income and expenditure in P.Y 2020-2021: (Amount in Rupees)
Income from manufacturing business 25,00,000
Interest on saving bank account 8,000
Dividend from ABC ltd 10,000
Insurance premium paid 1,00,000
Capital expenditure made as per section 35AD 5,00,000
Mr X is eligible to claim a profit linked deduction of Rs 6,00,000.
Also, the depreciation allowed (other than under 35AD) as per Income-tax Act,1961 amounts to Rs. 3,00,000.
Following is his computation of both AMT and Income tax liability as per normal provisions.
See less