Credit balance means excess of credit side over debit side. For example, At the beginning of the year, the credit balance of trade payable is 3,000 and there is a debit of trade payable of 1,000 during the year and an increase(credit) of trade payable of 4,000 then at the end there will be a creditRead more
Credit balance means excess of credit side over debit side.
For example, At the beginning of the year, the credit balance of trade payable is 3,000 and there is a debit of trade payable of 1,000 during the year and an increase(credit) of trade payable of 4,000 then at the end there will be a credit balance of 6,000 of trade payable at the end
.A Credit balance signifies all income and gains and all liabilities and capital that is there in business.
Liabilities and Capital
- Account Payables– Account Payables means the amount that is due to the customer by the entity. Its credit balance will always increase when there is an increase in account payables and will decrease when there is a decrease in account payables. For eg-: The stock that has been purchased in credit from creditors of 10,000 will result in an increase in credit balance.
- Bank Overdraft-Bank Overdraft means when the amount withdrawn from the bank is more than the balance left in the bank. For example, there is a bank balance of 2,000 in the bank but an amount of 4,000 has been withdrawn from the bank. So in such a case, there will be a credit balance of 2,000 which is in Bank Overdraft
- Bonds– Bonds are the amount that is withdrawn from people for a specific time period which gets redeemed at a coupon rate after such a specific period. For example- A 10% bond of 10,000 is given to a group of people which will be redeemed after 5 years.
- Income Tax Payables-Income Tax Payable means the amount the company left to pay to the government in earlier periods. For example- There is a tax liability of 10,000 in FY20-21 from which 8,000 was paid in the current year and 2,000 paid in FY21-22.
- Notes Payable– Notes Payable is a type of promissory note in which a person pays some amount to an entity that the entity will write in a specific period. For example Notes payable of 1,000 given by a person to an entity which will be returned in 3 months with interest
- Capital– Capital means the amount that is introduced by the company at the beginning of the business for the operations and survival of the business. For example- A capital of 10,000 has been introduced by the company.
Income and Gains
- Interest Received-Interest Received means the amount which is invested by the company in some other entity and interest received on it
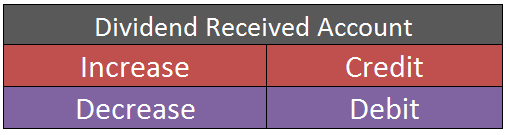
- Dividend Received– Dividend means the amount received from the entity in which amount invested by the company
- Rent Received– Rent is the amount that the company receives by letting out their land to another person or entity for use
- Gains on Sale of Furniture– Gain on Sale of Furniture means that the amount received from the sale of furniture is more than the amount of furniture. So the difference between the amount received from the sale and the cost of furniture is called a gain on the sale of furniture.
So after seeing all the above points we can conclude that the credit balance includes all the income in the P&L account and all the liabilities in the Balance sheet. So its balance increases when there is an increase in its account.
Debit Balance
Debit balance means excess of credit side over debit side.
For Example- At begining of the year the debit balance of trade receivables is 3,000 and there is a decrease(credit) of trade receivables of 1,000 during the year and an increase(debit) of trade receivables of 4,000 then at the end there will be a debit balance of 6,000 of trade receivables at the end
A Debit balance basically signifies all expenses and losses and all positive balances of assets. The debit balance increases when any asset increases and decreases when any asset decreases.
Asset
- Cash and Bank Balance
- Account Receivables
- Property, Plant, and Equipment
- Inventory
- Investments
- Bill Receivables
- Intangible Assets
Expenses and Loses
- Rent
- Depreciation
- General Expenses
- Loss on Sale of asset
- Printing and stationery
- Audit fees
- Outstanding fees
- Salaries and Wages
- Insurance
- Advertising
- Promotional expenses

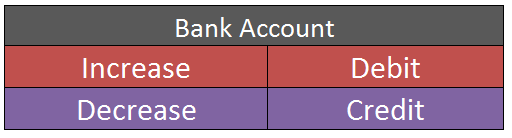
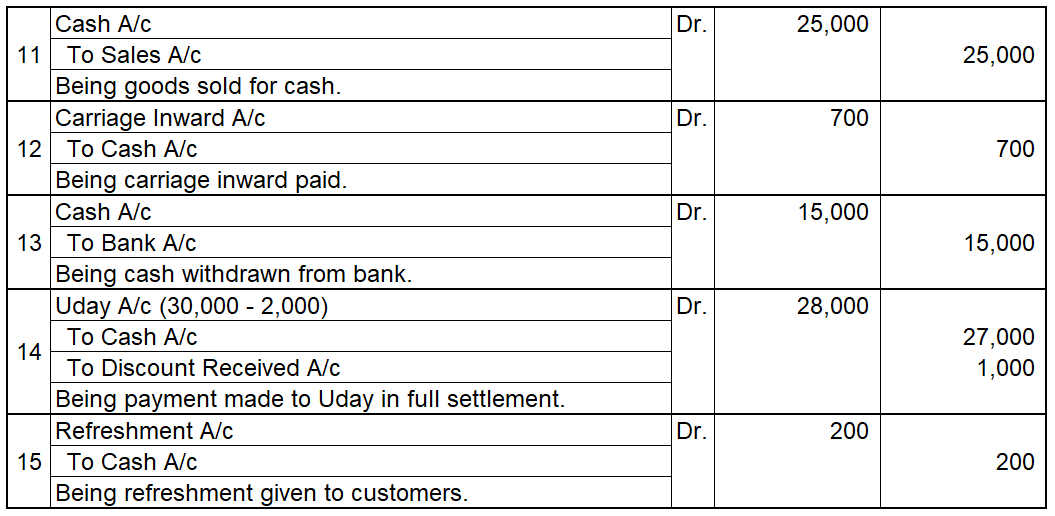
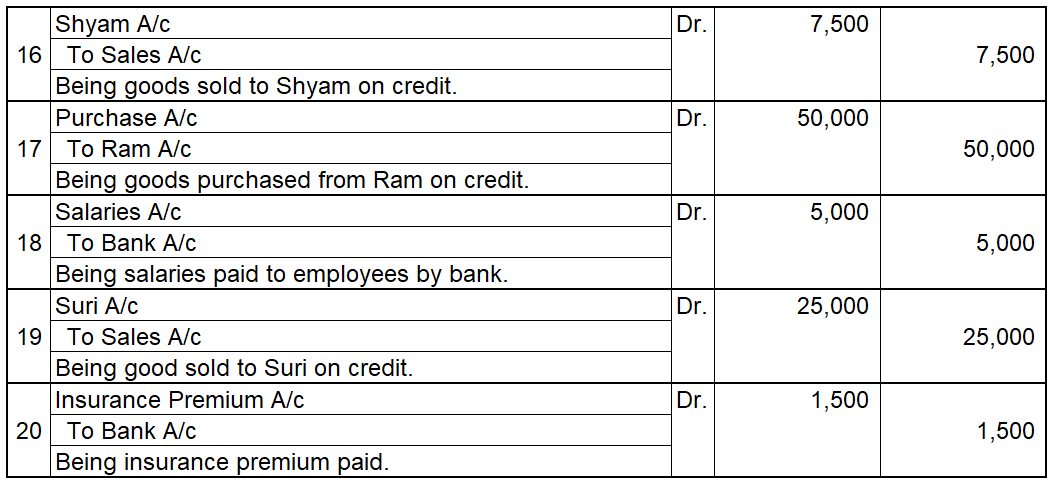
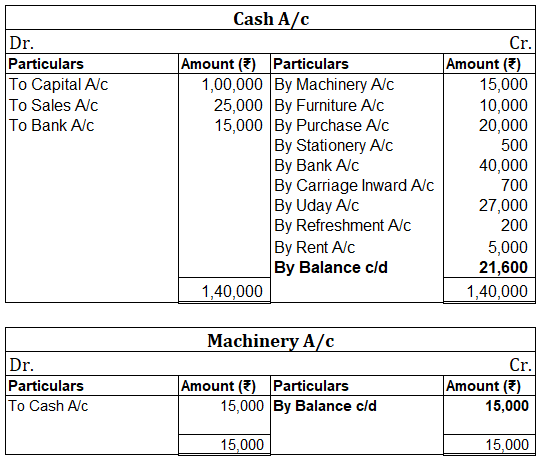
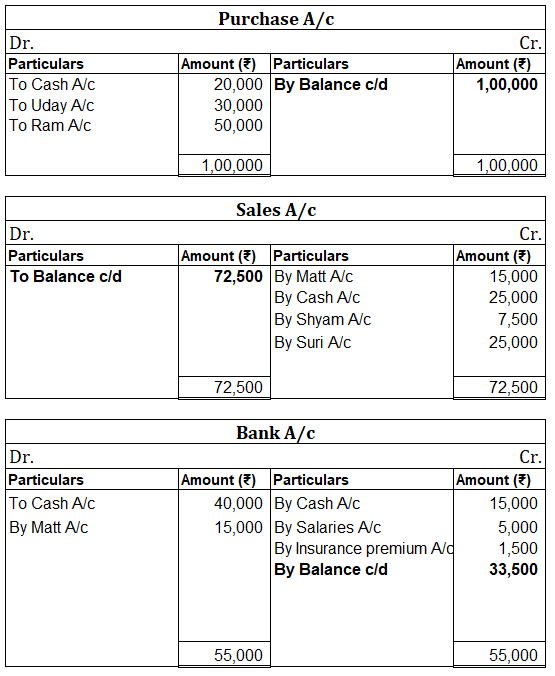
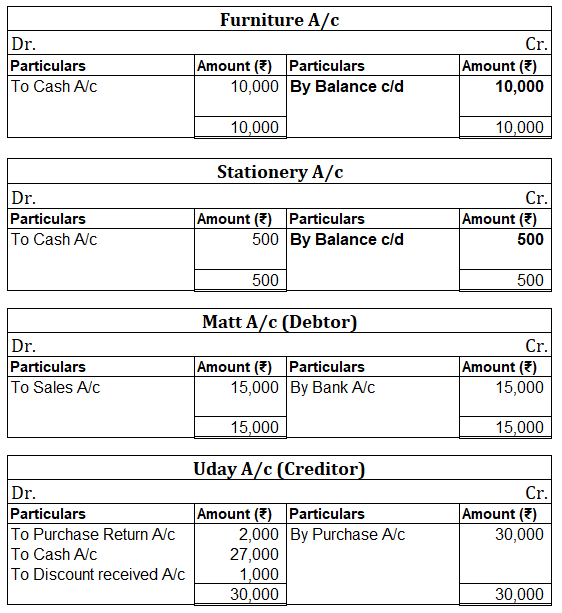
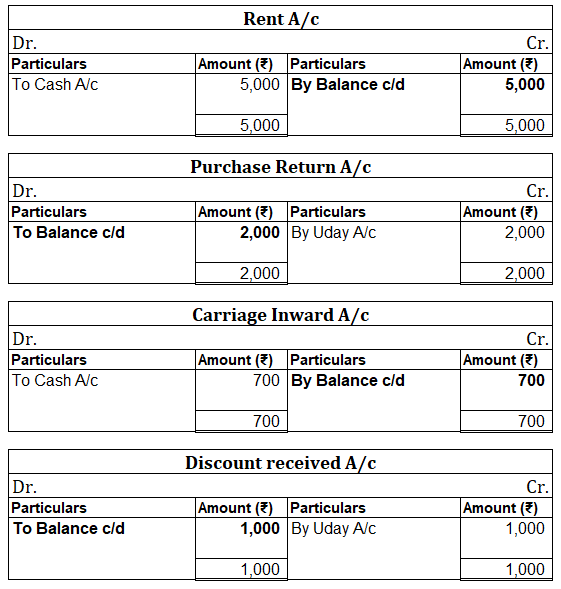
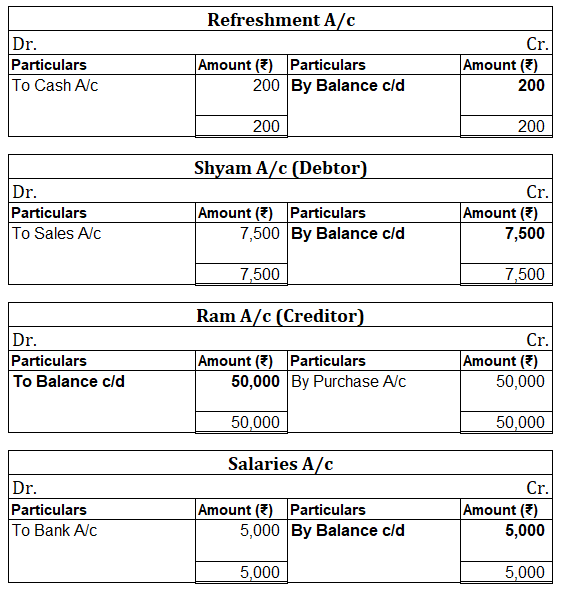
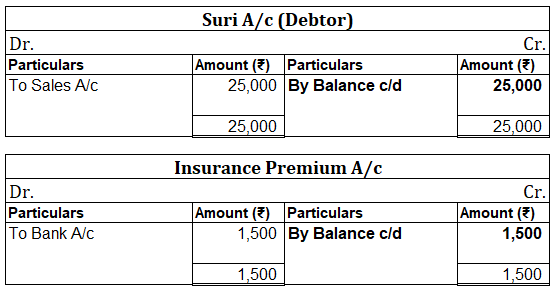
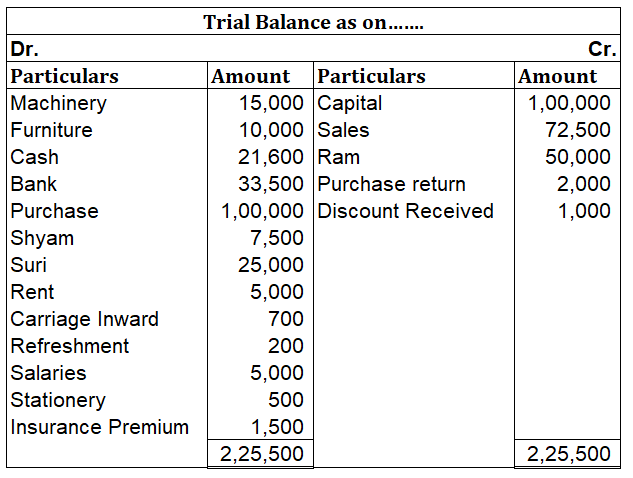
Debit Balance A debit accounting entry represents an increase in asset or expense account or a decrease in liabilities of an individual or enterprise. Debit balance is the amount in excess of debit entries over credit entries in the general ledger. The debit balance is shown as Dr. Credit Balance ARead more
Debit Balance
A debit accounting entry represents an increase in asset or expense account or a decrease in liabilities of an individual or enterprise.
Debit balance is the amount in excess of debit entries over credit entries in the general ledger. The debit balance is shown as Dr.
Credit Balance
A credit accounting entry represents a decrease in assets or an increase in liabilities or income accounts of an individual or enterprise.
The credit balance is the amount in excess of credit entries over debit entries in the general ledger. The credit balance is shown as Cr.
Credit Balance in the Passbook
A passbook is a record of a customer’s account transactions kept by the bank. The passbook is a copy of the bank account of the customer in the books of banks. “Credit balance in the passbook is also called bank balance”.
The bank balance is the amount available for withdrawal. A bank balance is an asset to the individual or an enterprise which can be used for the purchase of another asset or payment of liability or expenses.
All the transactions either debit or credit are recorded in the passbook. When the total amount of all credit entries in a passbook is more than the total of debit entries, it results in a credit balance. It means that the bank owes to an individual or enterprise.
The amount withdrawn by a customer from the bank is shown as a debit entry and the amount deposited by the customer is shown as a credit entry. The passbook’s credit balance is a positive or favourable balance while the passbook’s debit balance is a negative balance or unfavourable balance.
For example: An individual deposited $50,000 in a bank account and withdrew a total sum of $30,000. So here, the passbook will show a bank balance of $20,000 i.e. the credit balance of the passbook. It signifies the positive cash flow of the individual and that the bank owes $20,000 to the individual.
Debit balance in Pass Book
When the total amount of all debit entries in a passbook is more than the total of credit entries, it results in a debit balance. Debit balance in the passbook is also called “Overdraft”. It means that an individual or enterprise owes to the bank.
Reconciliation
It is the process of identifying and rectifying differences between the passbook and cashbook maintained by the bank and customer respectively. The aim is to ensure the accuracy of the transaction recorded in the cashbook and passbook.
Debit Balance Reconciliation
The debit balance in the cashbook and the credit balance in the passbook shows that some outstanding cheques are in the process of clearing and these cheques need to be adjusted for reconciliation of the balance of the passbook and cashbook.
Credit Balance Reconciliation
The credit balance in the cashbook and debit balance in the passbook shows that deposits already recorded in the cashbook are yet to be recorded in the passbook by the bank and these deposits need to be adjusted in the passbook for reconciliation of the balance of the passbook and cashbook.
Conclusion
The debit and credit balance of the passbook is the indicator of the financial position of an enterprise or individual. A credit balance signifies more deposits than withdrawals resulting in a positive bank balance.
See less