Meaning of Working Capital Firstly, let’s understand the meaning of the working capital. Working capital is the factor which demonstrates the liquidity position of the business to carry out day to day operations. It majorly includes cash & bank balances and liquid assets. Managing working capitaRead more
Meaning of Working Capital
Firstly, let’s understand the meaning of the working capital. Working capital is the factor which demonstrates the liquidity position of the business to carry out day to day operations. It majorly includes cash & bank balances and liquid assets.
Managing working capital is a crucial process to maintain short term liquidity and so ultimately resulting into achieving long term objectives efficiently. Working capital can be calculated by deducting business’s current liabilities from current assets.
To achieve the ideal working capital requirement for any business, it is important to understand various types of working capital and various ways to manage it.
Coming to Permanent Working Capital, also called as Fixed Working Capital, it is the minimum working capital required or maintained by businesses. Such type of working capital is maintained to take care of regular financial obligations like creditors, inventory, salaries etc.
Irrespective of scale of operations carried out in business, Permanent Capital is maintained by businesses which can be in form of Net Working Capital.
There is no specific formula for calculating Fixed Working Capital, it completely depends upon the business’s assets and liabilities. So accordingly, it can be estimated through the balance sheet of the business.
For calculating Permanent Working Capital, you can follow below steps:
- Calculate Net Working Capital for each day for a whole month
- Find the smallest value among them
- That will be Permanent Working Capital for the month
- Follow the above steps for every month
- There you have the annual figure for Permanent Working Capital
The requirement of Permanent Working Capital changes as the business expands. It is crucial to make sure that the working capital level does not fall below the Permanent Working Capital requirement.
Types of Permanent Working Capital:
Permanent working capital is further divided into two types:
- Regular working capital – This refers to capital required to maintain healthy cashflow for purchases of raw materials, payment of wages etc.
- Reserve working capital – This refers to amount which is more than regular working capital to take care of unexpected business expenses due to contingent events.

Sundry Debtors in Trial Balance The debtor is a company's asset, and assets are always debited in the trial balance. The trial balance is a statement maintained at the end of an accounting period, listing the ending balances in each general ledger account. There are two sides to this account, debit,Read more
Sundry Debtors in Trial Balance
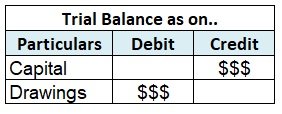
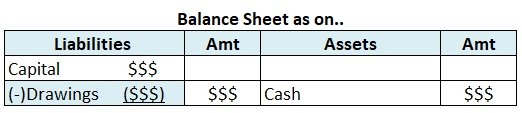
The debtor is a company’s asset, and assets are always debited in the trial balance.
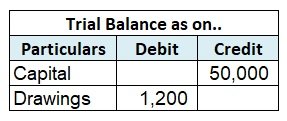
As we know, assets, expenses, and drawings are always debited. That applies not only in journals but here as well, hence, all of your assets are to be debited.
Trial Balance Statement
As we can see here, the sundry debtors (on the 4th) are debited like all the other assets, expenses, and losses. In the end, if the basic accounting equation i.e. assets=capital+liability is violated, a mismatch arises which in the balancing figure is shown under the name of suspense account. Such errors must not be found and corrected to avoid any mismatch in the balance sheet of the company.
Total Assets = Capital + Other Liabilities.
Therefore, this is how the sundry debtors are treated in the Trial Balance.
See less