Definition Not-for-profit organizations are also known as non-profit organizations set up to further cultural, educational, religious, professional, or public service objectives. Its aim is not to earn profit Accounting done by non-profit organizations is fund based. Type of accounting Non-pRead more
Definition
Not-for-profit organizations are also known as non-profit organizations set up to further cultural, educational, religious, professional, or public service objectives. Its aim is not to earn profit
Accounting done by non-profit organizations is fund based.
Type of accounting
Non-profit organizations do Fund Based Accounting.
Donations received or funds set aside for specific purposes are credited to a separate fund account and are shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet.
The income from or donations for these funds are credited to the respective fund account. On the other hand, expenses or payments out of these funds are debited.
Accounting when done on this basis is known as Fund Based Accounting.
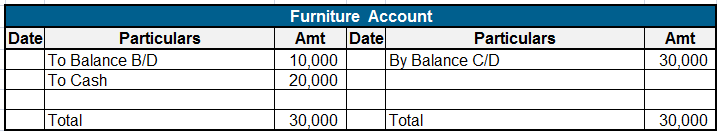
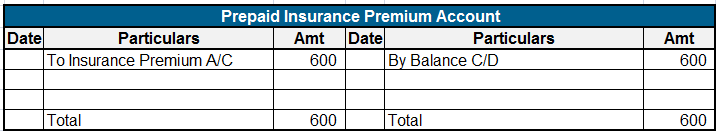
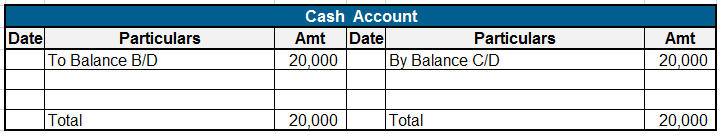
Let me explain to you with an example :
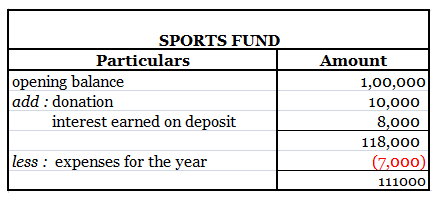
The sports fund has a balance of Rs 100000 which is invested as a fixed deposit in a bank earning 8% interest. A further donation of Rs 10000 is received towards it. Expenses incurred towards prizes are Rs 7000; Rs 3000 towards trophies and Rs 4000 distribution of cash prizes. The accounts are shown as follows :
Categories of funds
In the case of non-profit organizations, funds may be classified under the following heads :
Unrestricted fund :
The unrestricted fund does not carry any restriction with respect to its use. In other words, management can use the amounts in the funds as it deems appropriate, but to carry out the purpose for which the organization exists.
This is known as the general fund or the capital fund to which the surplus for the year is added and in case of deficit, deducted.
Restricted fund :
A restricted fund is a fund, the use of which is restricted either by the management or by the donor for a specific purpose.
Examples of such funds are endowment funds, annuity funds, loan funds, prize funds, sports funds, etc.
- Government grant: grant received from the government for a specific purpose is restricted to be used for the purpose it is granted. It is accounted for in the books following fund-based accounting.
- For example, a grant received from the government for ‘the polio eradication program is credited to the polio eradication fund, and income earned relating to the fund is credited to the fund while expenses are debited.
- Endowment fund: it’s a fund usually a non-profit organization, arising from a bequest or gift, the income of which is devoted to a specific purpose.
- Annuity fund: an annuity fund is established when a non-profit organization receives assets from a donor with a condition to pay
- Loan fund: loan fund is set up to grant loans for specific purposes say loans to pursue higher studies.
- A fixed assets fund is a fund earmarked for investment in fixed assets or already invested in fixed assets.
- Prize funds: it is a fund set up to use for distribution as prizes say for achievements or contributions to the welfare of society.

Definition Section 43 of the companies act 2013 prescribes that the share capital of a company broadly can be of two types or classes : Preference shares Equity shares Preference shares Preference shares are the shares that carry the following two preferential rights : Preferential rights to receivRead more
Definition
Section 43 of the companies act 2013 prescribes that the share capital of a company broadly can be of two types or classes :
Preference shares
Preference shares are the shares that carry the following two preferential rights :
Classes of preference shares
Preference shares are broadly classified as follows :
With reference to the dividend
Cumulative preference shares are those preference shares that carry the right to receive arrears of dividends before the dividend is paid to the equity shareholders.
Non-cumulative preference shares are those that do not carry the right to receive arrears of dividends.
Participation in surplus profit
Participating preference shares of the company may provide that after the dividend has been paid to the equity shareholders, the holders of preference shares will also have a right to participate in the remaining profits.
Non-participating preference shares are those preference shares that do not carry the right to participate in the remaining profits after the equity shareholders have paid the dividend.
Convertibility
Convertible preference shares are those preference shares that carry the right to be converted into equity shares.
Non-convertible preference shares are those that do not carry the right to be converted into equity shares.
Redemption
Redeemable preference shares are those preference shares that are redeemed by the company at the time specified for the repayment or earlier.
Irredeemable preference shares are preference shares the amount of which can be returned by the company to the holders of such shares when the company is wound up.
Equity shares
Equity shares are those shares that are not preference shares.
Equity shares are the most commonly issued class of shares that carry the maximum ‘risk and reward ‘ of the business the risks of losing part or all the value of the shares if the business incurs losses.
The rewards are the payment of higher dividends and appreciation in the market value.
See less