Trading A/c is a Nominal A/c which follows the rule “Debit the expenses and losses, Credit the incomes and gains” So, the Credit side of Trading A/c shows income from the sale of goods. It includes Sales, Closing stock (if adjustment for it has not been made yet) and Gross Loss (if any). TRADRead more
Trading A/c is a Nominal A/c which follows the rule “Debit the expenses and losses, Credit the incomes and gains”
So, the Credit side of Trading A/c shows income from the sale of goods. It includes Sales, Closing stock (if adjustment for it has not been made yet) and Gross Loss (if any).
TRADING ACCOUNT
Trading A/c is prepared for calculating the Gross Profit or Gross Loss arising from the trading activities of a business.
Trading activities are mostly related to buying and selling of goods. However, in between buying and selling, a lot of activities are involved like transportation, warehousing, etc. So, all the expenses that are directly related to manufacturing or purchase of goods are also recorded in the Trading A/c.
CREDIT SIDE OF TRADING ACCOUNT
It includes,
SALES – When goods are sold to earn a profit, it is called sales. It can be cash sales or credit sales.
Suppose you are in the business of manufacturing and trading shirts. You sold shirts worth $ 20,000 during the year. This $20,000 is your sales.
SALES RETURN – When the goods sold by you are returned by the customer, it is known as sales return. Sales return is deducted from the sales.
Continuing with the above example, the customers returned shirts of $1,000 because they didn’t like them. This return is known as sales return or return inward (as goods are coming back i.e. in)
CLOSING STOCK – Stock is nothing but goods that are either obtained for resale or manufactured for sale and are yet unsold on any particular date.
The value of stock at the beginning of an accounting year is called Opening stock while the value of the stock at the end of an accounting year is called Closing stock.
Closing stock is valued at cost price or market price whichever is less.
It includes,
- Closing stock of raw materials
- Closing stock of semi-finished goods
- Closing stock of finished goods
For example – On 31st March 2023, there was unused raw material worth $1,000 and shirts worth $5,000 remained unsold.
So, we have Closing Stock of Raw material – $1,000
Closing Stock of Finished Goods – $5,000
Normally, the closing stock is given outside the Trial Balance because its valuation is made after accounts have been closed. It is incorporated in the books by transferring it to the Trading A/c. So, it is shown on the credit side of Trading A/c as well as on the assets side of the Balance sheet.
However, if the closing stock is given inside the Trail Balance, it means that the closing stock must have already been deducted from the Purchases account. So, closing stock will only be shown on the assets side of the Balance sheet.
GROSS LOSS – If purchases and direct expenses exceed sales, then it is a Gross loss. In other words, when Debit side > credit side.
DEBIT SIDE OF TRADING ACCOUNT
It includes
OPENING STOCK – The value of the stock at the beginning of an accounting year is called Opening stock.
The closing stock of the last year becomes the opening stock of the current year.
PURCHASES – Goods that have been bought for resale or raw materials purchased for the manufacturing of the product are terms as Purchases. These goods must be related to the business you are doing. It includes cash as well as credit Purchases.
PURCHASES RETURN – When goods bought are returned to the suppliers due to any reason. This is known as Purchase return. Purchase return is deducted from the Purchases.
WAGES – Wages are paid to the workers who are directly engaged in the loading, unloading and production of goods.
CARRIAGE or CARRIAGE INWARDS or FREIGHT – It refers to the cost of transporting goods from the supplier.
MANUFACTURING EXPENSES – All expenses incurred in the manufacture of goods such as Coal, Gas, Fuel, Water, Power, Factory rent, Factory lighting etc.
DOCK CHARGES – These are charged by port authorities when unloading goods at a dock or wharf. Such charges paid in connection with goods purchased are considered direct expenses and are debited to Trading a/c.
IMPORT DUTY or CUSTOM DUTY – It is a tax collected on imports and specific exports by a country’s customs authorities.
If import duty is paid on the import of goods, then they are shown on the Dr. side of the Trading A/c.
ROYALTY – Royalty refers to the amount paid for the use of assets belonging to another person. It includes royalty for the use of intangible assets, such as copyrights, trademarks, or franchisee agreements. It is also paid for the use of natural resources, such as mining leases.
Royalty is charged to the Trading A/c as it increases the cost of production.
GROSS PROFIT – When sales exceed the amount of purchases and the expenses directly connected with such purchases i.e. when Credit side> Debit side.
See less
Definition Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable. Bad debts will be treated in the following ways : On the debit side of the profit and loss account. In the curreRead more
Definition
Bad debts are a debt owed to an enterprise that is considered to be irrecoverable or we can say that it is owed to the business that is written off because it is irrecoverable.
Bad debts will be treated in the following ways :
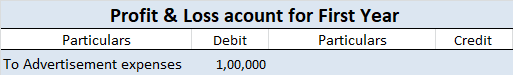
On the debit side of the profit and loss account.
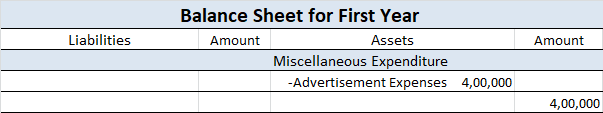
In the current assets side of the balance sheet, these are deducted from sundry debtors.
For example loans from banks are declared as bad debt, sales made on credit and amounts not received from customers, etc.
Now I will show you an extract of the profit and loss account and balance sheet
Current assets are defined as cash and other assets that are expected to be converted into cash or consumed in the production of goods or the rendering of services in the ordinary course of business.
For example, debtors exist to convert them into cash i.e., receive the amount from them, bills receivable exist again for receiving cash against it, etc.
Current liabilities are defined as liabilities that are payable normally within 12 months from the end of the accounting period or in other words which fall due for payment in a relatively short period.
For example bills payable, short-term loans, etc.
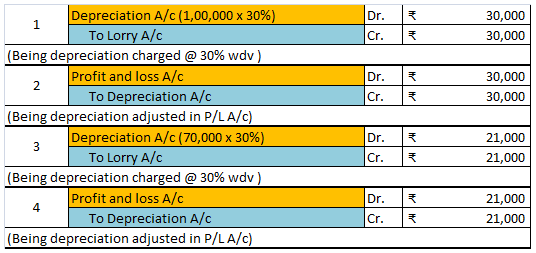
Accounting treatment
Now let me try to explain to you the accounting treatment for bad debts which is as follows :
Reasons for bad debts
There are several reasons why businesses may have bad debts some of them are as follows:-
Accounting methods
There are two methods for accounting for bad debts which are mentioned below:-
Related terms
So there are a few related terms whose meanings you should know
See less