Working capital is defined as the difference between current assets and current liabilities of a business. Current assets include cash, debtors and stock whereas current liabilities include creditors and short term loans etc. FORMULA Current Assets - Current Liabilities = Working Capital Zero workinRead more
Working capital is defined as the difference between current assets and current liabilities of a business. Current assets include cash, debtors and stock whereas current liabilities include creditors and short term loans etc.
FORMULA
Current Assets – Current Liabilities = Working Capital
Zero working capital is when a company has the exact same amount of current assets and current liabilities. When both are equal, the difference becomes zero and hence the name, Zero working capital. Working Capital may be positive or negative. When current assets exceed current liabilities, it shows positive working capital and when current liabilities exceed current assets, it shows negative working capital.
Zero working capital can be operated by adopting demand-based production. In this method, the business only produces units as and when they are ordered by the customers. Through this method, all stocks of finished goods will be eliminated. Also, raw material is only ordered based on the amount of demand.
This reduces the investment in working capital and thus the investment in long term assets can increase. The company can also use the funds for other purposes like growth or new opportunities.
EXAMPLE
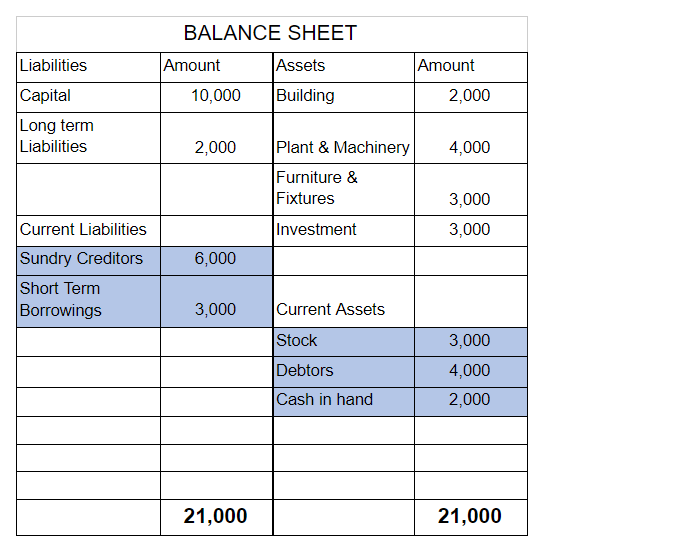
Suppose a company has Inventory worth Rs 3,000, Debtors worth Rs 4,000 and cash worth Rs 2,000. The creditors of the company are Rs 6,000 and short term borrowings are Rs 3,000.
Now, total assets = Rs 9,000 ( 3,000 + 4,000 + 2,000)
And total liabilities = Rs 9,000 ( 6,000 + 3,000)
Therefore, working capital = 9,000 – 9,000 = 0

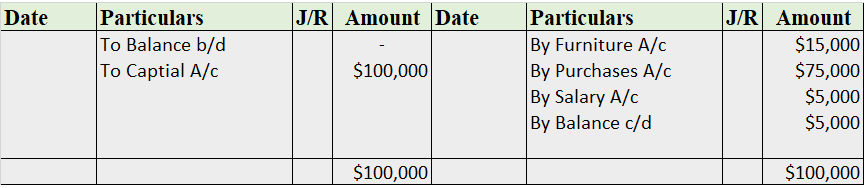
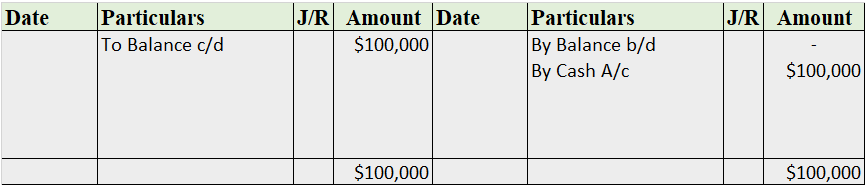
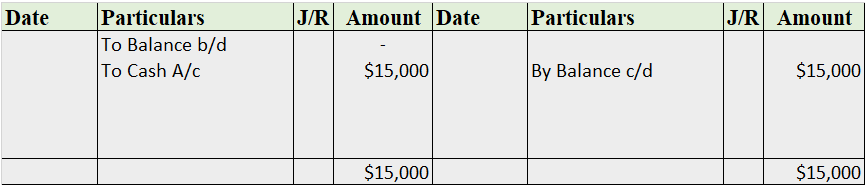
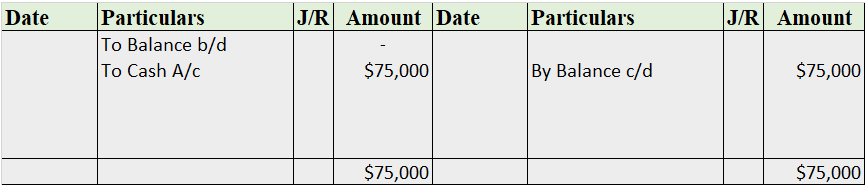
A contra account is a general ledger account that is used to reduce the value of the account related to it. Basically, a contra account is the opposite of its associated account. If the associated account has a debit balance, then the contra account would have a credit balance. They are used to mainRead more
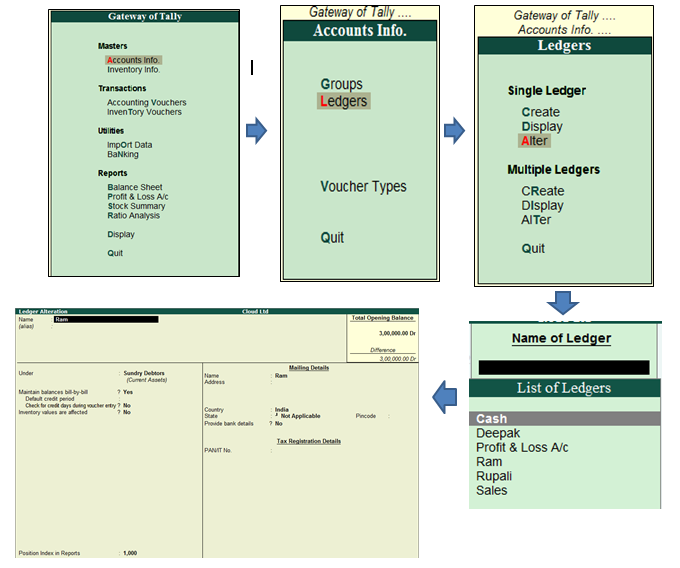
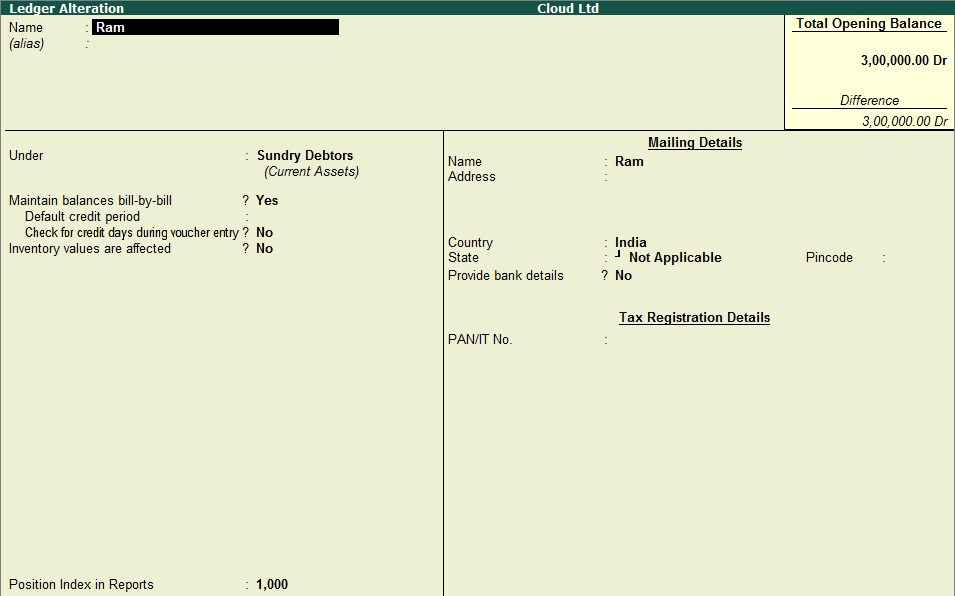
A contra account is a general ledger account that is used to reduce the value of the account related to it. Basically, a contra account is the opposite of its associated account. If the associated account has a debit balance, then the contra account would have a credit balance. They are used to maintain the historical value of the main account while all the deductions are recorded in the contra account, which when clubbed together show the net book value.
For example
if the cost of machinery was Rs. 50,000 and the company wants to preserve its original cost, then the accumulated depreciation of such machinery is recorded separately. Let’s say Rs 10,000 was the accumulated depreciation. Then such amount is recorded in the contra account named accumulated depreciation account. This makes the net value of the machinery Rs 40,000.
Types
There are various types of contra accounts such as contra asset, contra equity, contra revenue, and contra liability.
Accountants make use of contra accounts instead of reducing the value of the actual account to keep the financial statements clean.
See less