International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is a not-for-profit, public interest organization. The main objective of the IFRS Foundation is to raise the standard of financial reporting and bring about global harmonization of accounting standards. IFRS was established to develop high-quality,Read more
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is a not-for-profit, public interest organization. The main objective of the IFRS Foundation is to raise the standard of financial reporting and bring about global harmonization of accounting standards.
IFRS was established to develop high-quality, understandable, enforceable, and generally accepted accounting standards. International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) develops IFRS. There are currently 16 IFRSs in issue.
Benefits of IFRS Standards:
- It brings transparency by international comparability and quality of financial information.
- It strengthens accountability by reducing the information gap between providers and users of the capital.
- It contributes to economic efficiency by improving capital allocation and, helps investors in identifying opportunities and risks across the world.
Following are the uses of IFRS:
- As national requirements.
- As the basis for all or some national requirements.
- As an international benchmark for those countries which develop their own requirements.
- By regulatory authorities for domestic and foreign companies.
- By companies themselves.
Challenges faced by companies if IFRS is not implemented:
- The financial statements will differ for the companies who have offices worldwide and use only national accounting standards.
- Increased complexity while preparing financial statements.
- Difficulty in comparing and verifying financial statements.
- Accounting of transactions will differ from country to country if IFRS is not implemented.

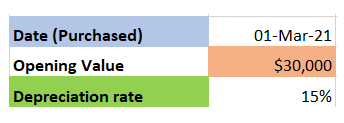
Fictitious assets are not actually assets. They are expenses/losses not written off in the year in which they are incurred. They do not have any physical presence. Their expense is spread over more than one accounting period. A part of the expense is amortized/written off every year against the compRead more
Fictitious assets are not actually assets. They are expenses/losses not written off in the year in which they are incurred. They do not have any physical presence. Their expense is spread over more than one accounting period.
A part of the expense is amortized/written off every year against the company’s earnings. The remaining part (which is yet to be written off) is shown as an asset in the balance sheet. They are shown as assets because these expenses are expected to give returns to the company over a period of time.
Here are some examples of fictitious assets:
To make it simple I’ll explain the accounting treatment of preliminary expenses with an example.
The promoters of KL Ltd. paid 50,000 as consultation fees for incorporating the company. The consultation fee is a preliminary expense as they are incurred for the formation of the company. The company agreed to write off this expense over a period of 5 years.
At the end of every year, the company will write off 10,000 (50,000/5) as an expense in the Profit & Loss A/c.
The remaining portion i.e. 40,000 (50,000 – 10,000) will be shown on the Assets side of the Balance Sheet under the head Non – Current Assets and sub-head Other Non – Current Assets.
Here are the financial statements of KL Ltd.,
Note: As per AS 26 preliminary expenses are fully written off in the year they are incurred. This is because such expenses do not meet the definition of assets and must be written off in the year of incurring.
Source: Some fictitious assets examples are from Accountingcapital.com & others from Wikipedia.
See less