TDS stands for Tax Deducted at Source It is the tax deducted on certain incomes as specified under sections 192 to 194N of the Income Tax Act,1961 by the person who is responsible to pay such income. For example, an employer is liable to deduct the TDS on the salary paid to the employee subject to tRead more
TDS stands for Tax Deducted at Source
It is the tax deducted on certain incomes as specified under sections 192 to 194N of the Income Tax Act,1961 by the person who is responsible to pay such income.
For example, an employer is liable to deduct the TDS on the salary paid to the employee subject to the provisions of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
TDS is deducted either,
- at the time of payment
OR
- At time of credit to the account of the payee or at the time of payment; whichever is earlier
We know that Income tax liability is calculated after the income for a year is earned. In the next year, which is called the Assessment Year, income tax payable is calculated on the income earned in the Previous Year
For example:
Year 2021-2022 – This year (Previous Year) – Income is earned here.
Year 2021-2022 – Next Year (Assessment Year) – Income tax is assessed here.
But, the government collects the income tax from the income of the assessee in the Previous Year itself by the following ways:
- TDS – Tax Deducted at Source
- TCS – Tax Collected at Source
- Advance Tax
Some of the most common sections are given below:
- Section 192 – Salary
- Section 194A – Interest other on securities deposits with the bank, post office etc) – @10%
- Section 194B and 194BB – Winning from lotteries, crossword puzzle – @30%
- Section 194 – DA – Payment in respect of Life Insurance Policy – @5%.
So, according to sections 192 to 194N, some amount of income tax is deducted from the income of the assessee in the Previous Year itself.
In the Assessment Year, the assessee also gets a tax credit for the TDS i.e. the Income Tax liability gets reduced by the amount of Tax Deducted at Source in the Previous Year.
See less

What is Impairment of Assets? Impairment of assets means a decline in the value of assets due to unforeseen circumstances. Assets are impaired when the carrying value of assets increases its market value or “realizable value”. Impairment can be caused due to factors that are internal or external toRead more
What is Impairment of Assets?
Impairment of assets means a decline in the value of assets due to unforeseen circumstances. Assets are impaired when the carrying value of assets increases its market value or “realizable value”.
Impairment can be caused due to factors that are internal or external to the firm. Internal factors such as physical damage, obsolescence or poor management and external factors such as a change in legal or economic circumstances, increased competition or reduction in asset’s fair value in the market result in impairment.
Impairment Vs Depreciation
Asset impairment is often confused with asset depreciation, which is rather a recurring and expected event, unlike impairment that reflects an abrupt decrease in the value of the asset.
Impairment Loss
Impairment is always treated as a loss in accounting. It is the amount by which the carrying value or the asset’s book value exceeds its fair market value.
Before recording Impairment loss, a company must determine the recoverable value of the asset which is higher of the asset’s net realizable value or value in use. Then it is to be compared with the book value of the asset.
If the carrying value exceeds the recoverable value then the impairment loss is to be recorded at the exceeding value i.e. difference of carrying value and realizable value.
Example
Suppose a company Royal Ltd. has an asset with a carrying value of 50,000, which has suffered physical damage. According to the company’s calculation, the asset has a net realizable value of 30,000 and a value in use of 25,000.
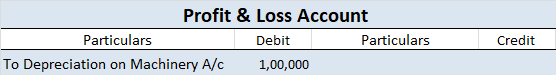
Then, the recoverable value would be higher of the asset’s net realizable value or value in use, i.e., 30,000 which is still lower than the carrying amount of 50,000. Therefore, Royal ltd. will have to record 20,000 (50,000-30,000) as impairment loss.
This is will increase Royal Ltd’s expenses by 20,000 and decrease the asset’s value by the same amount.
See less