Introduction In GST, a supply is a taxable event. This means whenever there is a supply of goods or services or both, GST is charged. Supply includes the exchange of goods or services between supplier and recipient by way of sale, barter, lease etc for consideration and in the course or furtheranceRead more
Introduction
In GST, a supply is a taxable event. This means whenever there is a supply of goods or services or both, GST is charged. Supply includes the exchange of goods or services between supplier and recipient by way of sale, barter, lease etc for consideration and in the course or furtherance of business. The rate of GST on any supply depends on the type of good or service supplied.
Composite supply and mixed supply are two special types of supplies, in which two or more goods or services or both are offered together in a bundle. As two or more goods are supplied together, the question arises at which rate the GST is to be charged on such supplies as such goods or services may have different rates of GST applicable to them. Sections 8 of the CGST act, 2017 deals with the tax liability of such supplies.
Composite supply
A composite supply is a type of supply in which two or more goods or services or both are supplied together in the ordinary course of business. Such goods or services are natural bundles. By natural bundle, we mean the goods or services are complementary to each, they are naturally provided together and are to be used along with each other.
For example, mobile phones and chargers are supplied as a bundle. This concept of the natural bundle is the main determiner of a composite supply.
In such supplies, there is one main product which is called the principal supply. Like in the above example, the mobile phone is the principal supply. Other goods or services are dependent on the principal supply.
A composite supply will be taxable as the rate of GST applicable on the principal supply.
For example, suppose the rate of GST on mobile phones is 18% and that on the charger is 12%, then the whole supply will be taxable at the rate of 18%.
Mixed supply
A mixed supply is a type of supply in which two or more goods or services or both are supplied together but they do not complement each other and are not a natural bundle. They are not supplied in the ordinary course of business, For example, a combo of bottled honey and face cream.
In mixed supply, the good or service which attracts the highest rate of GST is considered the rate of supply for the whole supply.
For example, suppose bottled honey attracts 5% GST and face cream 18% GST, then the whole supply will be charged 18% GST.
See less

A balance sheet is a financial statement that reports the position or value of assets, liabilities and equity at a particular date, which is usually the closing date of a financial year. Formats of balance sheet A balance sheet may be presented in two formats: T-form or Horizontal format This formatRead more
A balance sheet is a financial statement that reports the position or value of assets, liabilities and equity at a particular date, which is usually the closing date of a financial year.
Formats of balance sheet
A balance sheet may be presented in two formats:
T-form or Horizontal format
This format is the same as the format of ledger accounts. There are two columns with the headings ‘Liabilities’ for the left column and ‘Assets’ for the right column and columns adjacent to both columns for amounts. The liabilities and equity (capital) are shown on the liabilities side because they both have credit balance and assets are shown on the asset side. Most of the non-corporates prepare their balance as per this format. The T-form balance sheet looks as given below:
Vertical format
The vertical format of the balance sheet is mostly prepared by corporate entities. Here, the liabilities and assets are shown in the same column as compared to two separate columns in the horizontal format. This results in having a longer shape. Hence, it is called a ‘vertical’ balance sheet. Generally, companies prepare their balance sheet as per this format.
Also, many times, there are two columns for the amount in this format presenting the amount of both the current year and the previous year. This format looks like as given below:
Grouping and marshalling
Beside the structure of the balance sheet i.e. horizontal and vertical, the grouping and marshalling of the items inside the balance sheet are also very important.
Grouping refers to the presenting of similar items under a heading or group. This is done in order to present the balance sheet in a concise manner. This is very important to do. For example, a business can have numerous creditors, but they are all presented under one ‘Creditors’ heading or two or more heading specifying different types of creditors.
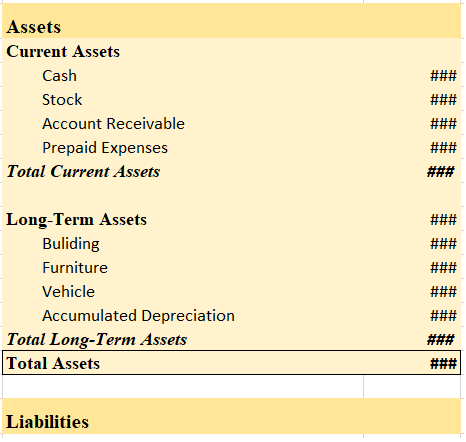
The assets of a business are grouped under the heading such as Plant, Property and equipment, Current assets, Non-current investments etc.
Marshalling means the arranging of items as per a particular order. We know that a balance sheet consists of many items and to make the statement more useful and easy to comprehend, the items are arranged in one of the following orders:
In case of liabilities, the items which are due for repayment soon are kept at the top, like bank overdraft etc. The items which are due for repayment after a long time or at the time of winding capital are kept at the bottom, like long term loans and capital funds. Given below is a format of horizontal balance sheet in which the items are marshalled in order of liquidity:
- Order of permanence: This type of arrangement is just the opposite of the order of liquidity. Here the items which are least liquid are placed at the top and the more liquid items are placed at the bottom. Like in the case of assets, cash appears at the bottom and non-current assets at the top. On the liabilities side, equity and non-current liabilities are at the top while current liabilities are at the bottom. Mostly all balance sheets are marshalled in order of permanence.
See less