When a partnership firm decides to admit a new partner into their firm, the old partners have to forego a part of their share for the new partner. Therefore, sacrificing Ratio is the proportion in which the existing partners of a company give up a part of their share for the new partner. The partnerRead more
When a partnership firm decides to admit a new partner into their firm, the old partners have to forego a part of their share for the new partner. Therefore, sacrificing Ratio is the proportion in which the existing partners of a company give up a part of their share for the new partner. The partners can choose to forego their shares equally or in an agreed proportion.
Before admission of the new partner, the existing partners would be sharing their profits in the old ratio. Upon admission, the profit-sharing ratio would change to accommodate the new partner. This would give rise to the new ratio. Hence Sacrificing ratio formula can be calculated as:
Sacrificing Ratio = Old Ratio – New Ratio
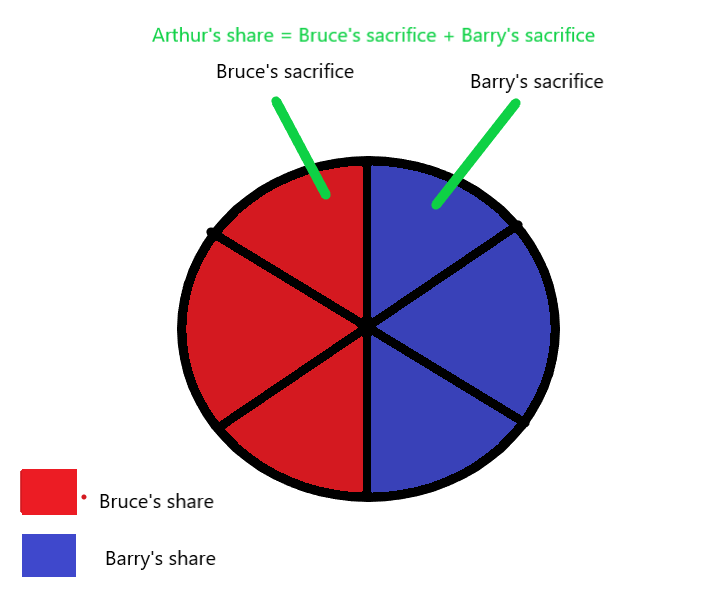
To further understand the formula, let’s say Bruce and Barry are sharing a pizza of 6 slices equally (3 slices each). They decide to share their pizza with Arthur such that they all get equal slices (2 slices each). Hence, we can use the formula to calculate their sacrifice as follows:
Bruce’s sacrifice = 3 – 2 = 1 slice
Barry’s sacrifice = 3 – 2 = 1 slice
Therefore, their sacrificing ratio = 1:1. In this same way, we can solve various problems to calculate the sacrifice of partners during a change in their profit sharing ratio.
For example, Joshua and Edwin are partners, sharing profits in the ratio 7:3. They admit Adam into their partnership such that the new profit-sharing ratio is 5:2:3. Therefore, their sacrificing ratio can be calculated as:
Joshua’s sacrifice = old share – new share = 7/10 – 5/10 = 2/10
Edwin’s sacrifice = old share – new share = 3/10 – 2/10 = 1/10
Hence, sacrificing ratio of Joshua and Edwin is 2:1. Once the denominators are equal, we ignore them and only consider numerators while showing sacrificing ratio.
See less
A profit and loss account is a financial statement which shows the net profit or net loss of an enterprise for an accounting period. It reports all the indirect expenses and indirect income including gross profit or loss derived from trading accounts for an accounting period. When the total revenueRead more
A profit and loss account is a financial statement which shows the net profit or net loss of an enterprise for an accounting period. It reports all the indirect expenses and indirect income including gross profit or loss derived from trading accounts for an accounting period.
When the total revenue i.e. credit side of profit and loss a/c is more than the total of expenses i.e. the debit side of profit and loss a/c, it results in net profit whereas when the total revenue is less than the total of expenses, it results in a net loss.
The debit balance of the profit and loss account is the net loss incurred during the accounting period by an enterprise. It is transferred to a capital account thereby reducing the capital or can be shown as a debit balance on the asset side.
Accounting entry for loss transferred is as follows :
Capital A/c …Dr.
To Profit & Loss A/c
(being net loss transferred to capital account)
Example
A Business has a total income of $50,000 in an accounting year and has expenses amounting to $60,000 in that particular year. The profit and loss account will show a net loss of $10,000 ($60,000-50,000). Net loss will be transferred to capital A/c. Capital of the business will be reduced by $10,000. This loss can also be shown on the asset side of the balance sheet.
Extract of a Profit and loss a/c showing net loss is as under:
Profit and loss A/c for the year ended …..
The debit balance for a non-corporate entity is shown as a reduction from the capital account
Extract of the Balance sheet showing the debit balance of Profit & Loss A/c is as under :
Balance Sheet as on…
Less: Profit & Loss A/c
While the Debit balance of profit and Loss A/c of a corporate entity is shown as a reduction in Reserves and surplus. If the business doesn’t have reserves then the debit balance is shown on the asset side.
Extract of the Balance sheet showing the debit balance of Profit & Loss A/c is as under :
Balance Sheet as on..
Less: Profit & Loss A/c
Conclusion: Debit balance of profit and loss a/c represents that expenses are more than the income of a business in an accounting period. Debit balance of profit and loss a/c indicates that company need to increase its income or cut down on unnecessary expenses.
The business needs to find out the reason of excessive expenses because accumulated losses are not good for the health of the company.
See less