Outstanding expenses are those expenses that have been incurred during the accounting period but are yet to be paid. Basically, any expense which has become due for payment but is not paid will be called an outstanding expense. Outstanding expenses are treated as a liability as the business is yet tRead more
Outstanding expenses are those expenses that have been incurred during the accounting period but are yet to be paid. Basically, any expense which has become due for payment but is not paid will be called an outstanding expense.
Outstanding expenses are treated as a liability as the business is yet to make payment against them. Examples of outstanding expenses include outstanding rent, salary, wages, etc.
At the end of the accounting year, outstanding expenses have to be accounted for in the book of accounts so that the financial statements reflect the accurate profit/loss of the business.
Journal entry for recording outstanding expenses:
| Expense A/c | Debit |
| To Outstanding Expenses A/c | Credit |
| (Being expenses outstanding at the end of the year) |
The concerned expense A/c is debited as there is an increase in expenses. Outstanding expenses are a liability, hence they are credited.
Let me give you a simple example,
Max, a sole proprietor pays 1,00,000 as salary for his employees at the end of every month. Due to the Covid-19 lockdown, he could not pay his employees’ salaries for March month. So the salary for March (1,00,000) will be treated as an outstanding expense. The following entry is made to record outstanding salaries for the year.
| Salary A/c | 1,00,000 |
| To Outstanding Salaries A/c | 1,00,000 |
| (Being salaries outstanding at the end of the year) |
At the end of the year, outstanding salary will be adjusted in the P&L A/c and it will be shown as a Current Liability in the Balance Sheet.
See less
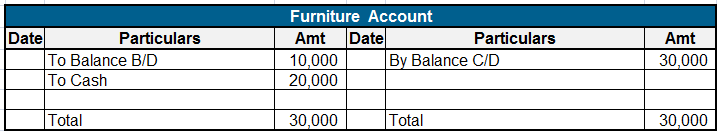
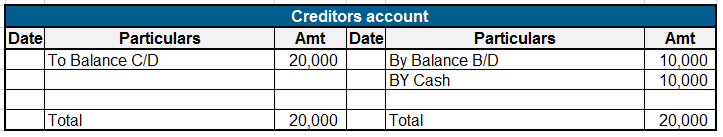
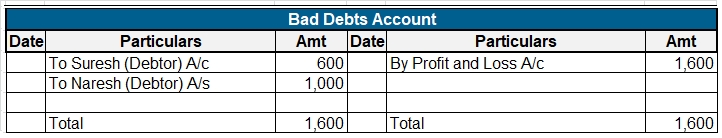
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is a not-for-profit, public interest organization. The main objective of the IFRS Foundation is to raise the standard of financial reporting and bring about global harmonization of accounting standards. IFRS was established to develop high-quality,Read more
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) is a not-for-profit, public interest organization. The main objective of the IFRS Foundation is to raise the standard of financial reporting and bring about global harmonization of accounting standards.
IFRS was established to develop high-quality, understandable, enforceable, and generally accepted accounting standards. International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) develops IFRS. There are currently 16 IFRSs in issue.
Benefits of IFRS Standards:
Following are the uses of IFRS:
Challenges faced by companies if IFRS is not implemented:
- The financial statements will differ for the companies who have offices worldwide and use only national accounting standards.
- Increased complexity while preparing financial statements.
- Difficulty in comparing and verifying financial statements.
- Accounting of transactions will differ from country to country if IFRS is not implemented.
See less