Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence. Normal wear & tear refers to the damage caused to an asset due to its continuous usage. Even when the asset is properly maintained, wear and tear occurs. Hence, it is considered to be inevitableRead more
Depreciation of fixed capital assets refers to C. Normal wear & tear & foreseen obsolescence.
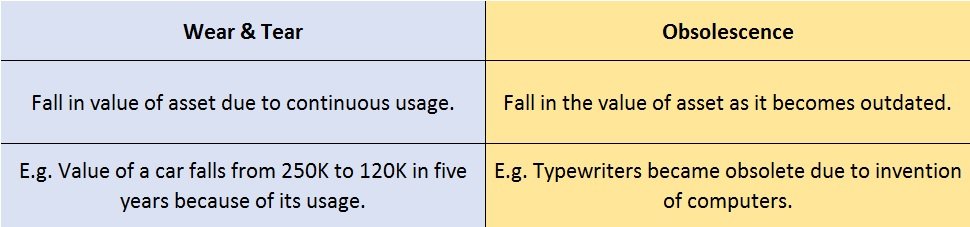
Normal wear & tear refers to the damage caused to an asset due to its continuous usage. Even when the asset is properly maintained, wear and tear occurs. Hence, it is considered to be inevitable and natural.
For example, Kumar has purchased a car for 25,00,000. After five years he wishes to sell his car. Now the market price of his used car is 12,00,000. This reduction in the value of the car from 25,00,000 to 12,00,000 is because of its usage. This fall in the value of the asset due to usage is known as normal wear & tear.
In generic terms, obsolescence means something that has become outdated or is no longer being used. Foreseen obsolescence is nothing but obsolescence that is expected.
In the context of business, whenever the value of an asset falls because it has become outdated or is replaced by a superior version, we call it obsolescence. The fall in the value of the asset due to obsolescence expected by the purchaser of the asset is known as foreseen obsolescence.
When an asset becomes obsolete it doesn’t mean it is not in working condition. Even when an asset is in good working condition it can become obsolete due to the following reasons:
- Technology advancement.
- Change in demand (change in fashion, change in taste and preferences of the consumers, etc.)
For example, before the invention of computers, people used typewriters for getting their paperwork done. With the invention of computers, laptops, etc. it is easier to type as well as save our documents, spreadsheets, etc. Thus typewriters became obsolete with the invention of computers. It has become a technology of the past.
Here is a summarised version of wear & tear and obsolescence:

Capital Expense Capital expenses are incurred for acquiring assets including incidental expenses. Such expenses increase the revenue earning capacity of the business. These are incurred to acquire, upgrade and maintain long term assets such as buildings, machines, etc and are non-recurring in natureRead more
Capital Expense
Capital expenses are incurred for acquiring assets including incidental expenses. Such expenses increase the revenue earning capacity of the business. These are incurred to acquire, upgrade and maintain long term assets such as buildings, machines, etc and are non-recurring in nature.
Revenue Expenses
Revenue expenses are incurred to carry on operations of an entity during an accounting period. Such expenses help in maintaining the revenue earning capacity of the business and are recurring in nature.
These include ordinary repair and maintenance costs necessary to keep an asset working without any substantial improvement that leads to an increase in the useful life of the asset.
Suppose, company Takeaway ltd. purchases machinery for 50,000 and pays installation charges of 10,000. Salary of 15,000 is paid to the employees and existing machinery is painted costing 8,000. Here, the cost of machinery 50,000 and installation charges of 10,000 are treated as capital expenditure and the salary of 15,000 and painting cost of 8,000 is treated as revenue expenditure.
Identification
Points to categorize an expenditure as Capital or Revenue are as follows:
For example, a company Motors ltd. purchases furniture for 65,000, repays loans amounting to 1,00,000 and pays salary of 25,000.
Here the company creates an asset of 65,000 and reduces liability by 1,00,000 as shown below and therefore is considered as capital expenditure.
However, payment of salaries neither creates assets nor reduces liability. It only reduces profits and therefore is considered as revenue expenditure.
For example, a company Stars ltd purchases machinery for 1,20,000, furniture for 35,000 and has a rental expense of 80,000.
Here, the purchase of machinery is capital expenditure since it results in higher expense. However, the purchase of furniture cannot be regarded as a revenue expense and payment of rent cannot be regarded as a capital expense only because the rental expense is higher than the amount expended for the purchase of furniture.
For example, a company Caps ltd. purchases land for 1,00,00,000 on an equal monthly installment basis. Then such payments cannot be considered as revenue expense only because the payments are recurring. Since the installments are paid in lieu of the purchase of land which is a long term asset, the payments will be considered as capital expenditure.
For example, a company Marks Ltd. purchases machinery directly from the manufacturer for 50,000. For the manufacturer, the proceeds from the sale of machine are revenue in nature but the amount expended by Marks Ltd. will be categorized as capital expenditure.
Following conclusion can be inferred from the above explanation:
*Such transactions may or may not hold true as explained above.
See less