Brief Introduction The stock of finished goods left unsold at the end of the year is known as closing stock. As closing stock represent an asset i.e. the unsold finished goods, it has a debit balance. Closing stock appears on the credit side of the trading account and on the asset side of the balanRead more
Brief Introduction
The stock of finished goods left unsold at the end of the year is known as closing stock. As closing stock represent an asset i.e. the unsold finished goods, it has a debit balance.
Closing stock appears on the credit side of the trading account and on the asset side of the balance sheet. But, if closing stock is adjusted against purchase i.e. deducted from purchase account balance, then it doesn’t appear in the trading account.
It is always shown on the asset of the balance irrespective of its treatment as discussed above because it is an asset.
Though no ledger is maintained for closing stock in financial accounts of a business, the journal entry for the closing stock is passed and is as below:
Closing stock A/c Dr Amt
To Trading A/c Amt
(When the closing stock appears in trading a/c)
OR
Closing stock A/c Dr Amt
To Purchase A/c Amt
(When closing stock is adjusted against purchase A/c and not shown in trading a/c)
Generally, the closing stock is shown separately in the trial balance because it is already part of the purchase account balance.
Closing stock is ascertained at the end of the financial year and it has great importance as it directly affects the gross profit or loss of a business. Closing stock at end of a year becomes the opening stock of the next financial year.
Numerical Example
ABC trading reported the following particulars at the end of the financial year 20X2-20X3:
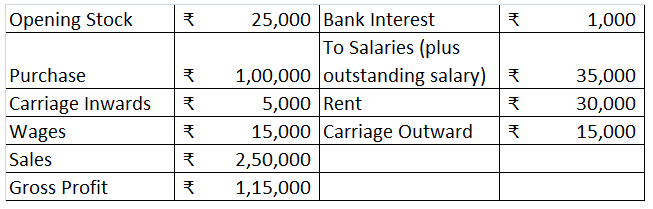
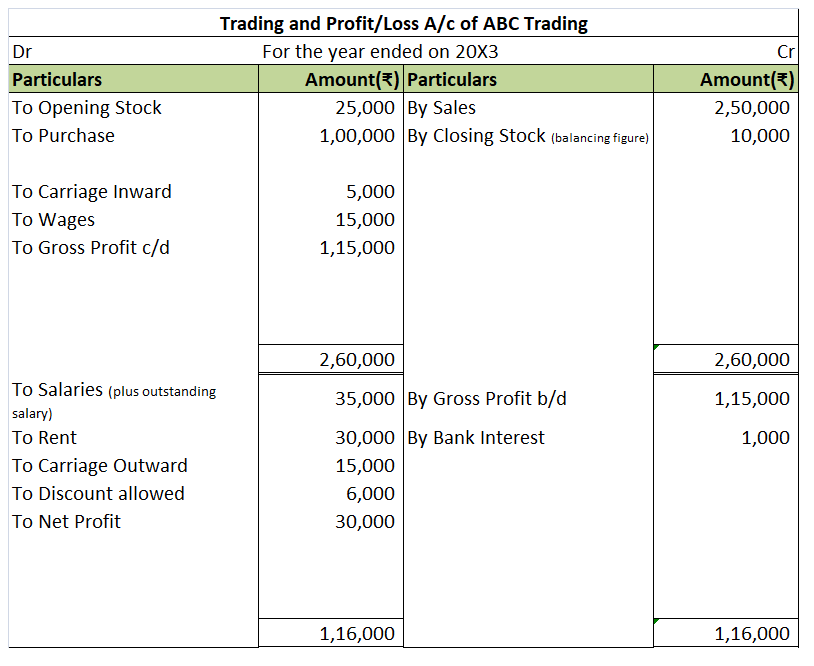
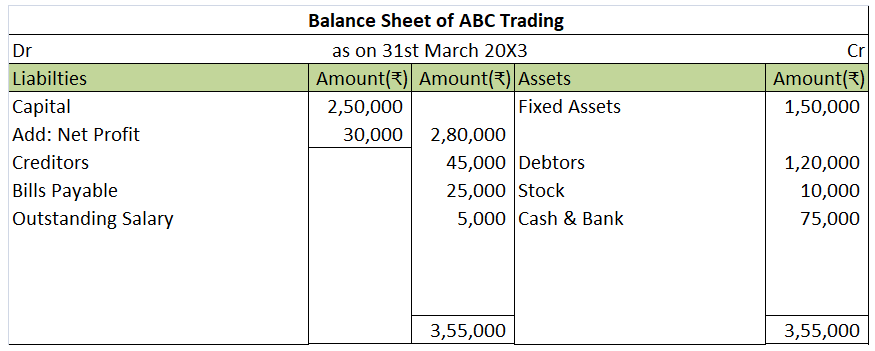
We will draw the trading and P/L account and balance sheet of ABC Trading using the above information.
As the closing stock is not given, we will calculate the closing stock as a balancing figure.
It can be also calculated using this formula:
Closing stock = Opening stock + Purchase + Gross Profit – Sales

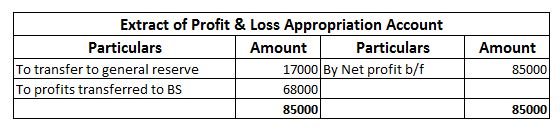
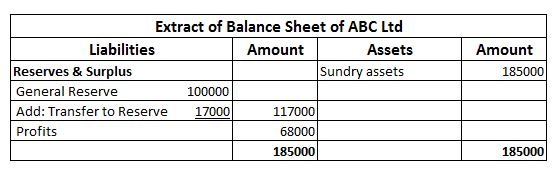
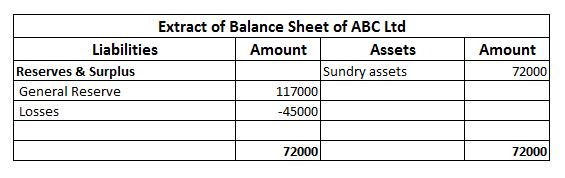

Workmen Compensation Reserve as the name suggests is a reserve created by the company to compensate its employees in the event of any uncertainty in future. It is created to protect the interest of workers in the company. Workmen Compensation Reserve Account is generally given effect in case of admiRead more
Workmen Compensation Reserve as the name suggests is a reserve created by the company to compensate its employees in the event of any uncertainty in future. It is created to protect the interest of workers in the company.
Workmen Compensation Reserve Account is generally given effect in case of admission, retirement of partners or dissolution of firm.
If there is a change in the estimated value of reserve it is given effect during the revaluation of assets and liabilities.
Journal entry if the existing reserve is less than the new estimated amount:
Revaluation A/c (Dr)
To Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c
The reserve is credited because we need to create more than the existing reserve, since the new estimated liability is more than the existing.
Journal entry if the existing reserve is more than the new estimated amount:
Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c (Dr)
To Revaluation A/c
The reserve is debited because we need to decrease the existing reserve, since the new estimated liability is less than the existing.
If a worker claims compensation, it is said to be a liability against the reserve. In case of dissolution, any such liability against workmen compensation reserve takes priority to be paid off according to the law.
Journal entry in case of claim against reserve is:
Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c (Dr)
To Workmen Compensation Claim
The amount is transferred from the reserve to a new liability, hence the reserve is debited and the claim is credited.
If there are not sufficient funds in the firm to pay the liability, partners will have to bring funds from their personal assets to pay the workers.
Journal entry when partner’s have to bring funds:
Partner’s Capital Account (Dr)
To Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c
Partner’s need to bring funds to fulfill the liability, hence there account is debited and since the reserve is increased, hence it is credited.
If there is no liability against the Workmen Compensation Reserve then it is distributed amongst the partners in their existing profit-sharing ratio.
Journal entry for distribution of reserve is:
Workmen Compensation Reserve A/c (Dr)
To Partner’s Capital Account
Since, reserve is more than required it is distributed among partners, hence their account is credited and as the reserve decreases, it is debited.
See less