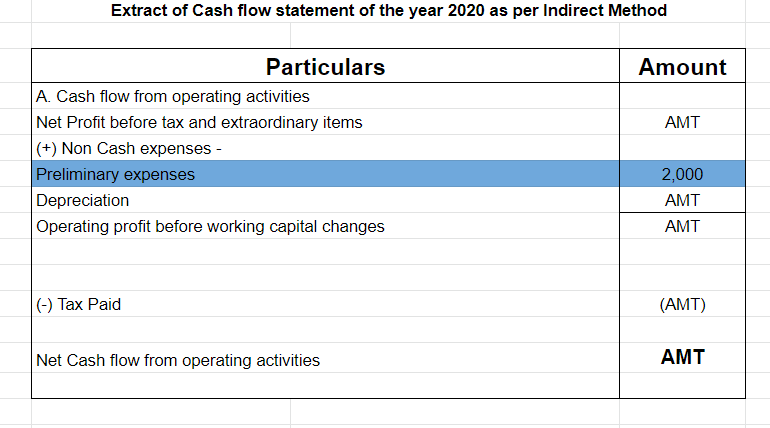
Preliminary expenses are those expenses that are incurred before the company’s business commences. These expenses are written off annually which does not involve any flow of cash. Therefore, in the cash flow statement, preliminary expenses are added back to net profit before tax and extraordinary itRead more
Preliminary expenses are those expenses that are incurred before the company’s business commences. These expenses are written off annually which does not involve any flow of cash. Therefore, in the cash flow statement, preliminary expenses are added back to net profit before tax and extraordinary items under the head operating activities (indirect method).
A cash flow statement is a financial statement that summarises the cash and cash equivalents entering and leaving the company. They can be classified into operating activities, investing activities and financing activities.
Reason for Treatment
Operating activities refer to those sources or usage of cash that relates to business activities.
As per the indirect method, the cash flow statement for operating activities begins with net profit before tax and extraordinary items. Since the company records non-cash expenditures also, they should add these back to net profit to find out the true cash flows. This is why preliminary expenses are added to net profit in the indirect method.
As per the direct method, all cash receipts are added and all cash expenses are subtracted to get cash flow from operating activities. Since preliminary expenses are a non-cash activity, they do not require any treatment in the direct method.
Preliminary expenses do not fall under the head investing activities as investing activities involve the acquisition or disposal of long term assets or investments. They do not fit in financing activities either as financing activities relate to change in capital or borrowings of the company.
Example
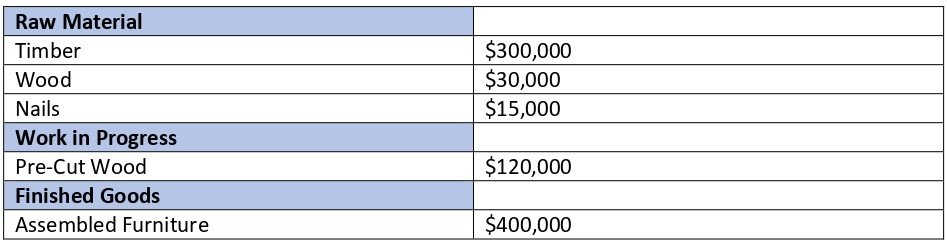
If the balance in preliminary expenses for the year 2019 was Rs.5,000 and its balance in 2020 reduced to 3,000, then its treatment in the cash flow statement would be:

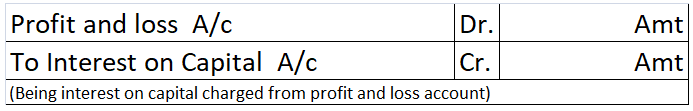

Capital Accounts record transactions of owners of a business and typically includes amount invested, retained, and withdrawn from the business. In the case of a partnership firm, there are multiple capital accounts as multiple people own the business. Capital Accounts in a partnership firm can be ofRead more
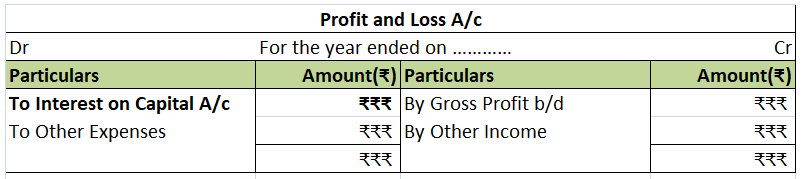
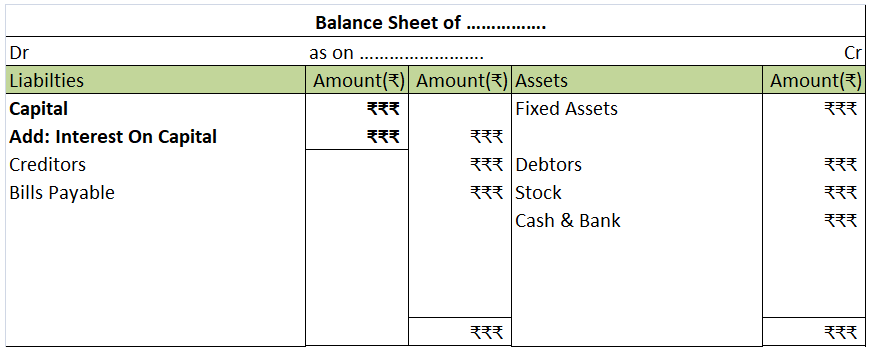
Capital Accounts record transactions of owners of a business and typically includes amount invested, retained, and withdrawn from the business. In the case of a partnership firm, there are multiple capital accounts as multiple people own the business.
Capital Accounts in a partnership firm can be of two types:
A fixed Capital Account is one where only non-recurring transactions related to capital accounts are recorded. For example:
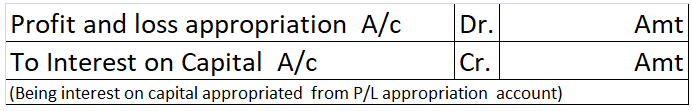
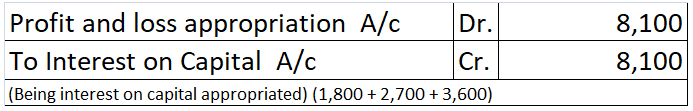
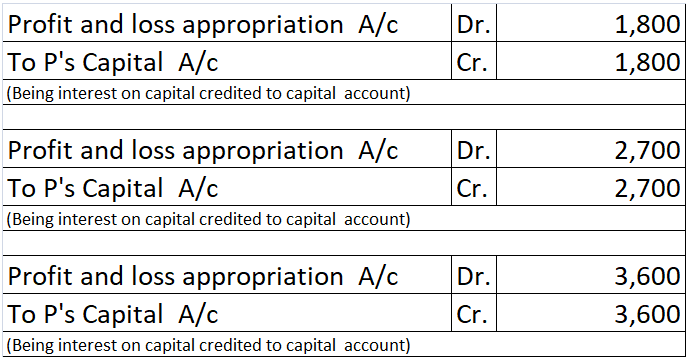
For transactions that are recurring in nature like interest on capital, the interest of drawings a separate account called Partner’s Current Account is created.
Fluctuating Capital Accounts are the ones where there is a single account to record all types of transactions related to the partner’s capital account, whether recurring or nonrecurring.
Fixed Capital Accounts are usually created in cases where there are numerous recurring transactions and partners want to keep a record of the fixed amount invested in the business by all the partners at any point in time.
Fluctuating Capital Account is usually created in cases where the number of recurring transactions is not high or partners want to keep a record of the amount due to all the partners in business at any point in time.
However, the decision to choose what kind of capital account should be implemented in the firm is complete with the partners. They may choose whatever they think is a more suitable fit.
To summarise the difference between the two following table can be used:
· Capital introduced
· Capital withdrawn
· Interest on capital
· Interest in drawings
See less