You must have knowledge of what depreciation is. Depreciation is the process of allocating the value of an asset over its useful life. It reduces the carrying value of the asset year by year till it is scraped. It is an expense (expense of using the asset for business purposes) and it is charged toRead more
You must have knowledge of what depreciation is. Depreciation is the process of allocating the value of an asset over its useful life. It reduces the carrying value of the asset year by year till it is scraped.
It is an expense (expense of using the asset for business purposes) and it is charged to profit and loss account.
Depreciation can be reported in the financial statement in two ways:
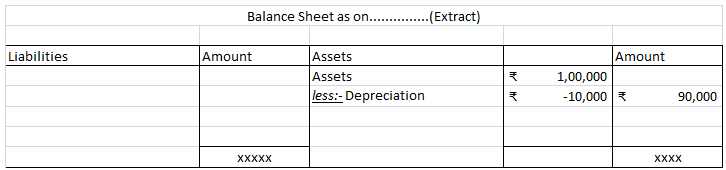
- Deduct depreciation from the asset account and show the asset at “depreciation less” value. See the journal entries below:
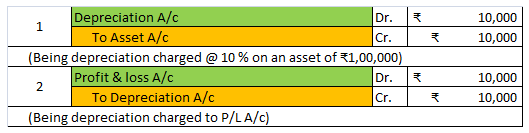
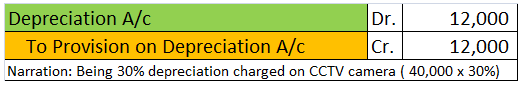
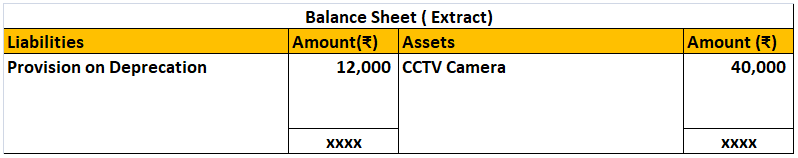
- Maintain a provision for depreciation account and show the asset account at original cost. In this method, no entry is passed through the asset account. See the journal entries below:
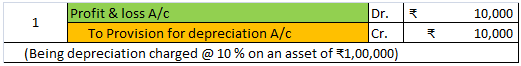
Provision for depreciation account represents the collection of total depreciation till date on an asset. That’s why it is also called accumulated depreciation account. When an asset is sold, its accumulated depreciation is credited to the asset account. See the journal entry below:
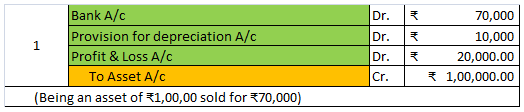
It is shown on the liabilities side of the balance sheet. It is a nominal account because it is shown as an expense in the statement of profit or loss.
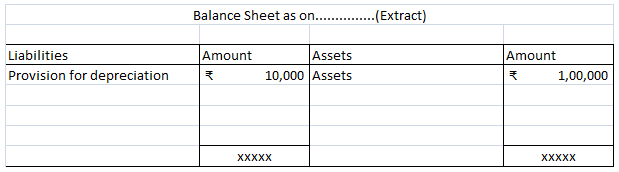
In case provision for depreciation account is not maintained then the balance sheet looks like this:



Firstly, let’s understand the meaning of both terms. Revenue receipts: The term 'revenue' suggests these are the amounts received by a business due to its operating activities. These receipts arise in a recurring manner in a business. Such receipts don’t affect the balance sheet. They are shown inRead more
Firstly, let’s understand the meaning of both terms.
Revenue receipts: The term ‘revenue‘ suggests these are the amounts received by a business due to its operating activities. These receipts arise in a recurring manner in a business. Such receipts don’t affect the balance sheet. They are shown in the statement of profit or loss. Such receipts are essential for the survival of the business.
Examples of revenue receipts are as follows:
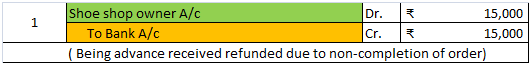
Capital receipts: The term ‘capital’ that such receipts are do not arise due to operating activities, hence not shown in the Profit and loss statement. These are the money received by a business when they sell any asset or undertake any liability. These receipts do not arise in a recurring manner in a business. They don’t affect the profit or loss of the business. They are not essential for the survival of the business.
Examples of capital receipts are as follows:
I have given a table below for more understanding:

See less