Meaning of Working Capital Firstly, let’s understand the meaning of the working capital. Working capital is the factor which demonstrates the liquidity position of the business to carry out day to day operations. It majorly includes cash & bank balances and liquid assets. Managing working capitaRead more
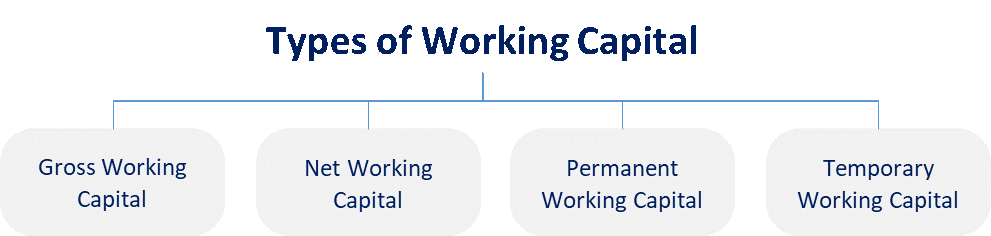
Meaning of Working Capital
Firstly, let’s understand the meaning of the working capital. Working capital is the factor which demonstrates the liquidity position of the business to carry out day to day operations. It majorly includes cash & bank balances and liquid assets.
Managing working capital is a crucial process to maintain short term liquidity and so ultimately resulting into achieving long term objectives efficiently. Working capital can be calculated by deducting business’s current liabilities from current assets.
To achieve the ideal working capital requirement for any business, it is important to understand various types of working capital and various ways to manage it.
Coming to Permanent Working Capital, also called as Fixed Working Capital, it is the minimum working capital required or maintained by businesses. Such type of working capital is maintained to take care of regular financial obligations like creditors, inventory, salaries etc.
Irrespective of scale of operations carried out in business, Permanent Capital is maintained by businesses which can be in form of Net Working Capital.
There is no specific formula for calculating Fixed Working Capital, it completely depends upon the business’s assets and liabilities. So accordingly, it can be estimated through the balance sheet of the business.
For calculating Permanent Working Capital, you can follow below steps:
- Calculate Net Working Capital for each day for a whole month
- Find the smallest value among them
- That will be Permanent Working Capital for the month
- Follow the above steps for every month
- There you have the annual figure for Permanent Working Capital
The requirement of Permanent Working Capital changes as the business expands. It is crucial to make sure that the working capital level does not fall below the Permanent Working Capital requirement.
Types of Permanent Working Capital:
Permanent working capital is further divided into two types:
- Regular working capital – This refers to capital required to maintain healthy cashflow for purchases of raw materials, payment of wages etc.
- Reserve working capital – This refers to amount which is more than regular working capital to take care of unexpected business expenses due to contingent events.

Let’s understand what a cashbook is: A petty cash book is a cash book maintained to record petty expenses. By petty expenses, we mean small or minute expenses for which the payment is made in coins or a few notes like tea or coffee expense, bus or taxi fare, stationery expense etc. Such expenses areRead more
Let’s understand what a cashbook is:
The manner in which entries are made
When cash is given to the petty cashier, entry is made on the debit side and in the petty cashbook and credit entry in the general cashbook.
Entries for all the expenses are made on the credit side.
Generally, the petty cashbook is prepared as per the Imprest system. As per the Imprest system, the petty expenses for a period (month or week) are estimated and a fixed amount is given to the petty cashier to spend for that period.
At the end of the period, the petty cashier sends the details to the chief cashier and he is reimbursed the amount spent. In this way, the debit balance of the petty cashbook always remains the same.
Format and items which appear in the petty cashbook
The format of the petty cashbook depends upon the type of petty cash book is prepared and the items appearing in it are nothing but petty expenses. Let’s see an example:-
A business incurred the following petty expenses for the month of April:-
Now we will prepare two types of cashbooks:
Here, the Petty cash book is of the same format as the general cash book.
The cash allocated for petty expenses is recorded on the debit side of the petty cash book and on the credit side of the general cash book.
Here, there are separate amount columns for each type of expense. As the name suggests, this type of petty cashbook helps to analyse the petty cash spending on basis of the type of expense.
See less