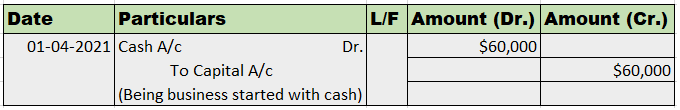
The receipt of cash is recorded by debiting the cash account to the account from which the cash is received. This source account may be the sales account, account receivable account or any other account from which cash is received. The journal entry is: An entity may receive cash in the following evRead more
The receipt of cash is recorded by debiting the cash account to the account from which the cash is received. This source account may be the sales account, account receivable account or any other account from which cash is received.
The journal entry is:

An entity may receive cash in the following events:
- Sales of goods or provision of services
- Payment from account receivables
- Sale of assets.
- Withdrawal of cash from the bank
- Introduction of additional capital in the business
- Subscription or donation received in case of non-profit oriented concerns.
- Other income in cash
This list is not exhaustive. There may be many such events. However, the cash account will be always debited.
Rules of accounting applicable on the cash account
As per the golden rules of accounting, the cash account is a real account as represents an asset. For real accounts, the rule, “Debit the receiver and credit the giver” applies.
Hence, when cash is received, cash is debited and the source (giver) is credited.
As per modern rules of accounting, the cash account is an asset account. Assets accounts are debited when increased and credited when decreased.
Hence, at receipt of cash, cash is debited as cash is increased.
See less
Under Activity-Based Costing, overheads are accurately assigned to different activities and their costs are determined through costing methods. Activities are those events that incur costs whereas overheads are expenditures that cannot be traced to any particular cost unit. A Cost driver refers to tRead more
Under Activity-Based Costing, overheads are accurately assigned to different activities and their costs are determined through costing methods. Activities are those events that incur costs whereas overheads are expenditures that cannot be traced to any particular cost unit.
A Cost driver refers to the factor that causes a change in the cost of an activity. Activity-Based Costing is done to establish a link between the activities and the product. The cost drivers are those links between the activities and the product.
Cost drivers are divided into four categories:
A Cost Centre refers to a department in a business where costs can be allocated. These departments run various processes and incur costs. They can be related to the production of goods or the provision of services. Different centres are allocated different budgets and hence it enables the business to run efficiently by tracking its incomes and expenses easily.
Proper management of cost centres can help the company cut additional costs from each department. It also helps in more accurate forecasts depending on future changes.
Cost centres and Cost Drivers are both important factors while following Activity-Based Costing. Some examples of cost drivers and cost centres are as follows :
See less