Whenever the proprietor/owner of a business withdraws cash or goods from the business for his/her personal use, we call it drawings. For example, Alex, proprietor of a soap manufacturing company, takes 50 pack of soaps costing 30 each for his personal use. So, 1,500 (50*30) will be considered as draRead more
Whenever the proprietor/owner of a business withdraws cash or goods from the business for his/her personal use, we call it drawings. For example, Alex, proprietor of a soap manufacturing company, takes 50 pack of soaps costing 30 each for his personal use. So, 1,500 (50*30) will be considered as drawings of Alex. One important thing to note here is whenever goods are withdrawn for personal use they are valued at cost.
Drawings are not an asset/liability/expense/income to the business. The drawings account is a contra-equity account. A contra-equity account is a capital account with a negative balance i.e. debit balance. It reduces the owner’s equity/capital.
Drawings being a contra-equity account has a debit balance, reducing the owner’s capital in the business. This is because withdrawals for personal use represent a reduction of the owner’s equity in the business.
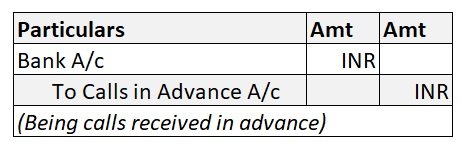
Drawings are not shown in the Income Statement as they are neither an expense nor an income for the business. However, the following journal entries are passed to record drawings for the year:
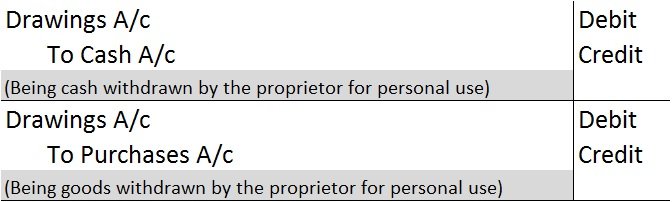
Drawings A/c is debited because it reduces the owner’s capital. Cash/Purchases A/c is debited as a withdrawal reduces the assets of the business.
At the end of the year, drawings A/c are closed by transferring it to the owner’s capital A/c. We post the following entry to close the drawings A/c at the end of the year:
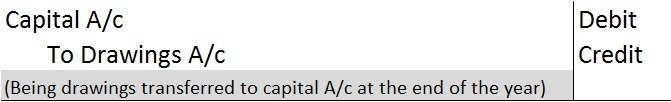
In the balance sheet, drawings are shown by deducting it from the owner’s capital A/c.
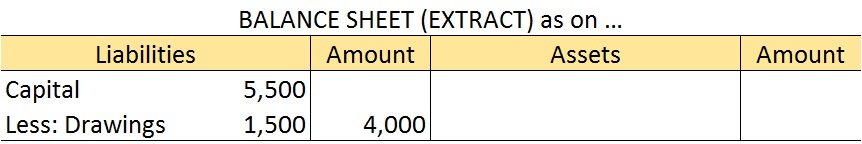
Let us take our earlier example of Alex. He withdrew soaps worth 1,500. At the end of the year, his capital was worth 5,500. The journal entry for recording the drawings is as follows:

In the balance sheet, drawings worth 1,500 are shown as follows:



Drawings mean the certain sum of amount or goods withdrawn by owners from the business for personal use. The drawings account is not an asset/liability/expense/income account, it is a contra account to the owner's equity or capital account. Drawings A/c will always have a debit balance. Drawings A/cRead more
Drawings mean the certain sum of amount or goods withdrawn by owners from the business for personal use. The drawings account is not an asset/liability/expense/income account, it is a contra account to the owner’s equity or capital account. Drawings A/c will always have a debit balance.
Drawings A/c debit balance is contrary to the Capital A/c credit balance because any withdrawal from the business for personal use will reduce the capital.
Effect on Trial Balance: Drawings will be shown in the debit column of the trial balance.
Effect on Financial Statements: The owner’s drawings will affect the company’s balance sheet by decreasing the asset that is withdrawn, and a corresponding decrease in the owner’s equity or capital invested.
Example:
Mr.B a sole proprietor withdraws $100 each month for personal use. At the end of the year Drawings A/c had a debit balance of $1,200.
Mr.B records drawings of $100 each month and debits drawings a/c and credits cash a/c. At the end of the year, he will transfer the balance and will debit capital a/c and credit drawings a/c by $1,200.
He will show a balance of $1,200 ($100*12) in the trial balance in the debit column. Assuming closing capital of $50,000.
In the financial statement, the balance of drawings a/c will be deducted from the owner’s capital because it is a contra account and this will reduce the owner’s capital for the year.
See less