Introduction In Tally, journal entries are made in the vouchers. For each type of journal entry, there is a specific voucher. It is the vouchers where the transactions are recorded along with all the relevant details. Hence, when we speak of journal entries in tally, it is the vouchers which we haveRead more
Introduction
In Tally, journal entries are made in the vouchers. For each type of journal entry, there is a specific voucher. It is the vouchers where the transactions are recorded along with all the relevant details. Hence, when we speak of journal entries in tally, it is the vouchers which we have to master.
In Tally, vouchers are of four types:
- Accounting vouchers
- Inventory vouchers
- Order voucher
- Payroll voucher
The vouchers under the above voucher types are as shown below:
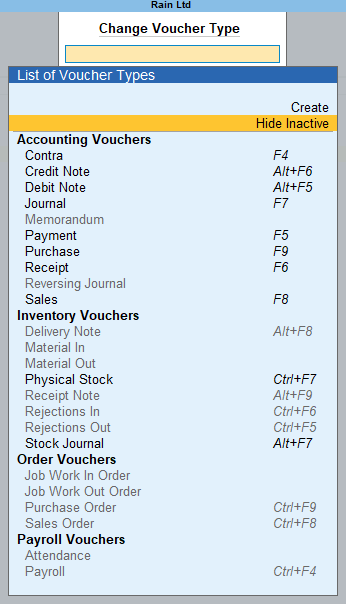
To open the voucher creation menu follow these steps:
In Tally ERP 9: Gateway of Tally→ Accounting Vouchers→ Voucher creation menu will open
In Tally Prime: Gateway of Tally→ Vouchers→ Voucher creation menu will open
Out of the above vouchers, the vouchers which I would suggest you practice are as follows (along with their short-cut keys):
- Contra Voucher – F4
- Payment Voucher – F5
- Receipt Voucher – F6
- Journal Voucher – F7
- Sales Voucher – F8
- Purchase Voucher – F9
- Credit note – Alt + F6
- Debit note – Alt + F5
All of the above are accounting vouchers. You can simply press the short-cut keys to open the respective voucher while in the voucher creation menu
If you are new to tally, I would suggest you practice only the accounting vouchers.
Here, I have discussed only the accounting vouchers:
Payment Voucher – F5
A payment voucher is used to record payments of cash or by the bank. Payment can be to creditors or for expenses.
There are two modes to this voucher which you can change by clicking the ‘Change Mode’ option on the right-hand side menu or simply pressing Ctrl + H. This menu will open.
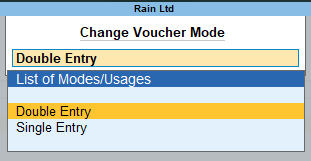
Select the ‘Double Entry’ mode for sake of simplicity. In this mode, the entry will be just like the conventional journal entry as in the double entry system of accounting.
You have to just select the account you want debit which can be an expense, creditor etc. and you can credit only the cash or bank accounts as it is a payment voucher. Below there is a narration field which you can fill too. After entering all the necessary details you have to accept the voucher.
Here, is a filled payment voucher in which I have recorded an expense payment entry.
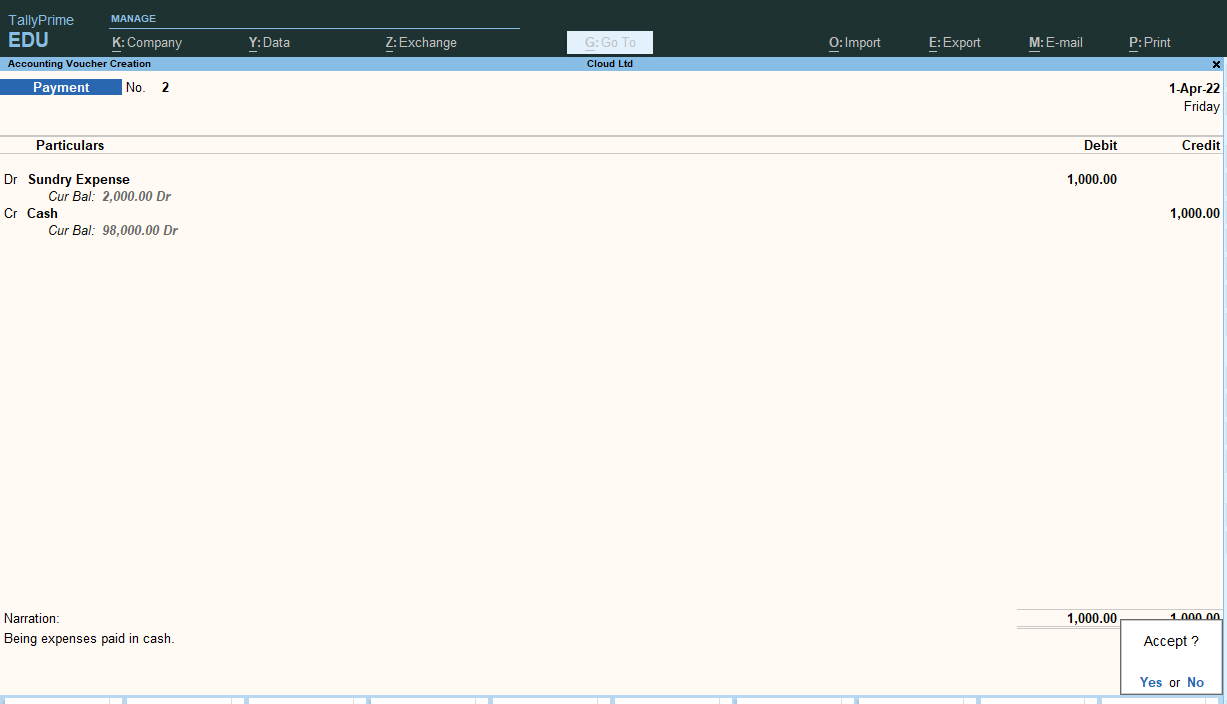
The journal entries which you can practice on payment vouchers are as follows:
- Payment of expenses like rent, electricity, wages, salaries, carriage, interest etc
- Payment to trade creditors.
- Purchase of Assets
Receipt Voucher – F6
A receipt voucher is used for the recorded receipt of cash in the business. Just like a payment voucher, I recommend you to use it in Double Entry mode. In Tally prime, it looks this:
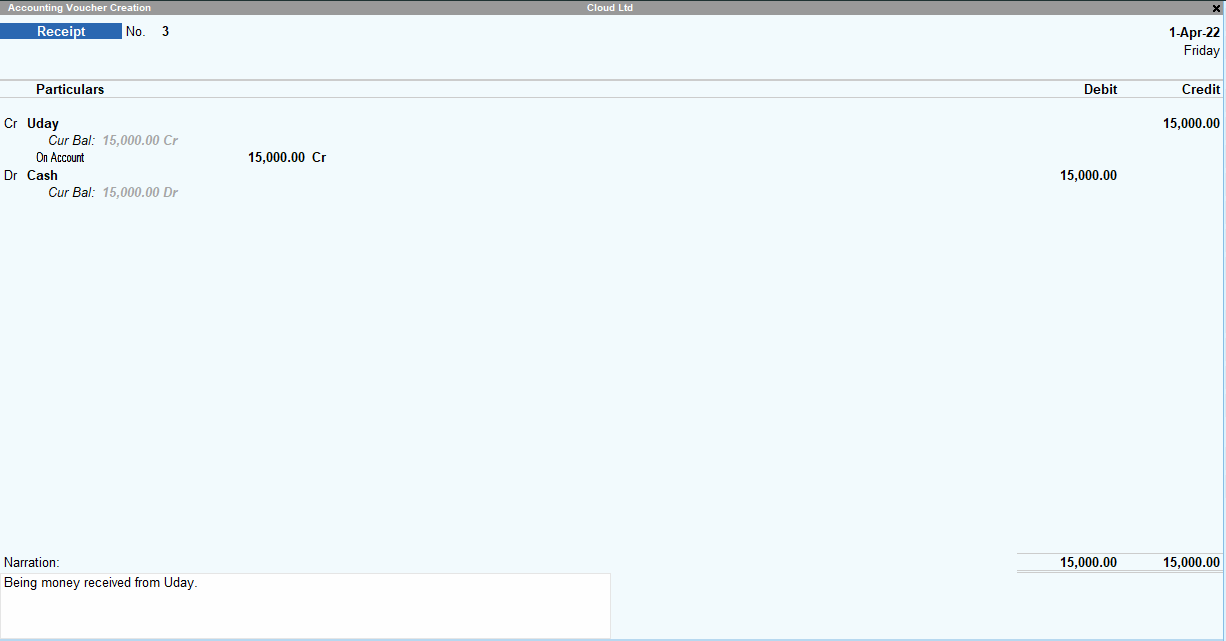
The receipt voucher given above is already filled. I have passed a ‘collection from the debtor’ entry here.
The journal entries you can practice in the receipt voucher are as follows:
- Receipt of cash from trade debtors.
- Receipt of interest from the bank.
- Commission received
- Sale of Assets.
Purchase Voucher – F7
A purchase voucher is a voucher for exclusively recording purchase of goods entries. Purchase whether cash or credit should be recorded in the purchase voucher only as it allows recording of additional details related to purchase as well as tracking with purchase order and receipt note.
The purchase voucher looks like this:
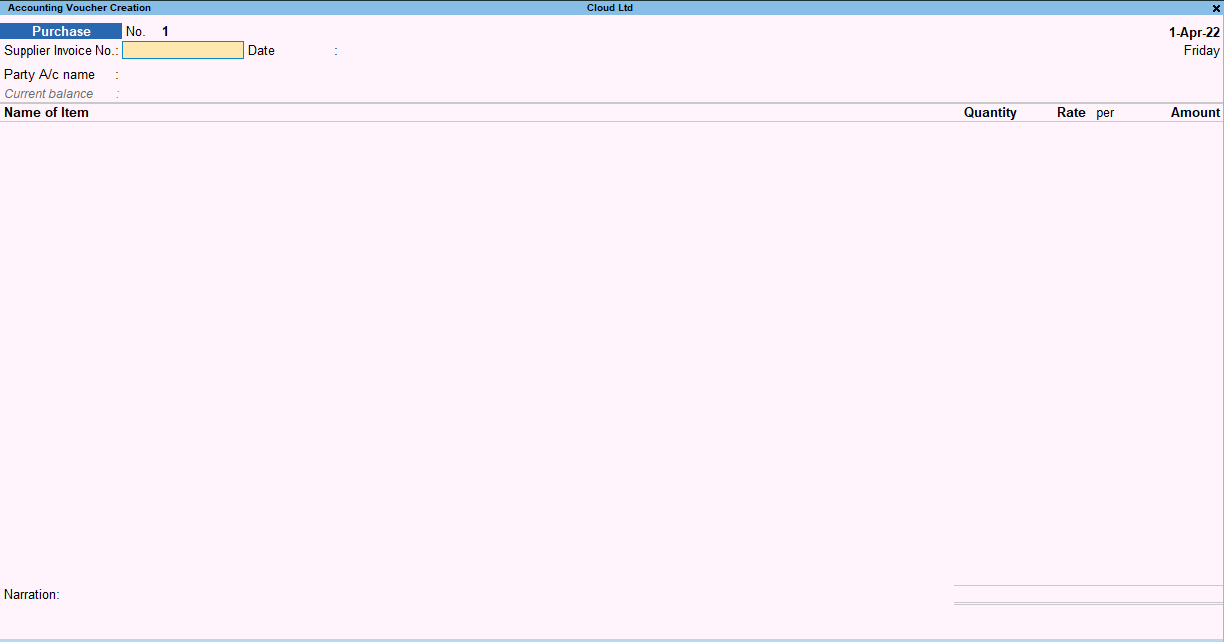
Here, the purchase voucher is opened in ‘Item invoice’ mode. Item invoice is easier to understand hence I advise you to this mode to use the purchase voucher. You can change the mode by pressing Ctrl + H.
If you wish to record transactions like journal entries then you can choose the ‘As Voucher’ mode.
The details which you have to fill in are as follows:
- Reference number or Bill number
- Party A/c Name or the name of the creditor. (If the creditor is not created, press Alt + C to create)
- Name of item purchased ( Press Alt + C to create the stock item if not created)
- Enter the quantity and rate of the item and the total amount will be auto-populated.
- The accounting details menu will open asking for the account to be debited for the purchase. Select the purchase account you want to debit or create a purchase account by pressing Alt + C if not created.

- Enter a narration if you want and accept the voucher.
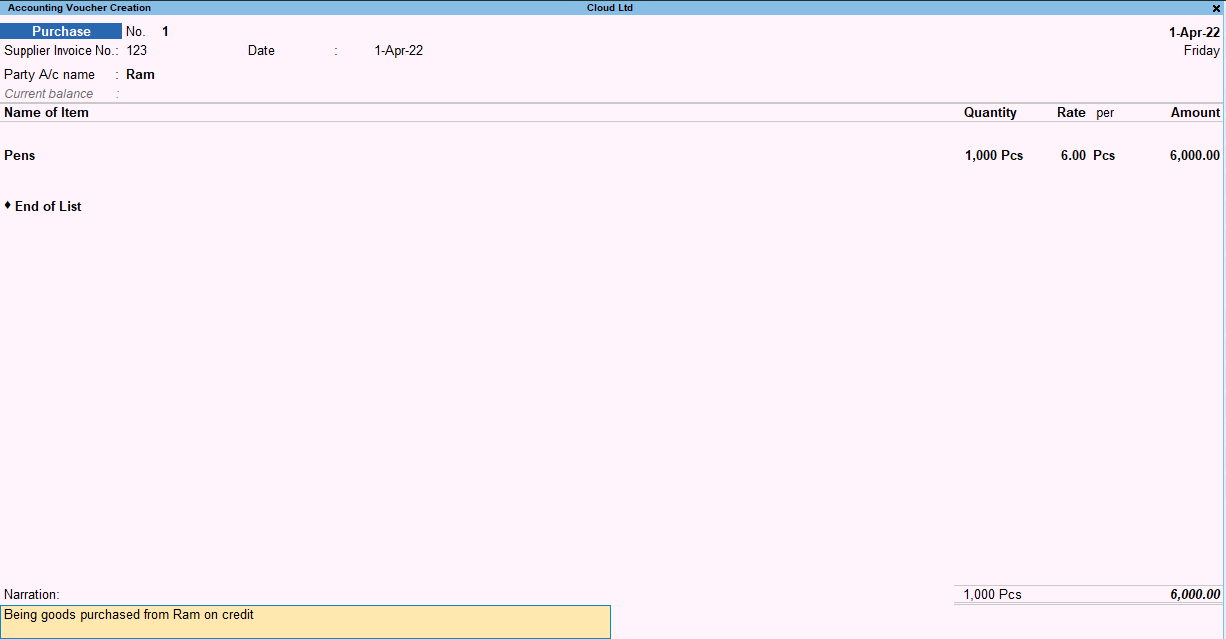
Below is a complete purchase voucher where a credit sale transaction is passed:
Sales Voucher – F8
A sales voucher is a voucher for exclusively recording sales of goods entries. Sales, whether cash or credit, should be recorded in the sales voucher only as it allows recording of additional details related to sales as well as tracking with Sales orders and Delivery notes.
Here also, I recommend you to use the sales voucher in Invoice mode
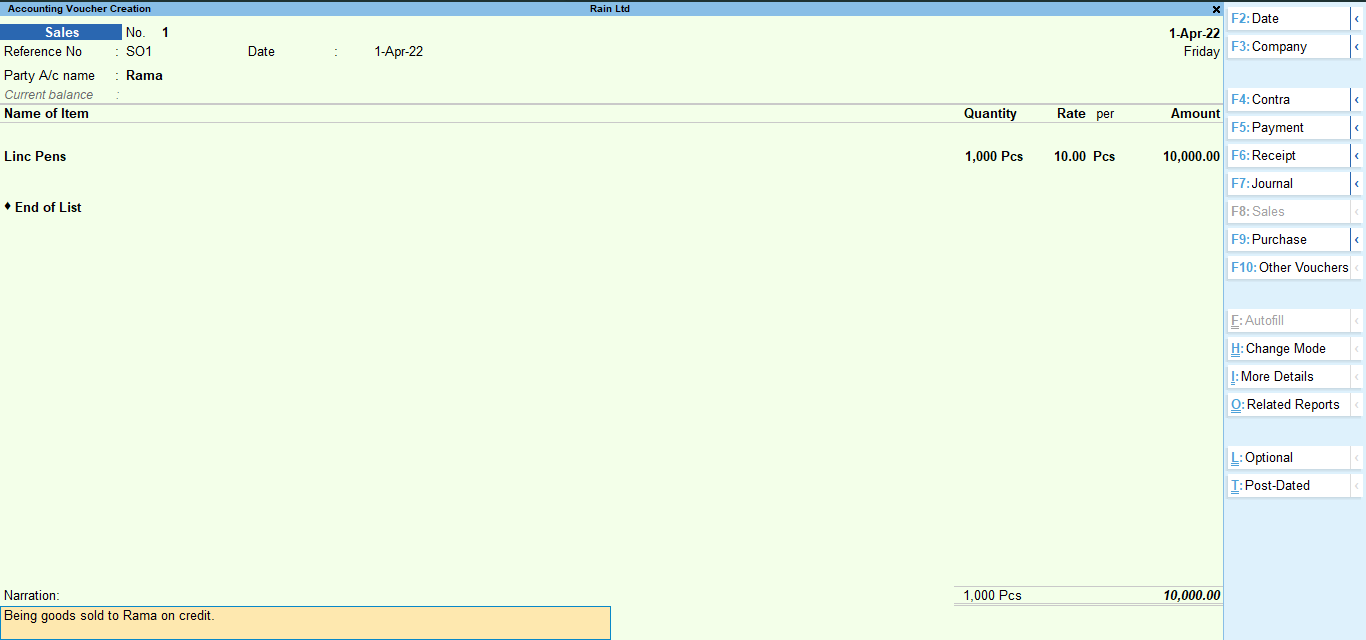
Filling up of details in sales voucher is same as in purchase voucher. The difference here is that in the ‘Accounting details’ section you have selected a sales account to be credited.

Here is a completed sales voucher where I have recorded a credit sale transaction:
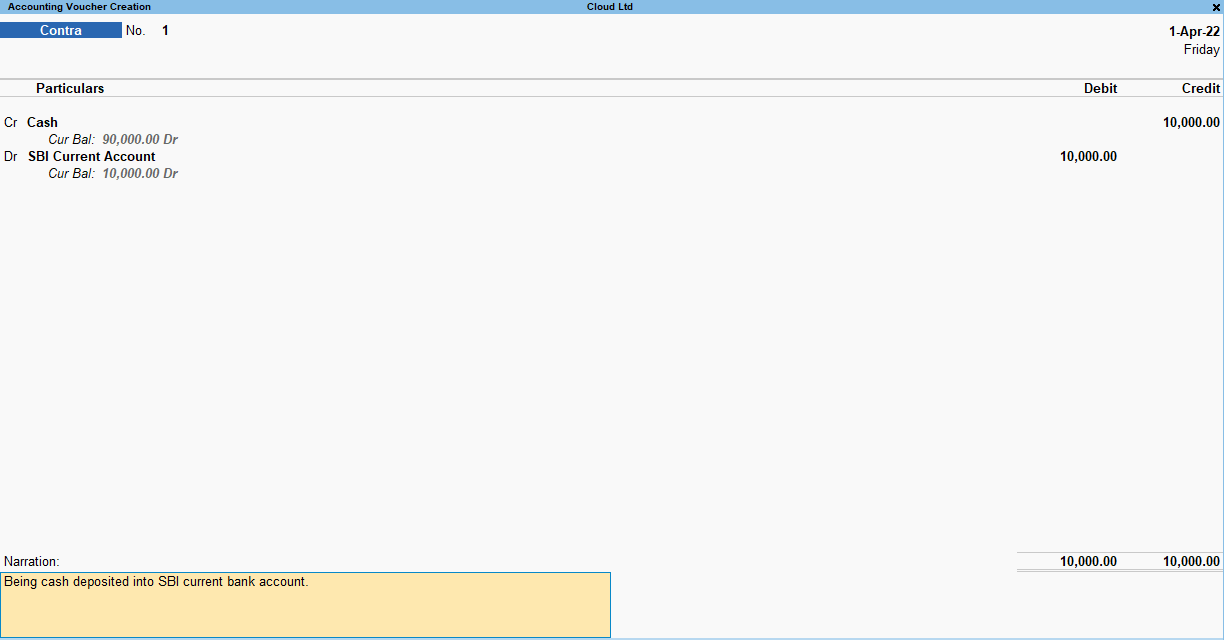
Contra Voucher – F4
A Contra voucher is used to record contra transactions. Contra transactions are those transactions which take place between:
- A Bank account and cash account
- Two different bank accounts
The journal entries which can be practised on contra voucher are as follows:
- Withdrawal of cash from the bank.
- Deposit from cash into the bank.
- Transfer of amount from one bank to another.
Given below is a completed Contra voucher in which ‘cash deposited into bank’ transaction is recorded:
Journal Voucher – F7
There are many transactions which cannot be passed in any of the vouchers discussed above. The examples of such transactions or journal entries are as follows:
- Depreciation of assets
- Entries related to the provision
- Prepaid Expenses
- Outstanding expenses
- Rectification of error entries
- Accrued income entries
- Any other entry which cannot be passed in any other voucher.
It is an important voucher in Tally as many crucial entries are recorded in it.
The journal voucher looks like this:
It looks like a journal book and it does not have any different mode like voucher discussed above:
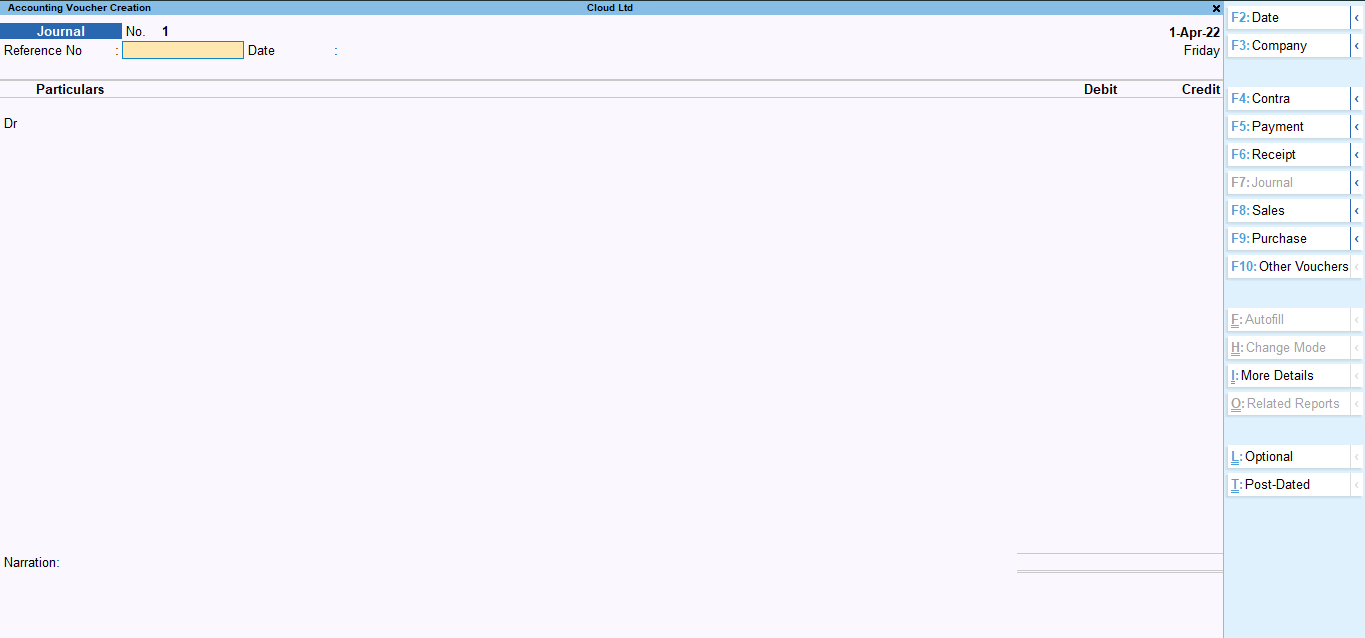
The journal entries to practice on journal vouchers are many. You can refer to the examples of transactions I have mentioned above.
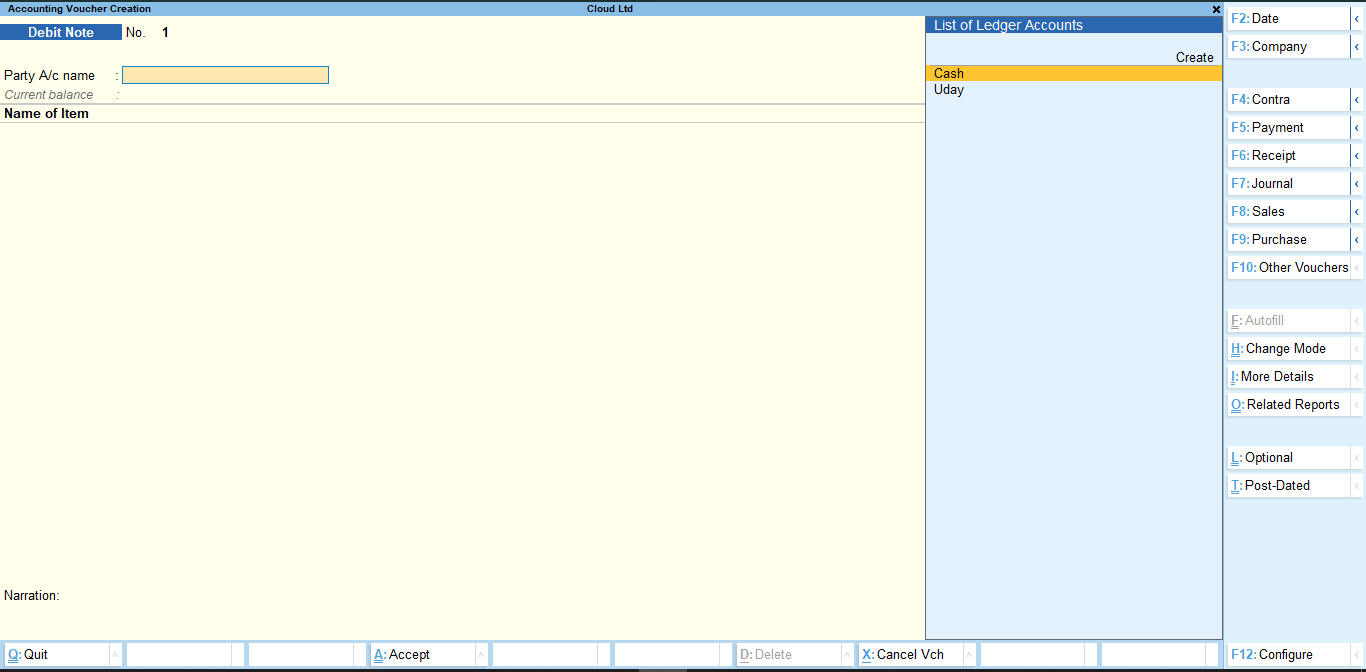
Debit Note Voucher – Alt + F5
A debit note voucher is to record purchase return transactions in Tally. Hence, the only transaction you can record here is of purchase return. The debit note voucher looks like this:
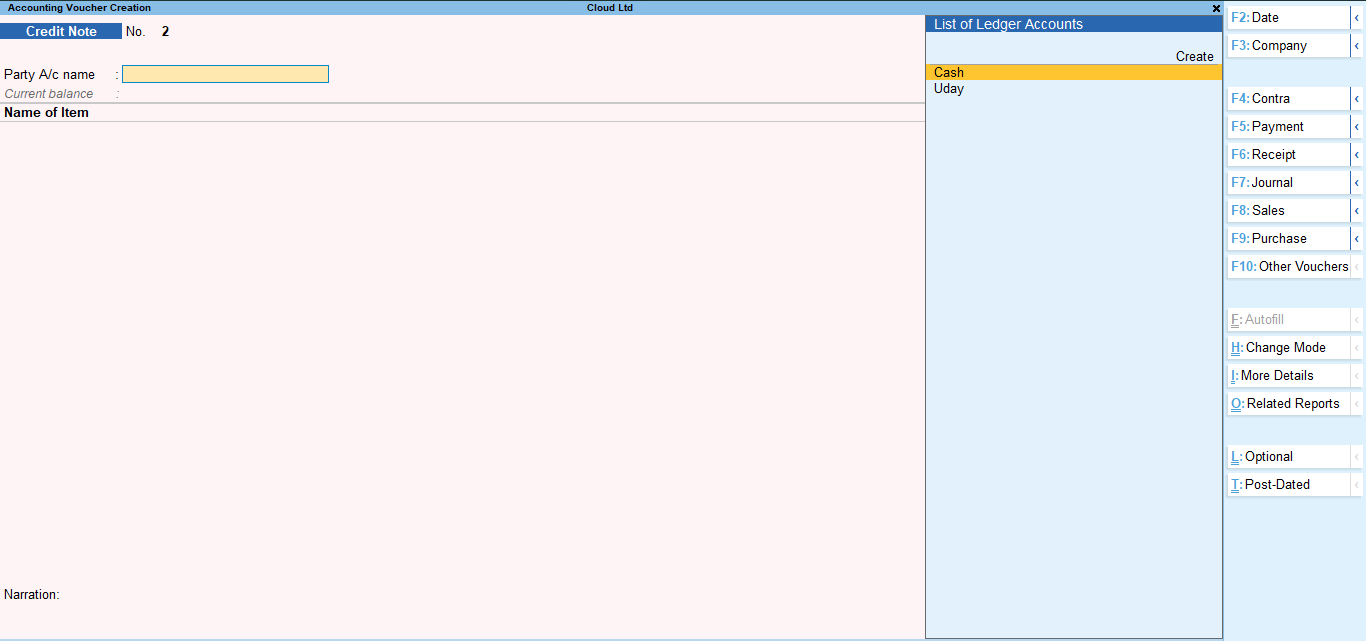
Credit Note Voucher– Alt + F5
In credit note vouchers, the sale return transactions are recorded. The credit note voucher looks like this:
That’s all. These are vouchers I would recommend one to practice on Tally.
See less

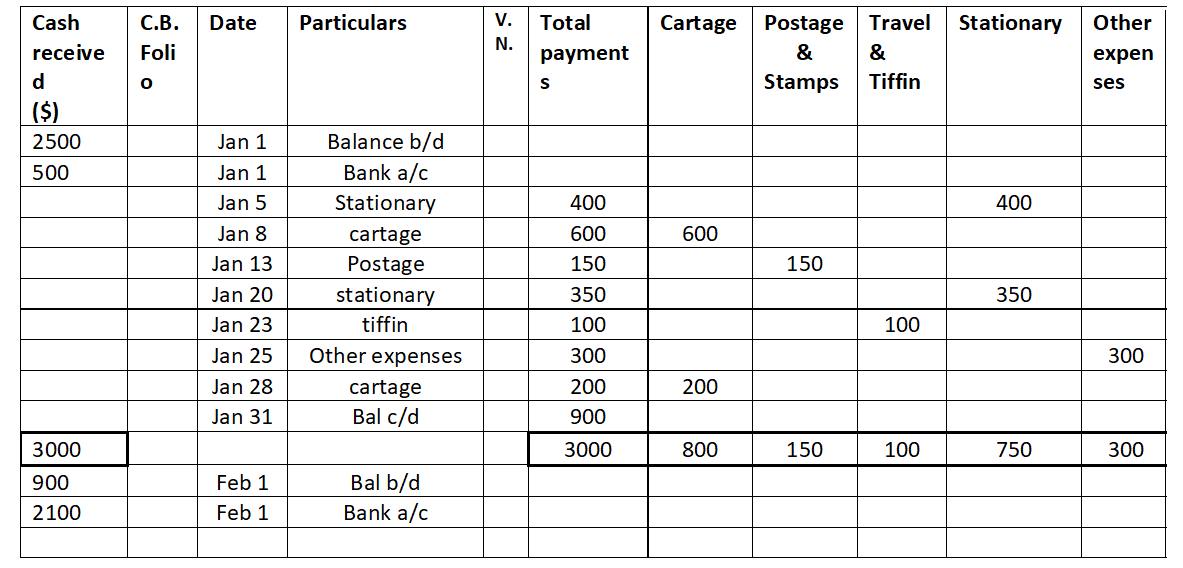
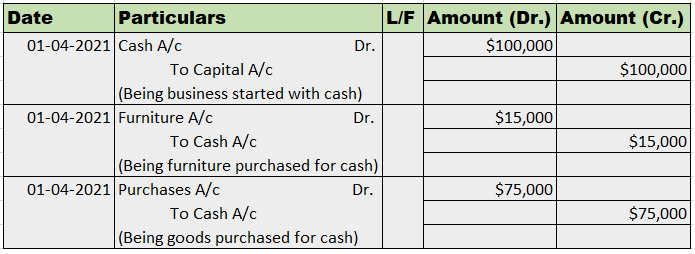
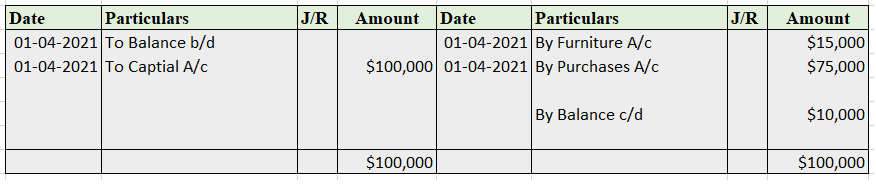
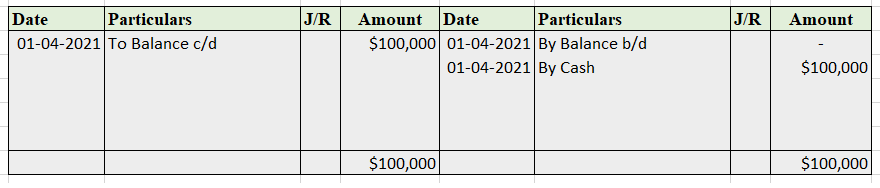
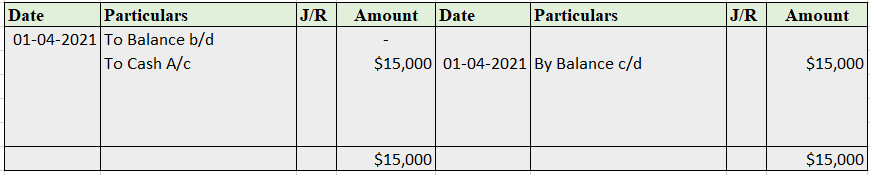
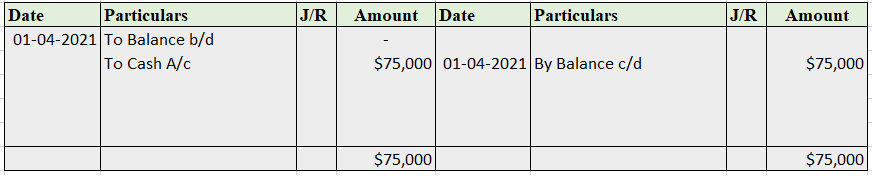
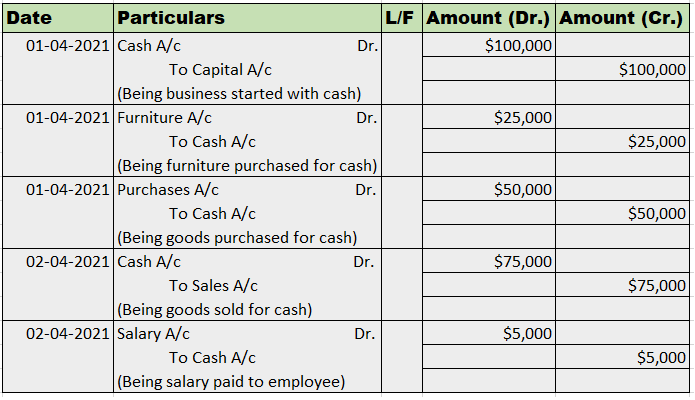
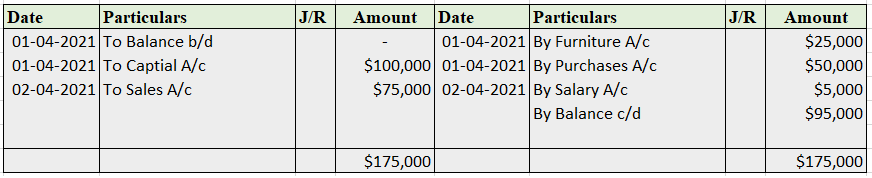
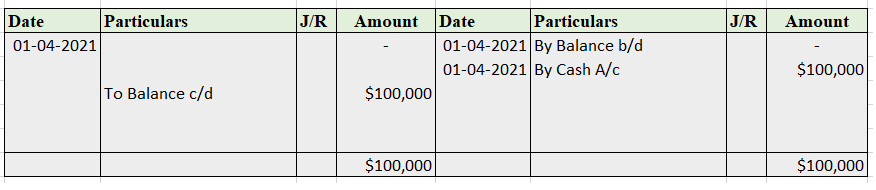
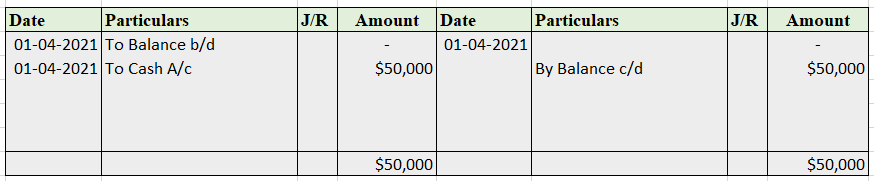
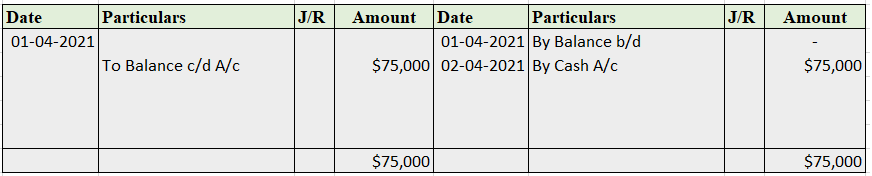
Sundry debtor refers to either a person or an entity that owes money to the business. If someone buys some goods/services from the business and the payment is yet to be received, a group of such individuals or entities is called sundry debtors. Sundry debtors are also referred to as trade receivableRead more
Sundry debtor refers to either a person or an entity that owes money to the business. If someone buys some goods/services from the business and the payment is yet to be received, a group of such individuals or entities is called sundry debtors. Sundry debtors are also referred to as trade receivables or account receivables.
The term ‘Sundry’ means various or several, referring to a collection of miscellaneous items combined under one head. Sundry debtors typically arise from core business activities such as sales of goods or services. The business treats them as an asset.
Example
Suppose you run a business, ABC Ltd. Mr. Y bought goods from you on credit. Therefore, Mr. Y will be recorded as Debtor (current asset) in your books of accounts. Similarly, a collection of such debtors is viewed as sundry debtors from the business’ point of view.
Journal Entry
Rules
As per the golden rules of accounting, we ‘debit the receiver and credit the receiver’. That’s how in this journal entry we’ll be debiting the sundry debtor’s account. Also, ‘debit what comes in and credit what goes out.’ That’s why sales a/c is credited and cash a/c is debited.
As per the modern rules of accounting, ‘debit the increase in asset and credit the decrease in asset’. That’s why we debit sundry debtors and cash a/c. And credit sales a/c when goods are sold and inventory decreases.
Why debtor is an asset?
As we know, a debtor refers to a person or entity who owes money to the business which means, the money is to be received by them in the future, making them an asset. On the other hand, creditors are a liability to the firm as we owe them money and it is to be paid by us in the near future, making it an obligation for the firm.
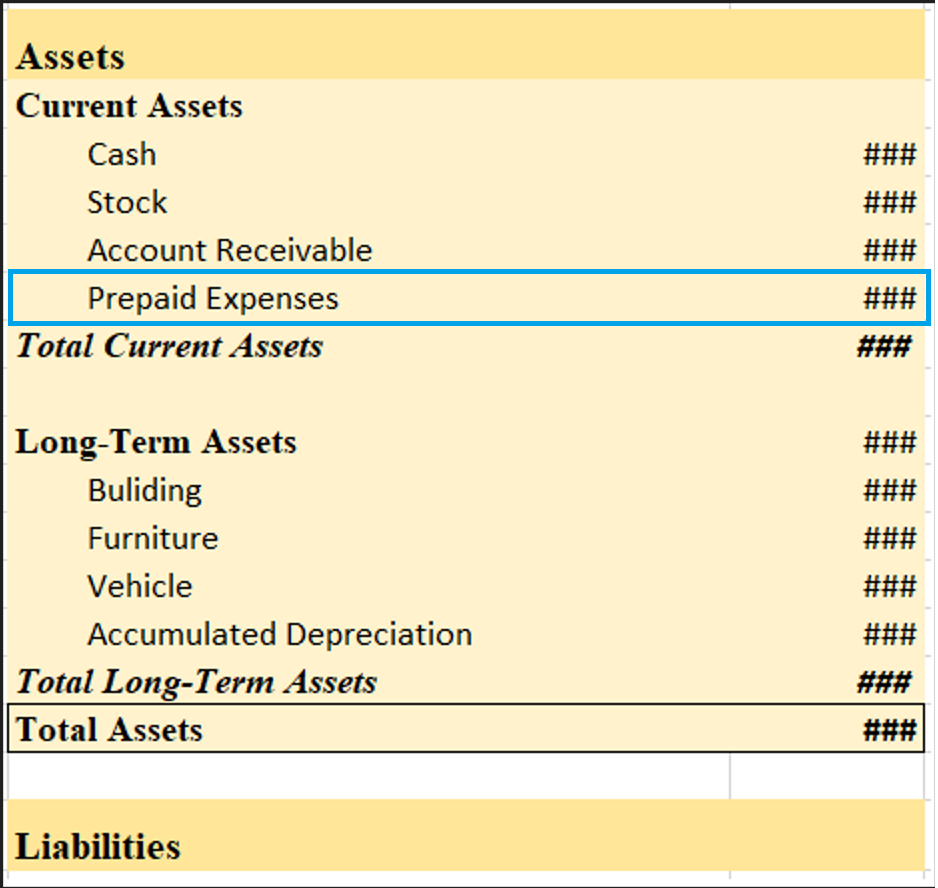
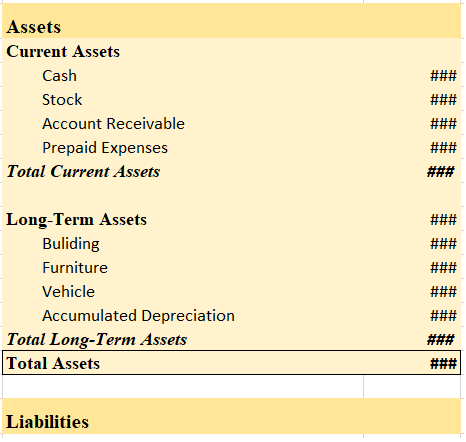
Sundry Debtors in Balance Sheet
Sundry debtors are shown under the current asset heading on the balance sheet. They are often referred to as account receivables.
Balance Sheet (for the year ending….)

See less