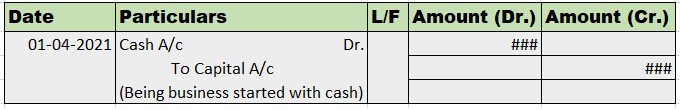
Let me explain to you in short what is unrecorded assets in the partnership. Basically, these are the assets that are not recorded in the books of accounts but are still present in the business in physical form. These assets are directly credited to the realization account at the time of dissolutionRead more
Let me explain to you in short what is unrecorded assets in the partnership. Basically, these are the assets that are not recorded in the books of accounts but are still present in the business in physical form. These assets are directly credited to the realization account at the time of dissolution of the partnership firm
Unrecorded assets are treated in two ways:
- Either they can be sold for cash.
- Taken over by any of the partners.
The journal entry for the unrecorded assets sold in cash is as follows:
| Bank A/c ……..Dr | xxx | |
| To Realization A/c | xxx | |
| (Being unrecorded assets sold for cash) |
To make the entries more simple for you let me give you a small example
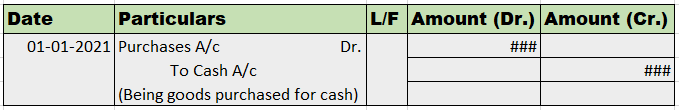
A partnership firm has decided to dissolve its business. The firm had old furniture which was completely written off. They decide to sell the furniture for Rs 3,000. Here we can see that the firm has decided to realize its furniture by selling them in cash. Therefore the journal entry would be
| Bank A/c ……..Dr | 3,000 | |
| To Realisation A/c | 3,000 | |
| (Being old furniture sold for cash) |
And the journal entry for unrecorded assets taken over by the partner is as follows:
| Partner’s capital A/c ……..Dr | xxx | |
| To Realization A/c | xxx | |
| (Being unrecorded taken over by the partner) |
For example:
A partnership firm has decided to dissolve its business. The firm had old furniture which was completely written off. One of the pieces of furniture was taken over by one of the partners for Rs 3,000. Here we can see that the firm has decided to realize its furniture by taking over the partner. Therefore the journal entry would be
| Bank A/c ……..Dr | 3,000 | |
| To Partnership A/c | 3,000 | |
| (Being old furniture taken by partner) |
As realization is a nominal account it debits all expenses and losses while credit all incomes and gains. Therefore when a business treats unrecorded assets either by selling them or is taken over by the partner’s, it brings a certain amount of cash into the business hence Bank A/c and Partner’s capital account is debited in the journal entry and appear on the credit side of the realization account.
See less


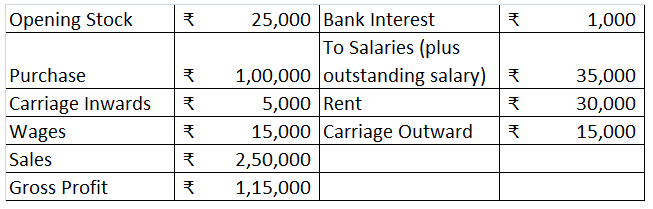
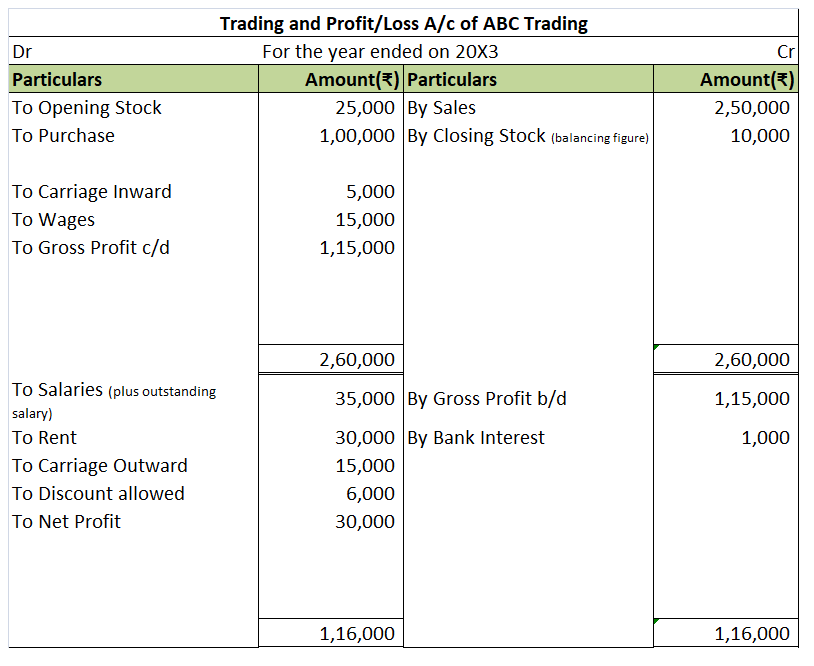
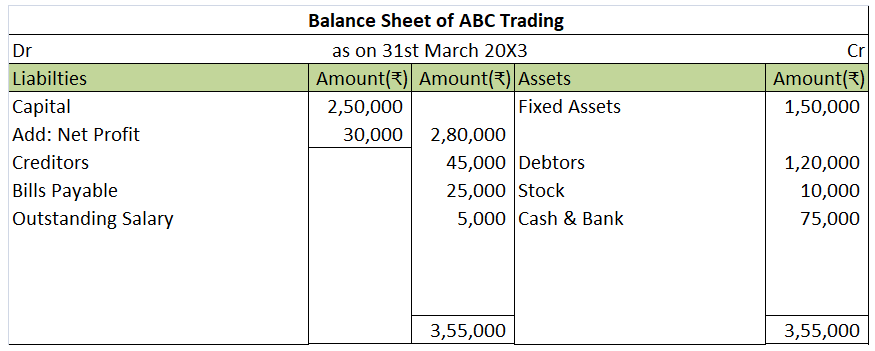
Interest on capital Interest on capital is interest payable to the owner/partners for providing a firm with the required capital to commence the business. It's a fixed return that a business owner is eligible to receive. When the business firm faces a loss, the interest on capital will not be providRead more
Interest on capital
Interest on capital is interest payable to the owner/partners for providing a firm with the required capital to commence the business. It’s a fixed return that a business owner is eligible to receive.
When the business firm faces a loss, the interest on capital will not be provided. It is permitted only when the business earns a profit. Such payment of interest is generally observed in partnership firms. It is provided before the division of profits among the partners in a partnership firm.
If an owner or partner introduces additional capital to the business, it is also taken into account for providing interest on capital.
Sample journal entry
Interest on capital is an expense for business, thus, debited as per the golden rules of accounting, debit the increase in expense, and the owner/partner’s capital a/c is credited as per the rule, credit all incomes and gain.
As per the modern rules of accounting, we debit the increase in expenditure and credit the increase in capital.
As we know, as per the business entity concept, business and owner are two different entities and a business is a separate living entity. Therefore, the capital introduced by the owner/partners is the amount on which they’re eligible to receive a return.
Example:
Tom is the business owner of the firm XYZ Ltd. He has contributed ₹ 10,00,000 to the business with 10% interest provided to Tom at the end of the year.
Solution:
Here interest on capital will be calculated as,
Interest on capital = Amount invested × Rate of interest × Number of Months/12
= 10,00,000 × 10% × 12/12
= ₹ 1,00,000

See less