Classified under advance income, Interest received in advance is unearned income that pertains to the following accounting period but is received in the current period. Such interest is not related to the current accounting period and the related benefits for such income are yet to be provided. HencRead more
Classified under advance income, Interest received in advance is unearned income that pertains to the following accounting period but is received in the current period. Such interest is not related to the current accounting period and the related benefits for such income are yet to be provided. Hence, it is a liability for the concern.
The treatment of such advance interest is based on the Accrual concept of accounting.
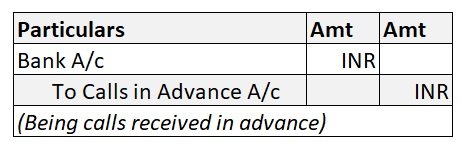
The journal entry for interest received in advance is:

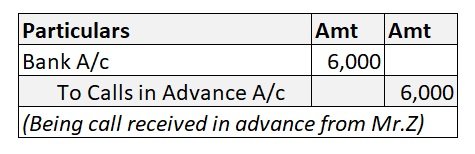
Now suppose, a firm Star shine receives interest on loan of 5,00,000 @ 7% p.a. extended to another firm. In the current accounting period, Star shine receives 50,000 as interest, excess being advance for the following year. Then the following journal entries should be passed:

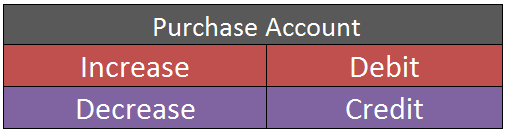
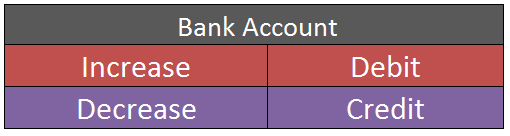
Cash received in form of interest is debited (Debit what comes in) and interest account is credited because of an increase in interest income (credit all incomes and gains).

Interest account is debited because we have to decrease the interest income since 15,000 relates to the next accounting year. Interest received in advance is credited because such interest of 15,000 is not yet earned and is a liability for the concern.
See less







The value of inventory at the end of the financial year or balance sheet date is called closing stock. Closing stock includes: Raw Material Work-in-Progress Finished Goods Example: If the value of raw material is Rs 10,000, value of WIP is Rs 5,000 and value of Finished Goods is Rs 15,000 then valueRead more
The value of inventory at the end of the financial year or balance sheet date is called closing stock. Closing stock includes:
Example:
If the value of raw material is Rs 10,000, value of WIP is Rs 5,000 and value of Finished Goods is Rs 15,000 then value of Closing Stock will be Rs (10,000 + 5,000 + 15,000) = Rs 30,000
Adjustment entries are done on the accrual basis of accounting, that is, income is recorded when earned and not received and expenses are recorded when incurred and not paid. Adjustment entries are usually made before or after the preparation of the trial balance at the end of the accounting period.
If the entries are made after the preparation of the trial balance, then two adjustment entries are recorded while preparing Trading and Profit & Loss A/c.
Since closing stock is an item outside the trial balance, the double-entry would be:
The journal entry
The second adjustment would be to show closing stock on the balance sheet and since the closing stock is an asset it is shown under the head Current Assets.
In case where adjustment for Closing Stock is to be done before preparation of Trial Balance, then it will be shown on the credit side of the Trial Balance, since it is an asset for the company and will have a credit brought down balance as shown in the image.
Later, while preparing Balance Sheet, Closing Stock will be shown on the Asset side of the Balance Sheet.
See less