A. Cash Book B. Statement C. Journal D. None of These
Introduction Working capital refers to the capital which is required by an enterprise to smoothly run its daily operations. It is the measure of the short-term liquidity of a business. Working capital is the total of the current assets of a business, net of its current liabilities. Working capitalRead more
Introduction
Working capital refers to the capital which is required by an enterprise to smoothly run its daily operations.
It is the measure of the short-term liquidity of a business.
Working capital is the total of the current assets of a business, net of its current liabilities.
Working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
The working capital consists of cash, accounts receivable and inventory of raw materials and finished goods fewer accounts payable and other short-term liabilities.
Without a proper level of working capital, a business cannot maintain regular production and pay its creditors and expenses.
Hence, for proper management of working capital, it is divided into types:
- Permanent working capital
- Temporary working capital
I have discussed them below:
Permanent Working Capital
It is the fixed level or minimum level of working capital that an enterprise needs to maintain to ensure production at the normal capacity and pay for its daily expenses. It is independent of the level of production.
It is also known as fixed working capital.
By ‘permanent’, it does not mean that it will forever remain at the same level or amount but it may change if the overall production capacity changes. But such changes in permanent working capital are not often.
Temporary Working Capital
It is the level of working capital that depends upon the level of production of a business. It is the excess working capital over the permanent capital that is required to meet seasonal high demand.
It is also known as fluctuating working capital because it tends to change often depending on the level of production.
Temporary working capital is required when high production is required to meet seasonal demands.
For example, a bakery will need more working capital to meet the increased demand for cakes and pastry during Christmas season
Graph showing permanent and temporary working capital
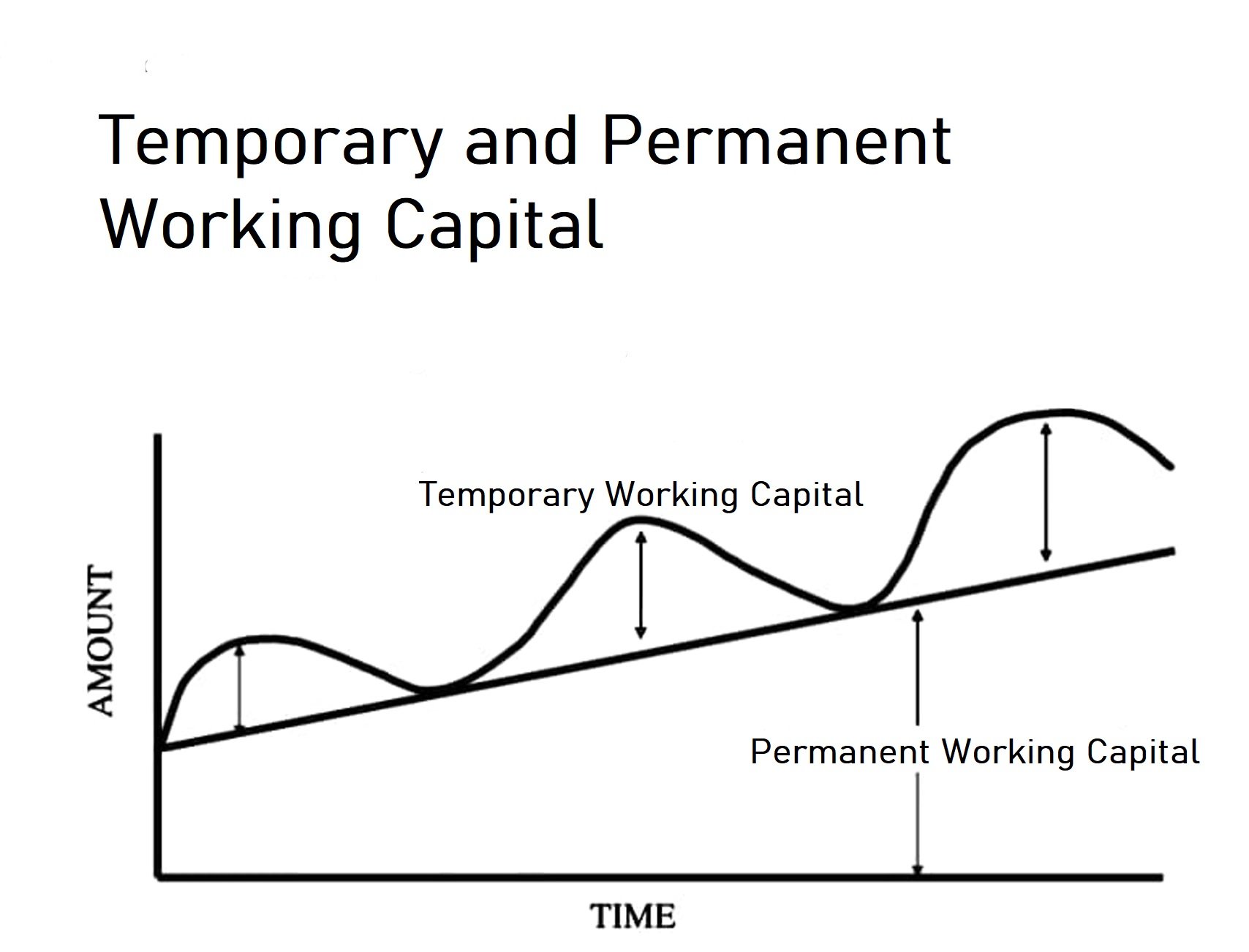
Here, the temporary working capital is fluctuating whereas the permanent working capital is gradually increasing with time.
See less
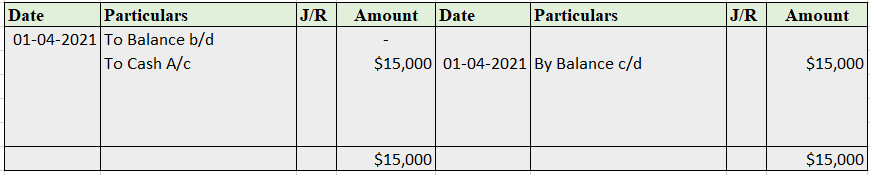
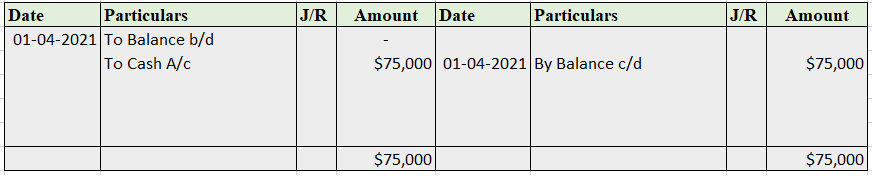
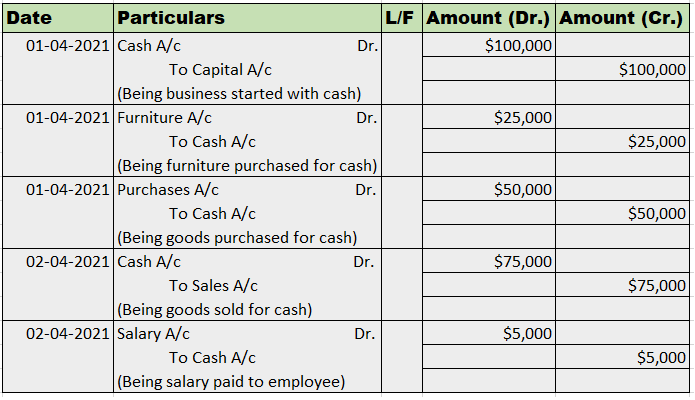
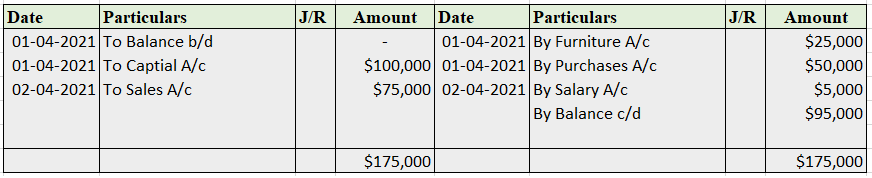
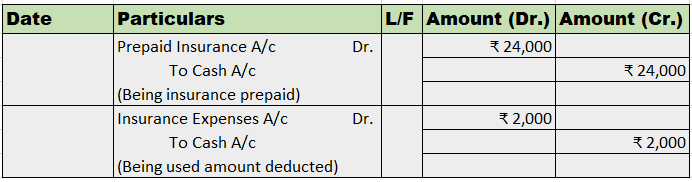
The correct option is A) Cash book let's understand what is petty cash book: A petty cash book is a cash book maintained to record petty expenses. Petty expenses, mean small or minute expenses for which the payment is made in coins or a few notes or which are smaller denominations like tea or coffeeRead more
The correct option is A) Cash book
let’s understand what is petty cash book:
Generally, the petty cashbook is prepared as per the Imprest system. As per the Imprest system, the petty expenses for a period (month or week) are estimated and a fixed amount is given to the petty cashier to spend for that period.
At the end of the period, the petty cashier sends the details to the chief cashier and he is reimbursed the amount spent. In this way, the debit balance of the petty cashbook always remains the same.
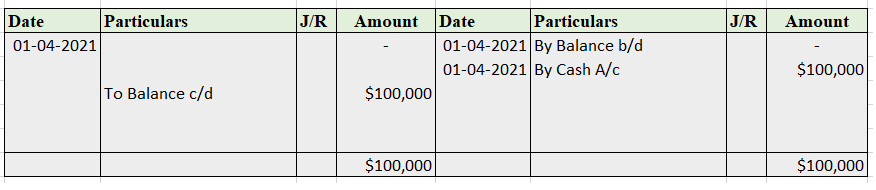
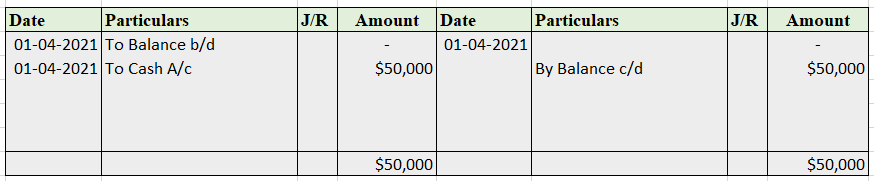
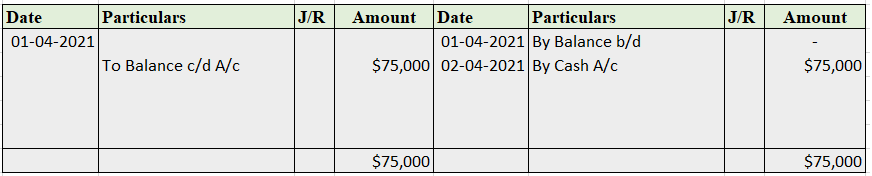
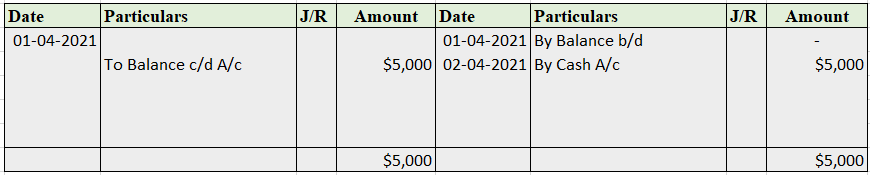
The petty cash book has two columns in which
Balance of Petty cash book
The balance of petty cash book is never closed and their balances are carried forward to the next accounting period which is considered one of the most significant qualities of an asset whereas Income doesn’t have any opening balance and their balances get closed at the end of every accounting year.
A petty cash book is placed under the head current asset in the balance sheet. The Closing Balance of the petty cash book is computed by deducting Total expenditure from the Total cash receipt (as received from the head cashier).
Format for petty cash book
Only small denominations are recorded in the petty cash book. It varies with the type, quantity, and need of a business. It involves cash and checks.
Conclusion
A simple petty cash book is a type of cash book because it records the small expenses which involve small transactions in the ordinary daily business.
A petty cash book is not as important as an income statement, balance sheet, or trail balance it doesn’t measure the accuracy of accounts so it is not treated as a statement.
No journal entries are made in the books of accounts while spending or purchasing using a petty cash book so, it is not treated as a journal.
See less