The accounting equation for a non-profit organisation is almost the same as in the case of the profit-oriented organisation. Let's first briefly understand what accounting equation and non-profit organisation are: Accounting Equation Accounting equation is an equation that depicts the relationship bRead more
The accounting equation for a non-profit organisation is almost the same as in the case of the profit-oriented organisation. Let’s first briefly understand what accounting equation and non-profit organisation are:
Accounting Equation
Accounting equation is an equation that depicts the relationship between assets, liabilities and capital of an entity.
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
As per this equation, the total assets of an entity are equal to the sum of its total liabilities and total capital. This equation holds good in every situation.
Non-Profit Organisation
A Non-Profit Organisation is an entity which exists for purposes other than for profit. Such organizations exist and operate for charitable purposes, promotion of culture and sports and welfare of society. The accounting for Non-profit organisation is slightly different from For-profit organisations. In the case of a non-profit organisation, the capital account is known as the capital fund.
Accounting Equation for non-profit organisations
The Accounting equation for a non-profit organisation is as follows:
Assets = Liabilities + Capital fund.
The difference is only in name. In the case of non-profit organizations, the capital is known as a capital fund. Rest everything is the same. The accounting equation will be prepared as normally prepared for business concerns.
See less
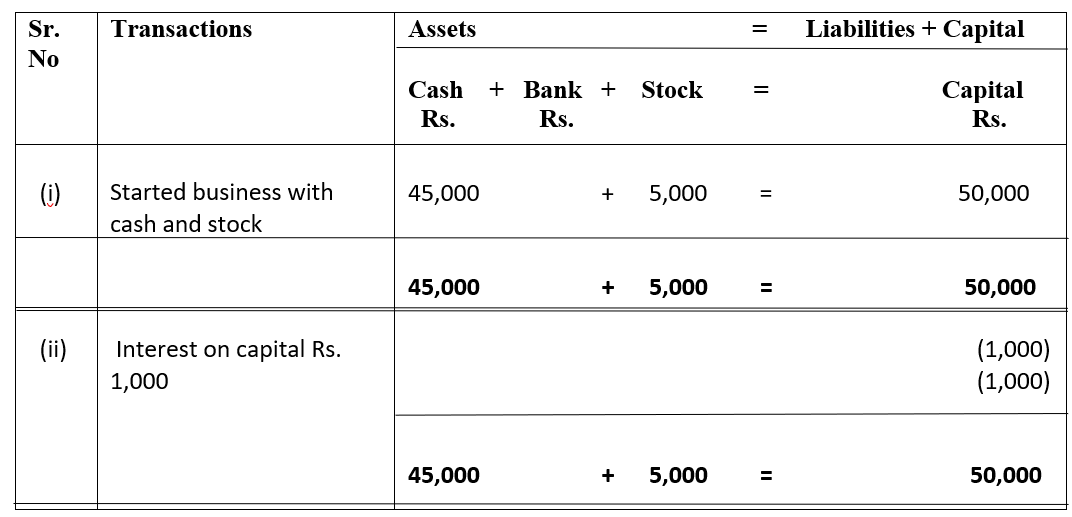
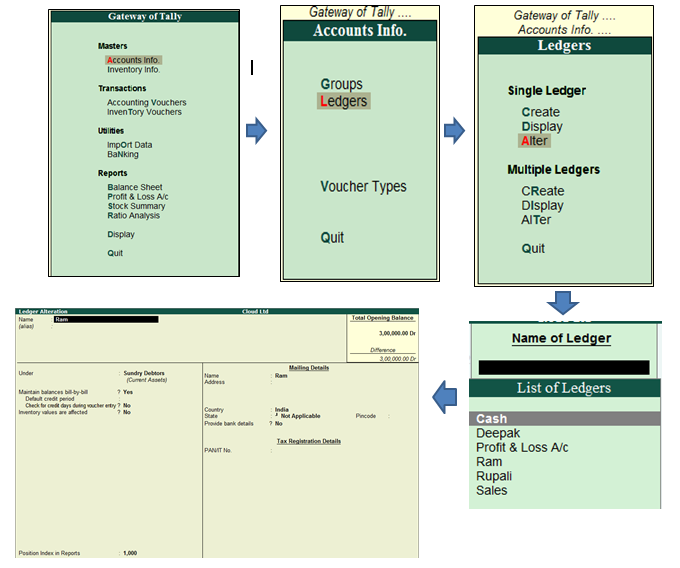
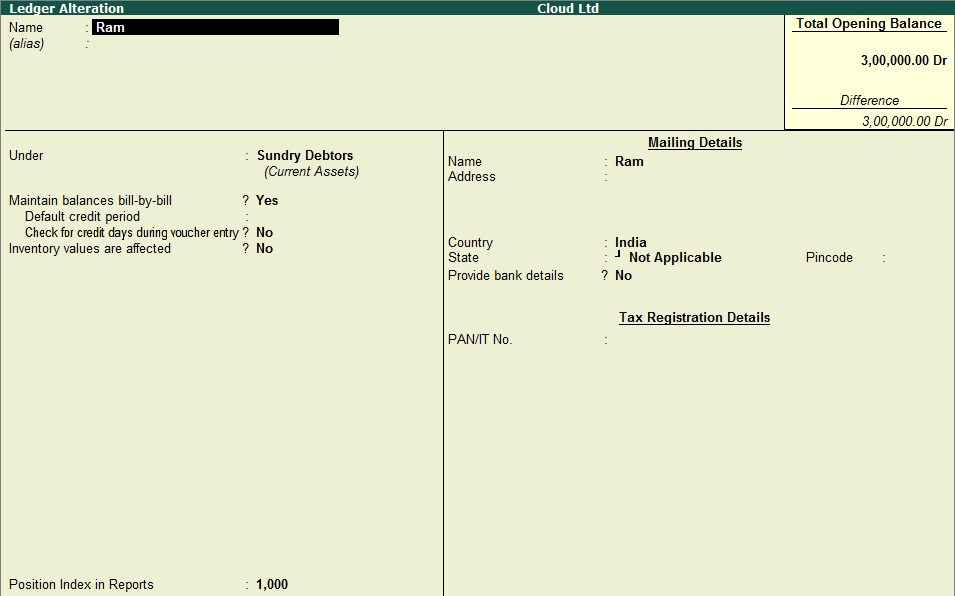
Introduction Often cash is withdrawn by the owner or proprietor of a business for his or her personal use. Such withdrawal of cash is an outflow of capital from business and it is known as drawings. The accounting treatment of cash withdrawn for personal use is expressed in the accounting equation aRead more
Introduction
Often cash is withdrawn by the owner or proprietor of a business for his or her personal use. Such withdrawal of cash is an outflow of capital from business and it is known as drawings.
The accounting treatment of cash withdrawn for personal use is expressed in the accounting equation as shown in the example below:
It is shown as a negative figure under both assets and capital heading. I will be explaining why it is so.
Accounting Equation
The accounting equation represents the relationship between assets, liabilities, and capital of an entity whether profit oriented or not, according to which, the total assets of a business equals to the sum of its total capital and total liabilities.
Assets = Liabilities + Capital
This equation holds good in every monetary transaction or event like the event given in the question.
Cash withdrawn for personal use
We know every transaction affects two accounts. In this case, too, the ‘cash withdrawn for personal use’ affects two accounts. Cash withdrawn for personal use is known as drawings.
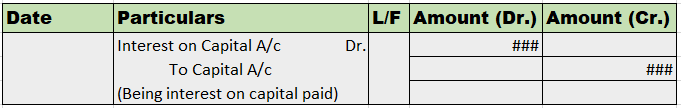
Let’s see the journal entry for drawings of cash from business:
Here the drawing account is debited because it is a contra-equity account i.e. it is a mirror image of the capital account or opposite of the capital account. Here the cash account is an asset account; hence it is credited as it is reduced.
As drawings represent the outflow of capital from the business, it is written off from the Capital account in the balance sheet.
Hence, in the accounting equation, the drawing amount is deducted from the Asset side and from the capital side, indicating a balance.
It does not appear in the statement of profit or loss despite having a debit balance because it is not an expense account.
See less