Fictitious assets can be defined as those fake assets which save revenue for the company. These do not exist physically but also do not qualify as intangible assets. These are merely the expenses or losses that are not fully written off in the accounting period in which they are incurred. These expeRead more
Fictitious assets can be defined as those fake assets which save revenue for the company. These do not exist physically but also do not qualify as intangible assets. These are merely the expenses or losses that are not fully written off in the accounting period in which they are incurred. These expenses are amortized over a period of time.
These assets do not have any realizable value except for the cash outflow. These are created to delay the recognition of the expense and defer it to future periods.
Fictitious assets actually qualify as an expense but are treated as assets only for the fact that they are expected to give returns over a course of more than one year. Examples are Advertisement expenses, preliminary expense, etc.
Treatment
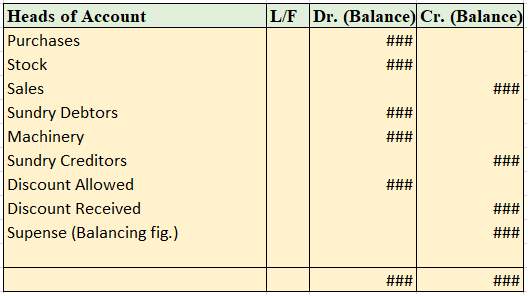
Fictitious assets are shown on the assets side of the balance sheet under the head miscellaneous expenditure. A part of these expenses are shown in the profit and loss statement and the remaining amount is carried forward to the following years.
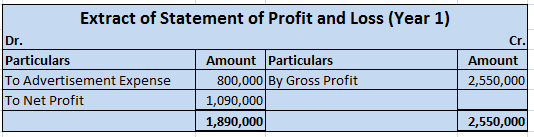
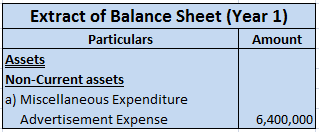
For example, a company Timber Ltd. incurs expenses relating to advertisement of its products worth 8,000,000 and this advertisement campaign can earn revenue for the company for around 10 years. Hence, such expense of 8,000,000 would be amortized over a period of 10 years.
For the first year, an amount of 800,000 (8,000,000/10) would appear in the profit and loss statement as expense and the rest 7,200,000 would appear as advertisement expense under the Miscellaneous expenditure on the assets side of the balance sheet.
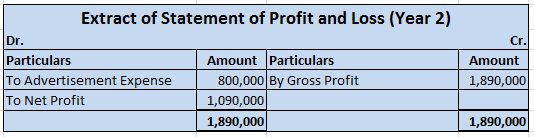
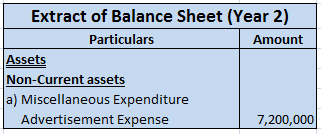
For the second year, an amount of 800,000 (8,000,000/10) would appear in the profit and loss statement as expense and the rest 6,400,000 would appear as advertisement expense under the Miscellaneous expenditure on the assets side of the balance sheet. And so on.
We can say that fictitious assets are deferred revenue expenditures as well as intangible assets. But goodwill, etc are not fictitious assets. Hence, all fictitious assets are intangible assets but all intangible assets are not fictitious assets.
Common fictitious assets that could generally be seen are:
- Advertisement expenses
- Preliminary expenses
- Discount allowed on the issue of shares
- Loss incurred on issue of debentures
- Underwriting Commission

Let us first understand what working capital is. Working capital means the funds available for the day-to-day operations of an enterprise. It is a measure of a company’s liquidity and short term financial health. They are cash or mere cash resources of a business concern. It also represents the exceRead more
Let us first understand what working capital is.
Working capital means the funds available for the day-to-day operations of an enterprise. It is a measure of a company’s liquidity and short term financial health. They are cash or mere cash resources of a business concern.
It also represents the excess of current assets, such as cash, accounts receivable and inventories, over current liabilities, such as accounts payable and bank overdraft.
Sources of Working Capital
Any transaction that increases the amount of working capital for a company is a source of working capital.
Suppose, Amazon sells its goods for $1,000 when the cost is only $700. Then, the difference of $300 is the source of working capital as the increase in cash is greater than the decrease in inventory.
Sources of working capital can be classified as follows:
Short Term Sources
Long Term Sources
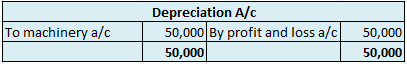
Another point I would like to add is that, although depreciation is recorded in expense and fixed assets accounts and does not affect working capital, it still needs to be accounted for when calculating working capital.
See less