As per the companies act 2013, the rate of depreciation for cars/vehicles and their useful life is mentioned below They are categorized by the companies act as follows: when these car/ motor vehicles are owned with no intention to sell within the accounting period and are generally used to generateRead more
As per the companies act 2013, the rate of depreciation for cars/vehicles and their useful life is mentioned below
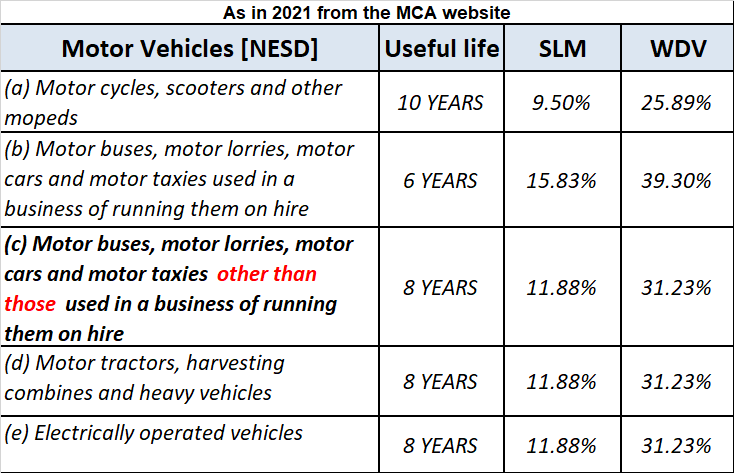
They are categorized by the companies act as follows:
- when these car/ motor vehicles are owned with no intention to sell within the accounting period and are generally used to generate revenue. For example, giving cars/motor vehicles on lease or hire purpose.
- cars/motor vehicles when used for purposes other than the business of hire. For example, a car is owned for official use.
Car/motor vehicles are considered as fixed tangible assets. Treatment of these cars/ motor vehicles is similar to those of other fixed assets. The depreciation will be shown as an expense in the profit and loss account and also the value of these assets will be adjusted in the balance sheet.
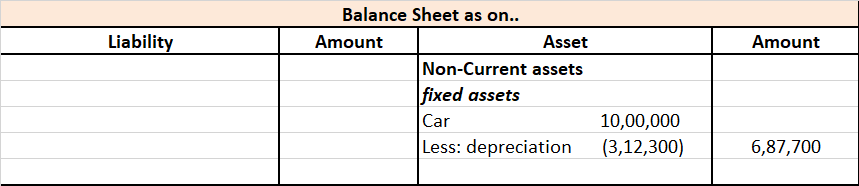
Explaining with a simple example: Mars.Ltd purchased a car for Rs 10,00,000, and use it for its official purpose. Its useful life as per act is taken as 6 years and the rate of depreciation as 31.23% as per the WDV method.
Therefore depreciation as per WDV is calculated as follows
Cost of car = Rs 10,00,000
Residual value = NIL
Rate of depreciation = 31.23%
depreciation for first-year = Rs (10,00,000 – NIL)*31.23%
= Rs 3,12,300
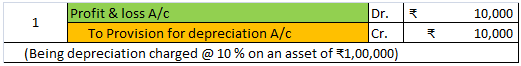
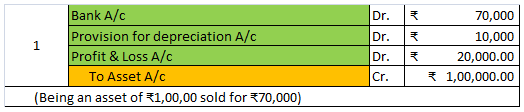
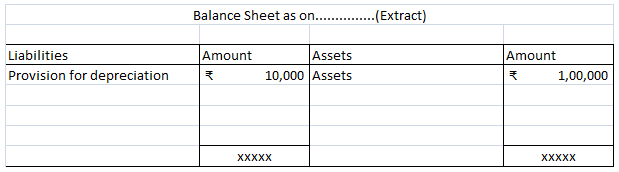
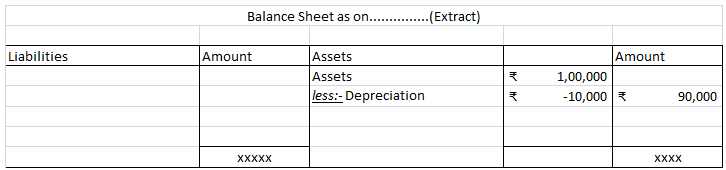
Calculated depreciation on this car will be shown in the profit and loss account as an expense and the same will be treated under the balance sheet every year. Here is the extract of profit and loss and the balance sheet for the above example.
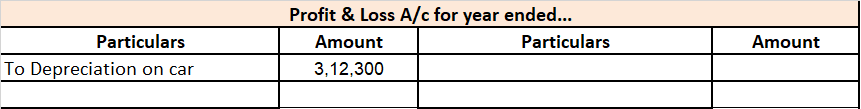

Depreciation refers to that portion of the value of an asset that is written off over the useful life of the asset due to wear and tear. Now, when we talk about depreciation, there are multiple methods to calculate depreciation such as: Straight Line Depreciation Method Diminishing Balance Method OrRead more
Depreciation refers to that portion of the value of an asset that is written off over the useful life of the asset due to wear and tear.
Now, when we talk about depreciation, there are multiple methods to calculate depreciation such as:
The most commonly used methods are discussed below:
1. Straight Line Depreciation Method: This is the simplest method for calculating depreciation where a fixed amount of depreciation is charged over the useful life of the asset.
Formula:
Suppose a company Bear Ltd purchases machinery costing 8,00,000 with useful life of 10 years and salvage value 1,00,000. Then depreciation charged to the machinery each year would be:
Depreciation = (8,00,000 – 1,00,000)/10 = 7,00,000/10 = 7,000 p.a.
2. Diminishing Balance Method Or Written Down Value Method: Under this method, a fixed rate of depreciation is charged every year on the opening balance of the asset which is the difference between the previous year’s opening balance and the previous year’s depreciation. Here the book value of asset reduces every year and so does the depreciation amount.
Formula:
Suppose a company Moon ltd purchases a building for 50,00,000 with a useful life of 5 years and decides to depreciate it @ 10% p.a. on Diminishing Balance Method. Then depreciation charged to the machinery would be:
3. Sum of Years’ Digits Method: In this method, the life of asset is divided by the sum of years and multiplied by the cost of the asset to determine the depreciating expense. This method allocates higher depreciation expense in the early years of the life of the asset and lower depreciation expense in the latter years.
Formula:
Suppose a company Caps Ltd purchases machinery costing 9,00,000 having a useful life of 5 years. Then the depreciation cost would be:
4. Double Declining Balance method: This method is a mixture of straight-line method and diminishing balance method. A fixed rate of depreciation is charged on the reduced value of the asset at the beginning of the year. This rate is double the rate charged under straight-line method.
Formula:
Suppose a company Paper Ltd purchases machinery for 1,00,000 with an estimated useful life of 8 years. Then the depreciation rate would be:
Straight line = 100%/8 = 12.5%
Double declining method = 2*12.5% = 25%
5. Sinking Fund Method: Under this method, the amount of depreciation keeps on accumulating till the asset is completely worn out. Depreciation is the same every year. Profits equal to the amount of depreciation is invested each year outside the company. At the time of replacement of the asset the investments and sold and the proceeds thereof are used to purchase the new asset.
6. Annuity Method: This method calculates depreciation by calculating its internal rate of return (IRR). Depreciation is calculated by multiplying the IRR with an initial book value of the asset, and the result is subtracted from the cash flow for the period.
7. Use Based Methods: Depreciation, under these methods, is based on the total estimated machine hours or total estimated units produced during the life of the machine. It is calculated by dividing the cost of the machine by the estimated total machine hours or estimated lifetime production in units and multiplying by the units produced or machine hours worked.
Formula:
Suppose a company Box Ltd purchases machinery for 25,000 (estimated life 5 years) whose estimated life production is 5,000 units. If it produces 700 units in the first year of operation then depreciation cost would be:
Depreciation = 25,000/5,000*700 = 3,500
See less