Subsidiary Books Introduction & Definition In large business organizations, it is practically impossible to keep a record of every single business affair, while neglecting them and not recording them wouldn't be an ideal choice, this is where subsidiary books come into the role. As we were introRead more
Subsidiary Books
Introduction & Definition
In large business organizations, it is practically impossible to keep a record of every single business affair, while neglecting them and not recording them wouldn’t be an ideal choice, this is where subsidiary books come into the role. As we were introduced to the basics of accounting in the 11th standard, we learned about different elements like journals, ledgers, trial balances, etc. It is practically impossible for a business to keep track of every single affair just through only those elements. Thus, the Subsidiary book is the next step here.
Subsidiary books are the books of original entry. They are a dedicated form of books that maintains an analysis of a specific account. It records financial transactions of a similar nature. They are sub-division of a journal.
In big business organizations, it’s very hard for a bookkeeper or accountant to record all the transactions in one journal and post them into various accounts. This is where special purpose books or subsidiary books may be required for more efficient bookkeeping. They are a subdivision of journals and for every type of transaction, there is a separate book.
Types of Subsidiary Books
There are eight types of subsidiary books that are required for recording transactions. The list of various subsidiary books is as follows:
- Cash Book
- Purchase Book
- Sales Book
- Purchase Return Book
- Sales Return Book
- Journal Proper
- Bills Receivable Book
- Bills Payable Book
Types of Subsidiary Books
Now, we’ll be taking a closer look at each and every subsidiary book.
Cash Book
The cash book is the most important subsidiary book, it’s a book of a prime entry recording all the cash spent or received by the business, either in cash form or from the bank. In simple words, recording all the transactions made by the business.
It is of three types i.e single-column cash book, double-column cash book, and triple-column cash book. As the name indicates, the column of cash, bank, and discount increases/decreases as per the column of the cash book stated.
Format
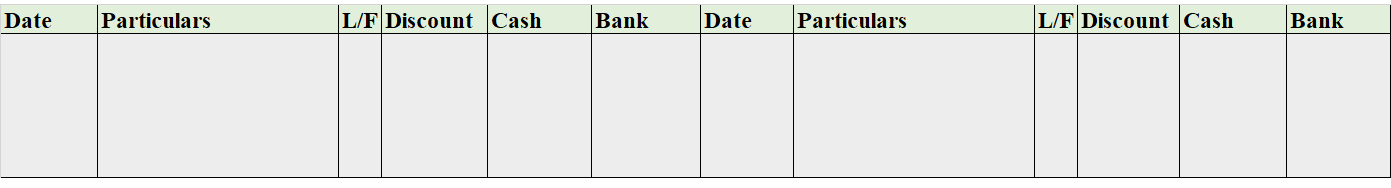
Note: this is a triple-column cash book format, for the double-column cash book format, we remove the discount column from both sides, and for the single column, we may remove the bank column as well.
Purchase Book
A purchase book is a subsidiary book that records all the transactions related to the credit purchase in a business. Thereby, the normal purchasing of assets is never recorded in the purchase book.
The credit purchases are directly recorded in the purchase book from the journals or the source documents. The source document indicates bills payable, invoices, etc.
Format
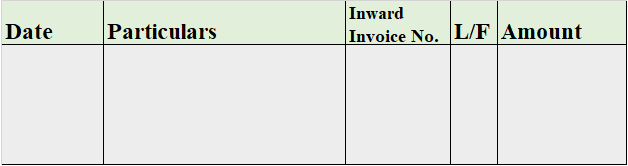
Sales Book
A sales book, similar to a purchase book, is a special book where all the credit sales are recorded. The sales book doesn’t record the transactions related to the normal sale of assets and hence, is a special type of book, just like the purchase book.
Format
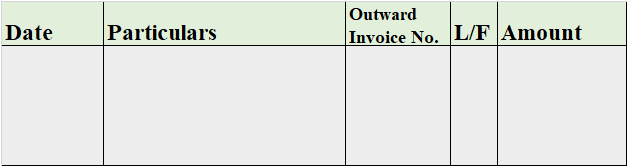
Purchase Return Book
The purchase return book, also known as the return outwards book, is that book that records the goods that were returned by us to the supplier. Thereby, called purchase return book.
When the goods are returned, a debit note is issued against every return and hence, recorded in the purchase return book.
Format
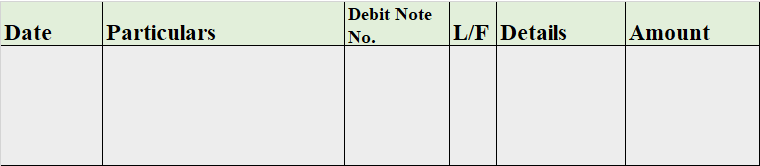
Sales Return Book
The sales return book, also known as the return inwards book, refers to that subsidiary book that records the goods which were returned to us by the customer.
For every good returned to us, a credit note is issued to the customer. And thus, it is recorded in the sales return book.
Format
Journal Proper
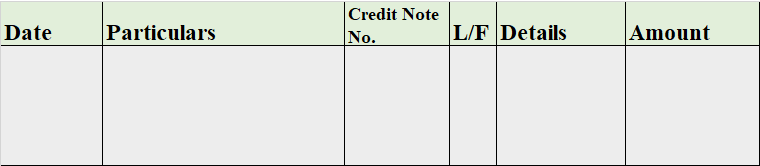
Just like we recently learned in class 11th about what a journal entry is and how it is made, it’s a little different from the journal proper. Journal proper is a subsidiary book that records all the transactions which are not recorded in other subsidiary books.
A journal is an original book of entries that records all the business transactions, while a journal proper is a subsidiary book in which all types of miscellaneous credit business transactions are recorded that do not fit anywhere in the other subsidiary books. Its format is the same as the journal entries’ format. Therefore, it’s also known as a miscellaneous journal.
Format
Bills Receivable Book
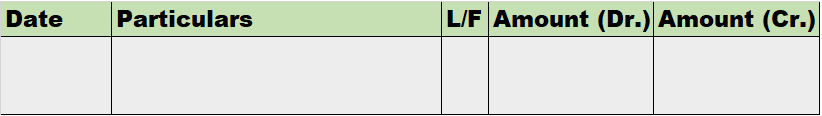
The bills receivable book is the book that draws the bills favorable to the business i.e when the goods or services are provided to any customer on credit, they become a debtor, and bills receivable is a written note received from the customer indicating that they formally agree to pay the sum of money owed.
Therefore, it helps in recording these types of transactions. The sum total of the bills receivable book is posted to the bills receivable account.
Format
Bills Payable Book
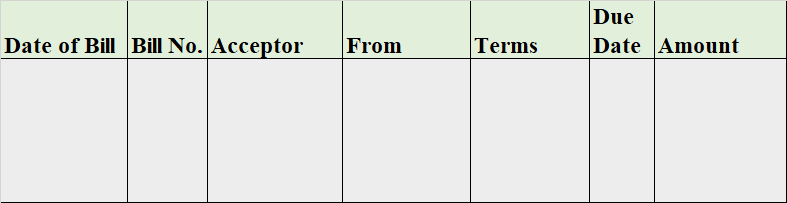
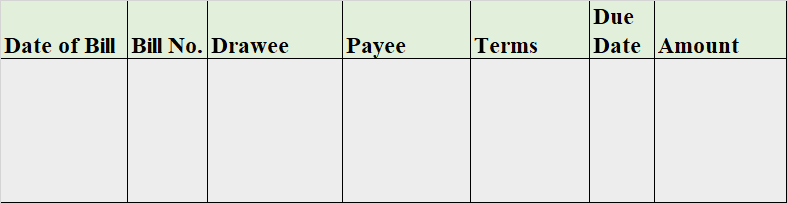
The bills payable book is the subsidiary book that records all the bills that are drawn on the company. The bills payable is drawn on the company when we buy a good/service on credit and agrees to pay the amount to the supplier by signing a written note with the date we agree to pay.
It’s a liability of the business and the total of the bills payable book is posted on the credit side of the bills payable account.
Format
See less

Definition Net profit is defined as the excess of revenues over expenses during a particular period. For a business i.e. company/firm, it is a liability towards shareholders/promoters/partners/proprietors, etc. as it is their capital that has earned these profits. When the result of this computationRead more
Definition
Net profit is defined as the excess of revenues over expenses during a particular period.
For a business i.e. company/firm, it is a liability towards shareholders/promoters/partners/proprietors, etc. as it is their capital that has earned these profits.
When the result of this computation is negative it is called a net loss.
Net profit may be shown before or after tax.
Formula :
Total Revenues – Expenses
Or
Total Revenues – Total Cost ( Implicit And Explicit Cost )
Liabilities
It means the amount owed (payable) by the business. liability towards the owners ( proprietor or partners ) of the business is termed an internal liability.
On the other hand, liability towards outsiders, i.e., other than owners ( proprietors or partners ) is termed as an external liability. For example – taxes owned, trade payables, etc.
For example creditors, bank overdrafts, etc.
Assets
An asset is a resource owned or controlled by a company and will benefit the business in current and future periods.
In other words, it’s something that a company owns or controls and can use to generate profits today and in the future.
For example – cash, building, etc.
Why debtors are treated as a liability?
Now let me explain to you why net profits are treated as a liability and not as an asset because of the following characteristics :
• Net Profit shows the credit balance of the Profit And Loss Account.
• It is treated directly in the balance sheet by adding or subtracting from the capital.
• Net Profit is a measure of the profitability of the company after taking into consideration all costs incurred during the accounting period.
• Net profit is the last line in an income statement and is the figure that concerns most people who use such a statement.
• Net income is reported on the income statement (profit and loss account) and forms a key indicator of a company’s performance.
Importance Of Net Profit
Now I will let you know the importance of net profit which is as follows :
Owners
Net profit allows owners to calculate the tax to be paid and how much earnings need to be distributed to the business owners.
Investors
Investors need to see net profit as they need to access the risk before investing they basically judge the revenue-generating capacity of a firm based on net profit.
Competitors
For making the comparison competitors tend to look at the net profit of the company to know how are they performing in the industry so that they can build themselves strong.
Creditors
Creditors look at the net profit for the purpose of obtaining business loans or we can say that determines a prospective debtor’s capacity to pay future debts.
Conclusion
Now after the above explanation, we can say that,
Net Profit is shown on the liability side as it belongs to shareholders so the company has to give it to shareholders so we are showing it under the liability side.
Net Profit with respect to the company is a liability as it has to pay it to shareholders.
Net Profit with respect to shareholders is an asset.
See less