As per Wiki, it is also called construction in progress. Capital work in progress is a non-current asset of an entity. It is also known as CWIP in short. CWIP is the work which is not yet completed but the amount for which has already been paid. Suppose, at the time of preparing a balance sheet, ifRead more
As per Wiki, it is also called construction in progress. Capital work in progress is a non-current asset of an entity. It is also known as CWIP in short.
CWIP is the work which is not yet completed but the amount for which has already been paid.
Suppose, at the time of preparing a balance sheet, if an asset is not completed, all the costs incurred on that asset up to the balance sheet date are to be transferred to an account called capital work in progress.
Example 1: A machinery under installation.
There are several expenses incurred while installing machinery, expenses such as labor charges, Initial delivery and handling costs, Assembly and installation cost, etc are included in CWIP and when the asset is completed and is ready to use, all the costs are transferred to the relevant accounts.
To make it simpler, let me show journal entries relating to this example.
When an expense is incurred/paid:

When an asset is complete and put to use:

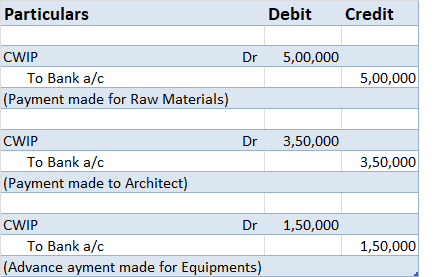
Example 2: A Contractor is constructing a building. The following expenditures are being incurred to date:
i) Raw materials – 5,00,000
ii) Payment to Architect – 3,50,000
iii) Advance for Equipments – 1,50,000
Following accounting entries will be passed to record the expenditure on CWIP assets:
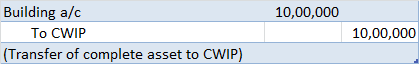
The following accounting entry will be passed once assets are ready to use:
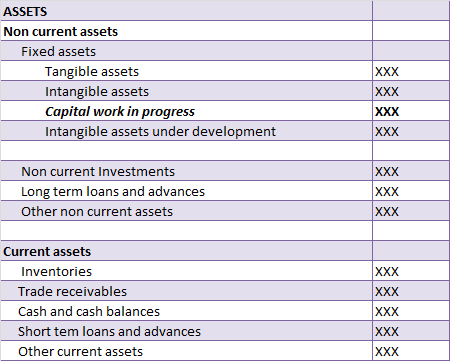
Disclosure in the Balance sheet
CWIP account is shown separately in the balance sheet below the fixed asset.
we cannot depreciate capital work in progress. It can only be depreciated when the asset is put to use.

Deferred Tax Liability A deferred tax liability represents an obligation to pay taxes in the future. These taxes are owed by a company but are not due to be paid until a future date. Companies that incur such an obligation prepare and maintain two financial reports every year: a tax statement and anRead more
Deferred Tax Liability
A deferred tax liability represents an obligation to pay taxes in the future. These taxes are owed by a company but are not due to be paid until a future date.
Companies that incur such an obligation prepare and maintain two financial reports every year: a tax statement and an income statement.
This is because companies maintain their books as per book accounting rules (GAAP/IFRS), but they have to pay taxes according to tax accounting rules, and they each have to follow their own guidelines.
For example, a tax statement follows the cash basis of accounting, and an income statement follows the accrual basis of accounting.
Companies calculate their profit as per the accounting rules as well as tax laws known as accounting income and taxable income, respectively. Some differences arise due to the application of different provisions of law.
These temporary differences are accounted for, recognized, and carried forward in the books of accounts and create deferred tax.
Example
Here is an example of deferred tax liability.
In the given example, tax as per income statement is 70,000, whereas as per tax statement it is 56,000. This temporary difference is termed as deferred tax liability of 14,000.
When accounting income is more than taxable income, it creates Deferred Tax Liability. It will be adjusted in the books of accounts during one or more subsequent year(s).
How Does it Arise?
There are several instances under which a company creates a deferred tax liability. Some other instances are:
Depreciation Methods
Treatment of Revenue & Expenses
Impact on Financial Statements
Recognising deferred tax liability and its subsequent effect on the company’s financial statement is important as it simplifies the process of auditing and analysing financial reports.
Balance Sheet
Cash Flow Statement
- The deferred tax liability is added back to the net income in calculating cash flow from operating activities to show the actual cash flow.
See less