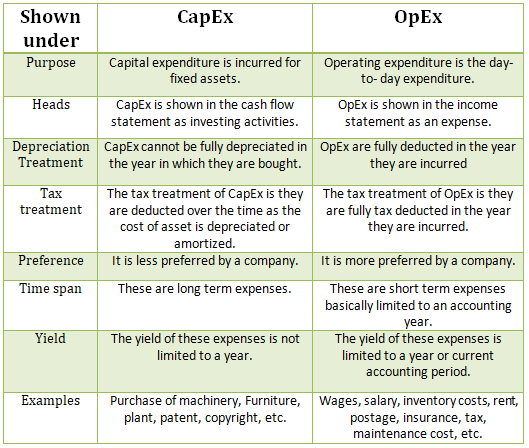
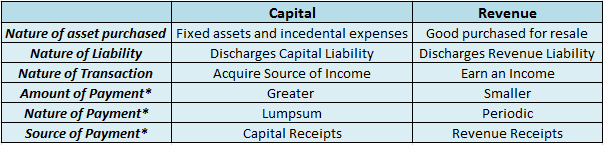
Let me first explain the meaning of both the terms CapEx and OpEx Capital expenditure (in short CapEx) is basically incurred for Fixed assets like building, furniture, machinery, etc., or an intangible asset like Goodwill, patent, etc. This expenses are incurred in order to acquire a new asset or imRead more
Let me first explain the meaning of both the terms CapEx and OpEx
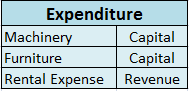
Capital expenditure (in short CapEx) is basically incurred for Fixed assets like building, furniture, machinery, etc., or an intangible asset like Goodwill, patent, etc. This expenses are incurred in order to acquire a new asset or improve an existing one or maintain the asset in use.
Capital expenditure is commonly found in the Cash flow statement under Investing activities as Investment in plant, machinery, equipment, etc.
Operating Expenditure (in short OpEx) are day-to-day expenses incurred by a firm in order to carry its normal business.
Expenses such as rent, advertisement, inventory costs, etc.
Operating Expenses are shown in the income statement of the company as expenses incurred during the period.
For Example: If a company purchases a printer, the printer would be a capital expenditure and the papers used for the printer would be operating expenditure.
Difference between CapEx and OpEx
Example 1: A company wants to lease machinery instead of buying it, in this case buying machinery would be capital expenditure, and leasing the machinery would be an Operating expense.
Example 2: Buying machinery would cost a company for 50000 and leasing the same would cost 35000. So in this case leasing will be more preferred by a company which means operating expenditure would be preferred instead of a capital expenditure.
From the point of view of tax treatment operating expenditure is more preferred over Capital expenditure because the expenses incurred during the year are deducted during the same year which reduces the tax levied on net income.
Some real Examples from the Company Amazon
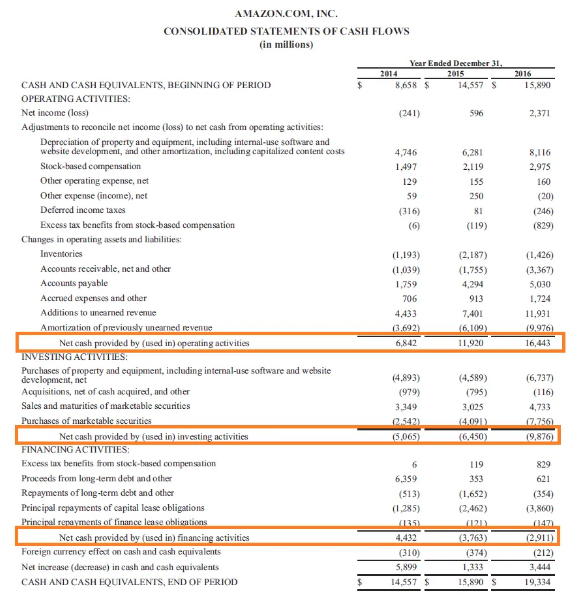
This is the cash flow statement of Amazon, where the investing activities shows the capital expenditure incurred by the company during the years.
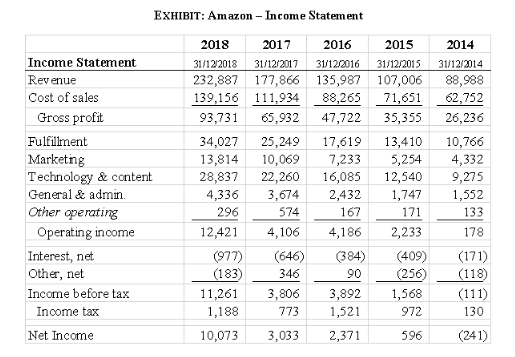
This is the income statement of Amazon, it shows the operating expenditure incurred by the company during the year.
See less
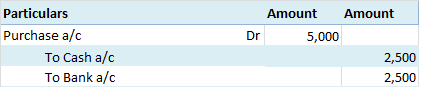
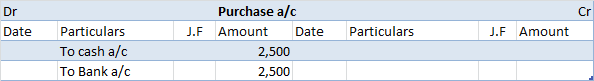
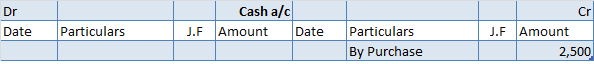
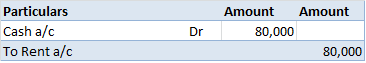
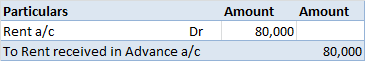
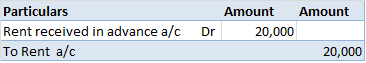
Depreciation refers to that portion of the value of an asset that a company uses in an accounting year to generate revenue. Assets are written off in form of depreciation over time also called the useful life of the asset. It denotes the wear and tear of an asset over time. Suppose, a company namedRead more
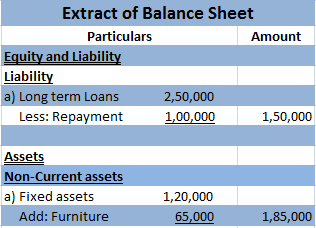
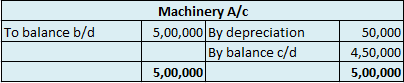
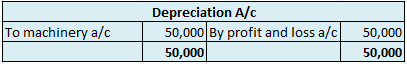
Depreciation refers to that portion of the value of an asset that a company uses in an accounting year to generate revenue. Assets are written off in form of depreciation over time also called the useful life of the asset. It denotes the wear and tear of an asset over time.
Suppose, a company named Johnson ltd. purchases machinery for 50,000 that has a useful life of 5 years with nil salvage value. Then the yearly depreciation to be charged can be calculated as:
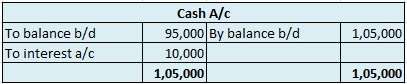
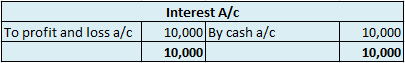
Is Depreciation a Cash Flow?
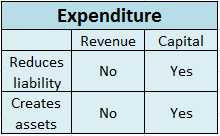
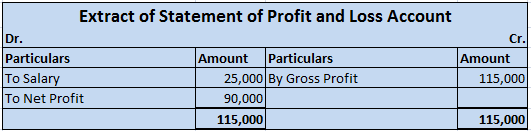
Cash flows are inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents in an entity. The payments made by the entity denote the outflows whereas the revenues or incomes of the entity denote the inflows. Talking about cash flows, depreciation is a non-cash item of expense which means it neither results in inflow nor outflow of cash resources.
In the adjacent Profit and Loss statement, a cash payment of 7,000 for electricity implies outflow of cash however, depreciation of 10,000 is merely an imputed cost to write off an asset or we can say, a part of profits set aside each year so that there are sufficient funds available to procure a new asset after the currently available asset is discarded.
However, cash flow statements are affected by depreciation. Depreciation is added back to the net profits while calculating cash flows from operating expenses since it is a non-cash item and has been deducted while calculating net profits in the profit and loss statement.
Depreciation does not directly impact the amount of cash generated or expended by a business but it is tax-deductible and will reduce the cash outflows related to income taxes. Thus, depreciation affects cash flow by reducing the amount of cash a business has to pay for income taxes.

See less