In a partnership firm, the partners may withdraw certain amounts from the firm for their personal use. Such amounts withdrawn by the partners are called drawings. This amount is usually deducted from their capital. The partners are required to pay an amount as interest, based on the time period forRead more
In a partnership firm, the partners may withdraw certain amounts from the firm for their personal use. Such amounts withdrawn by the partners are called drawings. This amount is usually deducted from their capital. The partners are required to pay an amount as interest, based on the time period for which the money was withdrawn. This amount is called Interest on Drawings.
The journal entry for interest on drawings is as follows:
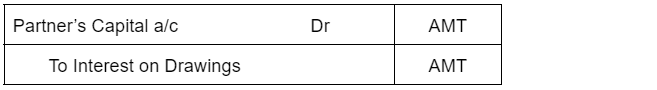
Since interest on drawings is an income to the firm, it is credited based on the rule that “increase in incomes are credited”. Since the partner has to bear the interest amount, his capital account is debited as a “ decrease in capital is debited”.
FORMULAS
The basic formula for interest on drawings is:
Interest on drawings = Amount of Drawings x Rate/100 x No. of months/12
- When equal amounts of drawings are withdrawn at the beginning of every month, then
Interest on Drawings = Total Drawings x Rate/100 x (12+1)/2 - When equal amounts of drawings are withdrawn at the end of every month, then the Interest on Drawings = Total Drawings x Rate/100 x (12-1)/2
- When the date of the drawing is not specified, it is assumed to be withdrawn evenly. Hence Interest on Drawings = Total Drawings x Rate/100 x 6/12
The calculations in 1,2 and 3 are done so that drawings can be calculated for the average period.
EXAMPLE
Jack is a partner who withdrew $20,000 on 1st April 2020. Interest on drawings is charged at 10% per annum. If we have to calculate interest on drawings as of 31st December, then
Interest on Drawings = 20,000 x 10/100 x 9/12 = $1,500
(Here, interest on drawings is outstanding for 9 months, that is from April to December)

Debit Balance A debit accounting entry represents an increase in asset or expense account or a decrease in liabilities of an individual or enterprise. Debit balance is the amount in excess of debit entries over credit entries in the general ledger. The debit balance is shown as Dr. Credit Balance ARead more
Debit Balance
A debit accounting entry represents an increase in asset or expense account or a decrease in liabilities of an individual or enterprise.
Debit balance is the amount in excess of debit entries over credit entries in the general ledger. The debit balance is shown as Dr.
Credit Balance
A credit accounting entry represents a decrease in assets or an increase in liabilities or income accounts of an individual or enterprise.
The credit balance is the amount in excess of credit entries over debit entries in the general ledger. The credit balance is shown as Cr.
Credit Balance in the Passbook
A passbook is a record of a customer’s account transactions kept by the bank. The passbook is a copy of the bank account of the customer in the books of banks. “Credit balance in the passbook is also called bank balance”.
The bank balance is the amount available for withdrawal. A bank balance is an asset to the individual or an enterprise which can be used for the purchase of another asset or payment of liability or expenses.
All the transactions either debit or credit are recorded in the passbook. When the total amount of all credit entries in a passbook is more than the total of debit entries, it results in a credit balance. It means that the bank owes to an individual or enterprise.
The amount withdrawn by a customer from the bank is shown as a debit entry and the amount deposited by the customer is shown as a credit entry. The passbook’s credit balance is a positive or favourable balance while the passbook’s debit balance is a negative balance or unfavourable balance.
For example: An individual deposited $50,000 in a bank account and withdrew a total sum of $30,000. So here, the passbook will show a bank balance of $20,000 i.e. the credit balance of the passbook. It signifies the positive cash flow of the individual and that the bank owes $20,000 to the individual.
Debit balance in Pass Book
When the total amount of all debit entries in a passbook is more than the total of credit entries, it results in a debit balance. Debit balance in the passbook is also called “Overdraft”. It means that an individual or enterprise owes to the bank.
Reconciliation
It is the process of identifying and rectifying differences between the passbook and cashbook maintained by the bank and customer respectively. The aim is to ensure the accuracy of the transaction recorded in the cashbook and passbook.
Debit Balance Reconciliation
The debit balance in the cashbook and the credit balance in the passbook shows that some outstanding cheques are in the process of clearing and these cheques need to be adjusted for reconciliation of the balance of the passbook and cashbook.
Credit Balance Reconciliation
The credit balance in the cashbook and debit balance in the passbook shows that deposits already recorded in the cashbook are yet to be recorded in the passbook by the bank and these deposits need to be adjusted in the passbook for reconciliation of the balance of the passbook and cashbook.
Conclusion
The debit and credit balance of the passbook is the indicator of the financial position of an enterprise or individual. A credit balance signifies more deposits than withdrawals resulting in a positive bank balance.
See less