Definition Contingent Asset is an asset the existence, ownership, or value of which may be known or determined only on the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more uncertain future events. However, the difference between Contingent assets is not disclosed whereas Contingent liabilities are discloRead more
Definition
Contingent Asset is an asset the existence, ownership, or value of which may be known or determined only on the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more uncertain future events.
However, the difference between Contingent assets is not disclosed whereas Contingent liabilities are disclosed by way of notes they do have different criteria for recognition which are discussed below.
For example:– a claim that an enterprise is pursuing through the legal process, where the outcome is uncertain, is a contingent asset.
Contingent liabilities are defined as obligations relating to existing conditions or situations which may arise in the future depending on the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more uncertain events.
For example:- Billis discounted but not yet matured, arrears of dividend on cum –preferences-shares, etc.
Meaning as per AS – 29
Now let me try to explain to you the meaning according to Accounting Standard 29 of the above contingent assets and liabilities which is as follows:-
• Contingent asset
A contingent asset is a possible asset that arises from past events the existence of which will be confirmed only by the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more uncertain future events.
Not wholly within the control of the enterprise.
It usually arises from unplanned or unexpected events that give rise to the possibility of an inflow of economic benefits to the enterprise.
• Contingent liability
A possible obligation that arises from past events the existence of which will be confirmed only by the occurrence or non-occurrence of one or more uncertain future events.
Not wholly within the control of the enterprise.
A present obligation that arises from past events but is not recognized because it is not probable that the outflow of resources embodying economic benefits will be required to settle the obligation or,
A reliable estimate of the amount of obligation cannot be made.
Recognition In Financial Statements
Contingent assets and liabilities are recognized as follows:-
• Contingent Assets
As per the prudence concept s well as present accounting standards, an enterprise should not recognize a contingent asset.
It is possible that the recognition of contingent assets may result in the recognition of income that may never be realized.
However, when the realization of income is virtually certain, the related asset no longer remains contingent.
• Contingent liability
As per the rules, it is not recognized by an enterprise.
When recognized?
Contingent assets are assessed continually and if it has become virtuality an outflow of economic benefits will arise.
The assets and the related income are recognized in the financial statements of the period in which the change occurs.
Contingent liability is assessed continually to determine whether an outflow of resources embodying economic benefits has become probable.
And if it becomes probable that an outflow or future economic benefits will require for an item previously dealt with as a contingent liability.
A provision is recognized in financial statements of the period in which the change probability occurs except in extremely rare circumstances where no reliable estimate can be made.
Disclosure
Now we will see how contingent assets and liability are disclosed which is mentioned below:-
• Contingent asset
These contingent assets are not disclosed in financial statements.
A contingent asset is usually disclosed in the report of the approving authority ( ie.e., Board Of Directors in the case of a company, and the corresponding approving authority in case of any enterprise), if ab inflow of economic benefits is probable.
• Contingent Assets
A contingent liability is required to be disclosed by way of a note to the balance sheet unless the possibility of an outflow of a resource embodying economic benefit is remote.
See less

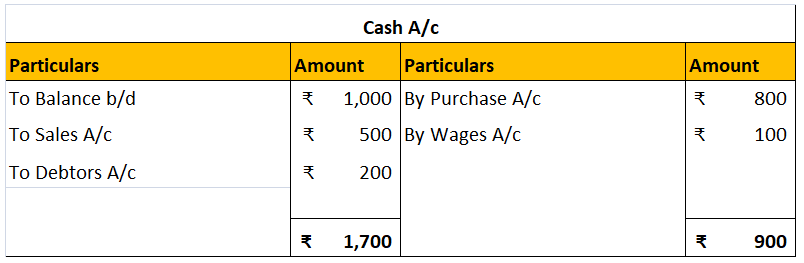
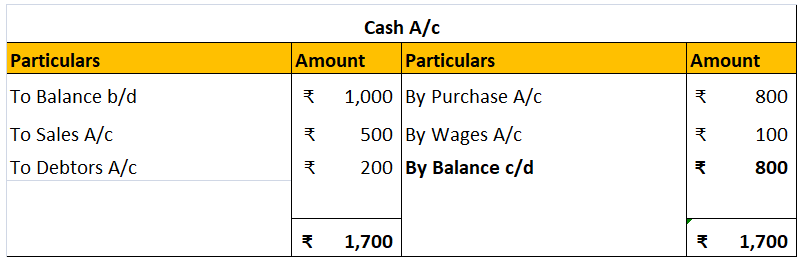
Bad Debt is the amount that is irrecoverable from the debtors. It is the portion of the receivables. It includes two accounts “Bad Debts A/c” and “Debtors A/c or Accounts Receivable A/c”. The amount cannot be recovered by the debtor for reasons like the debtor is no longer in the position to pay offRead more
Bad Debt is the amount that is irrecoverable from the debtors. It is the portion of the receivables. It includes two accounts “Bad Debts A/c” and “Debtors A/c or Accounts Receivable A/c”.
The amount cannot be recovered by the debtor for reasons like the debtor is no longer in the position to pay off the debt or has become insolvent.
There are two methods to write off bad debts:
1. Direct Method: In this method, the amount of bad debts is directly deducted from the total receivables and the second effect is transferred to the debit side of Profit and Loss A/c as an expense.
The journal entry for bad debts as per modern rules of accounting is as follows:
Journal entry for transferring bad debts to profit and loss account:
For example, A Ltd had a total receivable of Rs.2,50,000 and bad debts for the period amounted to Rs.10,000.
Here, the journal entries will be:
2. Allowance for Doubtful Debts: In this method allowance is the estimation of the debts which is doubtful to be paid. The company creates a reserve for such debts which are uncollectible.
Firstly, the company will create a reserve which will be based on the accounts receivable. The journal entry will be:
When a specific receivable is uncollectible it will be charged as an expense, and Allowance for Doubtful Debts will be “Debited” and Accounts Receivable will be “Credited”.
For example, Mr.B sold goods worth Rs.15,000 to Mr.D. He creates an allowance of Rs.15,000 in case Mr.D fails to pay the amount. At the end of the period, Mr.D defaults and does not pay the debt.
In this case, Mr.B will first record the journal entry for allowance and then will write off Mr.D’s account.