Definition Debit balance may arise due to timing differences in which case income will be accrued at the year's end to offset the debit. The amount is shown in the record of a company s finances, by which its total debits are greater than its total credits. The account which has debit balances are aRead more
Definition
Debit balance may arise due to timing differences in which case income will be accrued at the year’s end to offset the debit.
The amount is shown in the record of a company s finances, by which its total debits are greater than its total credits.
The account which has debit balances are as follows:
• Assets accounts
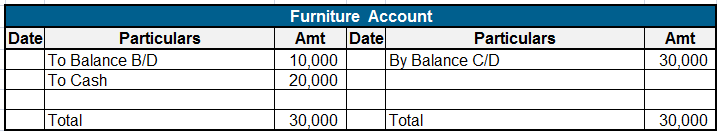
Land, furniture, building machinery, etc
• Expenses accounts
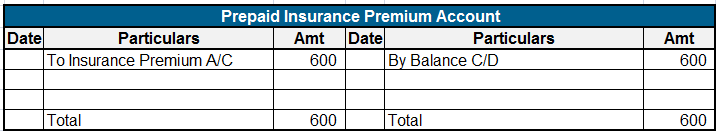
Salary, rent, insurance, etc
• Losses
Bad debts, loss by fire, etc
• Drawings
Personal drawings of cash or assets
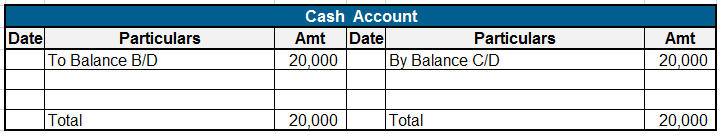
• Cash and bank balances
Balances of these accounts
In class 11th, we learned about all these accounts that have debit balances.
Where the total of the debit side is more than the credit side therefore the difference is the debit balance and is placed credit side as “ by balance c/d “
Here are some examples showing the debit balances of the accounts :

The reserves created for specific purposes in business are called specific reserves. According to the Companies Act, 2013, these reserves cannot be used for any other purposes. However, if the Article of Association of a company allows, these reserves can be used for other purposes as well. Amount tRead more
The reserves created for specific purposes in business are called specific reserves. According to the Companies Act, 2013, these reserves cannot be used for any other purposes. However, if the Article of Association of a company allows, these reserves can be used for other purposes as well.
Amount to any specific reserve is generally transferred from the Profit and Loss Appropriation Account.
Various specific reserves are:
Debentures are debt instruments of a company and they have to be redeemed, that is, paid back after the expiry of the specified period. According to Accounting Standards, companies are required to set aside a specific amount in Debenture Redemption Reserve, when they are due for redemption.
When shares or debentures are issued at a price higher than its book value/face value, the difference between the market value and book value is called Securities Premium. The amount of Securities Premium is transferred to Securities Premium Account. This amount is utilized to issue fully paid bonus shares, write off preliminary expenses, write off commission discounts, etc., to provide a premium on redemption of debentures.
The investments made by a company are subject to fluctuations in its market value. Company Law and Accounting Standards require companies to provide for such fluctuations by creating a reserve called Investment Fluctuation Reserve.
Companies are required to pay a dividend to their shareholders. It is often difficult for a company to maintain a consistent rate of dividend as the dividend paid is equivalent to the profit made by a company during the financial year which is not consistent. So, Dividend Equalisation Reserve is created to maintain a consistent rate of dividend on shares over time, in the event of both high and low profits.
See less