Business commencement with cash The term 'started the business with cash' is basically the commencement of business. In order to start any business, a certain sum of money has to be invested by the owner, which is known as the business's capital in accounting. Commencement of business refers to theRead more
Business commencement with cash
The term ‘started the business with cash’ is basically the commencement of business. In order to start any business, a certain sum of money has to be invested by the owner, which is known as the business’s capital in accounting.
Commencement of business refers to the starting or beginning of the business. In companies, it’s a declaration issued by the company’s directors with the registrar stating that the subscribers of the company have paid the amount agreed. In a sole proprietorship, the business can be commenced with the introduction of any asset such as cash, stock, furniture, etc.
Therefore, we may also call it the first journal entry of business because generally, people tend to start the business with cash rather than something else.
Journal entry
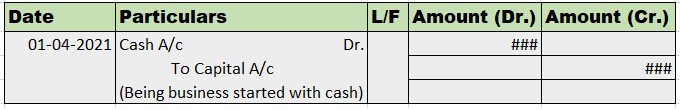
Explanation via rules
As per the golden rules of accounting, the cash a/c is debited as the rule says “debit what comes in, credit what goes out.” Whereas the capital a/c is credited because “debit all expenses and losses, credit all incomes and gains”
As per modern rules of accounting, cash is a current asset, and assets are debited when they increase. Whereas, on the increment on liabilities, they are credited, therefore, capital a/c is credited.
See less





Introduction Audit refers to an independent examination of the financial information of any entity to express an opinion on the financial statements of the entity. An audit is conducted to ensure that the financial statements of the entity whose books of accounts are audited reflect a true and fairRead more
Introduction
Audit refers to an independent examination of the financial information of any entity to express an opinion on the financial statements of the entity. An audit is conducted to ensure that the financial statements of the entity whose books of accounts are audited reflect a true and fair view of the affairs of the entity.
In audit reports, an auditor uses the term ‘true and fair’ is used to express that the financial statements are free from any kind of material misstatement and depict a correct financial image of the entity.
The term holds great significance in the audit reports of entities and auditors have to use this term carefully.
Meaning of ‘True’ and ‘Fair’
The term consists of two words, ‘True’ and ‘Fair’. Let’s understand what each of these words actually means.
True
The word ‘true’ suggests that the auditor, after examining the financial statements, has found no material misstatement whether due to error or fraud. The financial information depicted by the financial statements and the underlying accounting records is correct. The preparation and presentation of the financial statements are in accordance with the accounting standards applicable to the entity.
Fair
The word ‘fair’ means the financial information presented through the financial statement does not have an element of bias or sugar coating. There is a faithful presentation of financial information and the amounts at which the assets and liabilities, income and expenses and equity are shown is justified.
See less