Accrual accounting is an accounting method where revenue or expenses are recorded when a transaction occurs vs. when payment is received or made. The most common accrual accounting examples are sales on credit, purchases on credit, rent paid, electricity expense, depreciation, audit fees, and otherRead more
Accrual accounting is an accounting method where revenue or expenses are recorded when a transaction occurs vs. when payment is received or made. The most common accrual accounting examples are sales on credit, purchases on credit, rent paid, electricity expense, depreciation, audit fees, and other such things.
See less
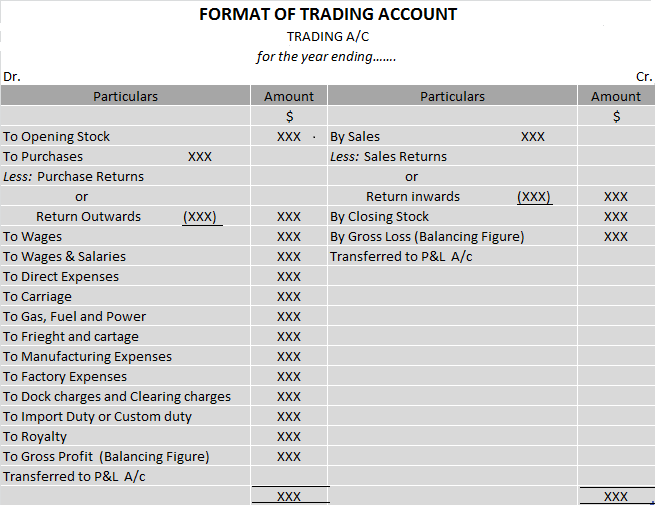
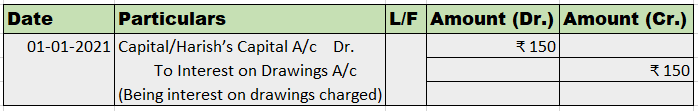
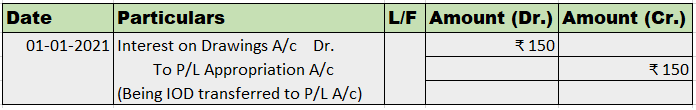

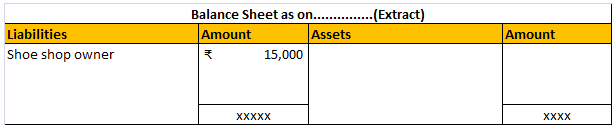

Buildings S.No. Particulars Rate 1 Buildings which are used mainly for residential purposes except hotels and boarding houses. 5% 2 Buildings other than those used mainly for residential purposes and not covered by sub-items (1) above and (3) below. 10% 3 Buildings acquired on or after the 1st day oRead more
See less