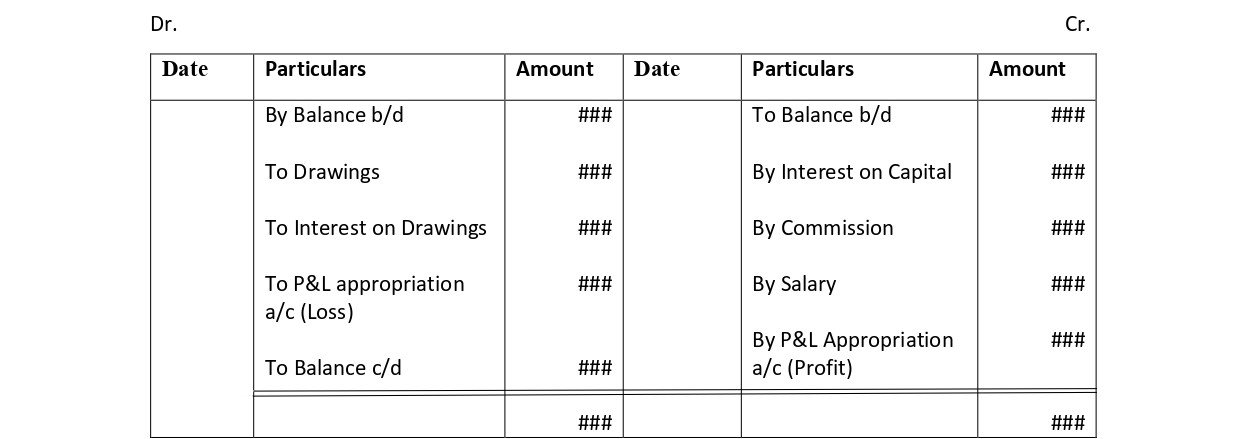
Interest on Drawings Interest on drawings is debited to the capital account. As Interest on drawings is charged on the drawings made by partners/proprietors from their respective capital accounts in a partnership firm or proprietary concern. Drawings refer to the amount withdrawn by an owner or parRead more
Interest on Drawings
Interest on drawings is debited to the capital account.
As Interest on drawings is charged on the drawings made by partners/proprietors from their respective capital accounts in a partnership firm or proprietary concern.
Drawings refer to the amount withdrawn by an owner or partner for his personal use. Thereby, interest on drawings is an income of a firm payable by the owner hence, it’s deducted/debited.
The Profit and Loss Account, on the other hand, shows the income and expenses of a business incurred over an accounting period. Accounts like interest on drawings and capital are not shown in the P&L a/c because they are internal transactions and P&L a/c focuses only on the financial statement that summarizes the revenues, costs, and expenses incurred during a specified period.
Partners’ Capital A/c
See less

Accrued expenses are those expenses that have already been incurred but not paid. The business has already received the benefit of these goods or services but is yet to pay for them. For example, X Ltd took an insurance policy on 30th September 20XX. The premium is to be paid annually on 30th SeptemRead more
Accrued expenses are those expenses that have already been incurred but not paid. The business has already received the benefit of these goods or services but is yet to pay for them.
For example,
Why does the concept of accrued expenses arise in accounting?
The concept of accrued expenses arises in accounting because accounting records transactions on an accrual and not cash basis.
Accounting on an accrual basis implies recording transactions as and when they are incurred while recording transactions on a cash basis means recording them as and when cash is actually paid for receiving those services.
For example,
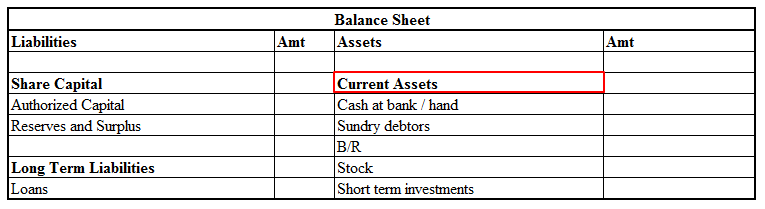
Treatment of Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses are classified as current liabilities. That is because the business has a short-term obligation to pay these expenses. The other party has a legal right to receive the amount due. In other words, accrued expenses become payable in the near term.
As current liabilities, accrued expenses are carried in the balance sheet on the liabilities side. They are also recognized in the income statement as an expense as per the concept of accrual basis of accounting.
Conclusion
Accrued expenses are the expenses for which the business has already received the benefit of goods or services but which are payable in an accounting period other than the one in which such benefit is received.
As per the accrual basis of accounting, they are recognized in the year in which the expense is incurred. The expense is carried forward as a current liability until the period in which it is actually paid.
See less