Introduction Ind AS 110 stands for Indian Accounting Standard 110. It deals with principles of preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements when an entity controls one or more other entities. It is often seen that an entity owns and controls one or more entities. Like a parent cRead more
Introduction
Ind AS 110 stands for Indian Accounting Standard 110. It deals with principles of preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements when an entity controls one or more other entities.
It is often seen that an entity owns and controls one or more entities. Like a parent company have many subsidiaries. For example, Alphabet is the parent company of Google. The parent and its subsidiaries prepare their financial statements separately to present to the true and fair view of their business.
Consolidated financial statements are the financial statements of the whole group i.e. taking the parent and its subsidiaries together. It reports the assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses of the whole group as a single economic entity.
It helps the stakeholders to know the overall performance and positions of assets and liabilities of the whole group.
When to prepare Consolidated Financial Statements(CFS)
The requirement for the preparation of CFS depends on the control model provided by Ind AS 110. As per this model, an investor controls an investee when:
- the investor is exposed to or has rights to, variable returns from its involvement with the investee and
- it has the ability to affect those returns through its power over the investee.
If both the conditions are fulfilled, then it can be said that the investor controls the investee and the investor has to prepare the consolidated financial statements with its investee. Every type of investor-investee relationship is judged as per Ind AS 110.
Exposure or right to variable returns
Variable returns mean no fixed returns and can vary as per the performance of the investee. Such returns can be both positive and negative. These returns include not only return on investment but also the benefits or expenses to which the investor is entitled to or has to bear respectively. Such returns are:
- Dividends
- Changes in the value of the investee.
- Fee for servicing investee’s assets and liabilities
- Tax benefits
- Access to proprietary knowledge
- Sourcing scare products
- Goodwill generation
It is not required by Ind AS 110 for an investor to be exposed or have the right to all such variable returns, but there should be significant exposure or right.
Power to affect the variable returns from investee
An investor has power over an investee if it has existing rights that give it direct ability to affect the relevant activities of the investee
An investor generally has many rights over the investee. These rights are of two types:
- Protective Rights: These are the rights to protect the self-interest of the investor from any risk arising from investment in the investee. Such right only protects the investor but it does not give him power over the investee. Hence, with protective rights, an investor cannot control the investee.
- Substantive Rights: These are rights with which an investor can have power over the investee. Such rights are generally the voting rights that are derived from the holding equity shares. Also having potential voting rights which are significant enough to control the investee qualify as substantive rights.
However, the investor may other substantive rights like power to appoint or remove the board of directors etc.
These rights should not only exist with investors but the investor should also have the ability to exercise such rights.
Scope of Ind AS 110
The investee can be any type of entity, the structure of the investee does not matter whether it is a partnership firm, LLP, company or any Special Purpose Entity (SPE).
If any investor control one or more other entities it will be called parent entity and it will present the consolidated financial statements.
Exemptions
If any parent entity fulfils any of these conditions, then the presentation of consolidated financial statements is not necessary:
- It is an investment entity.
- Its debt or equity securities are not listed on any recognized stock exchange or any other public market.
- It is a wholly-owned or partially owned subsidiary of another entity and all of its owners have been informed about and do not have any objections to the parent not preparing the consolidated financial statements.
- Its ultimate or any intermediate parent entity has prepared consolidated financial statements for the whole group.
- It did not file or is in process of filing its financial statement with the concerned securities commission or any other regulatory body for issuing its securities in the public market.


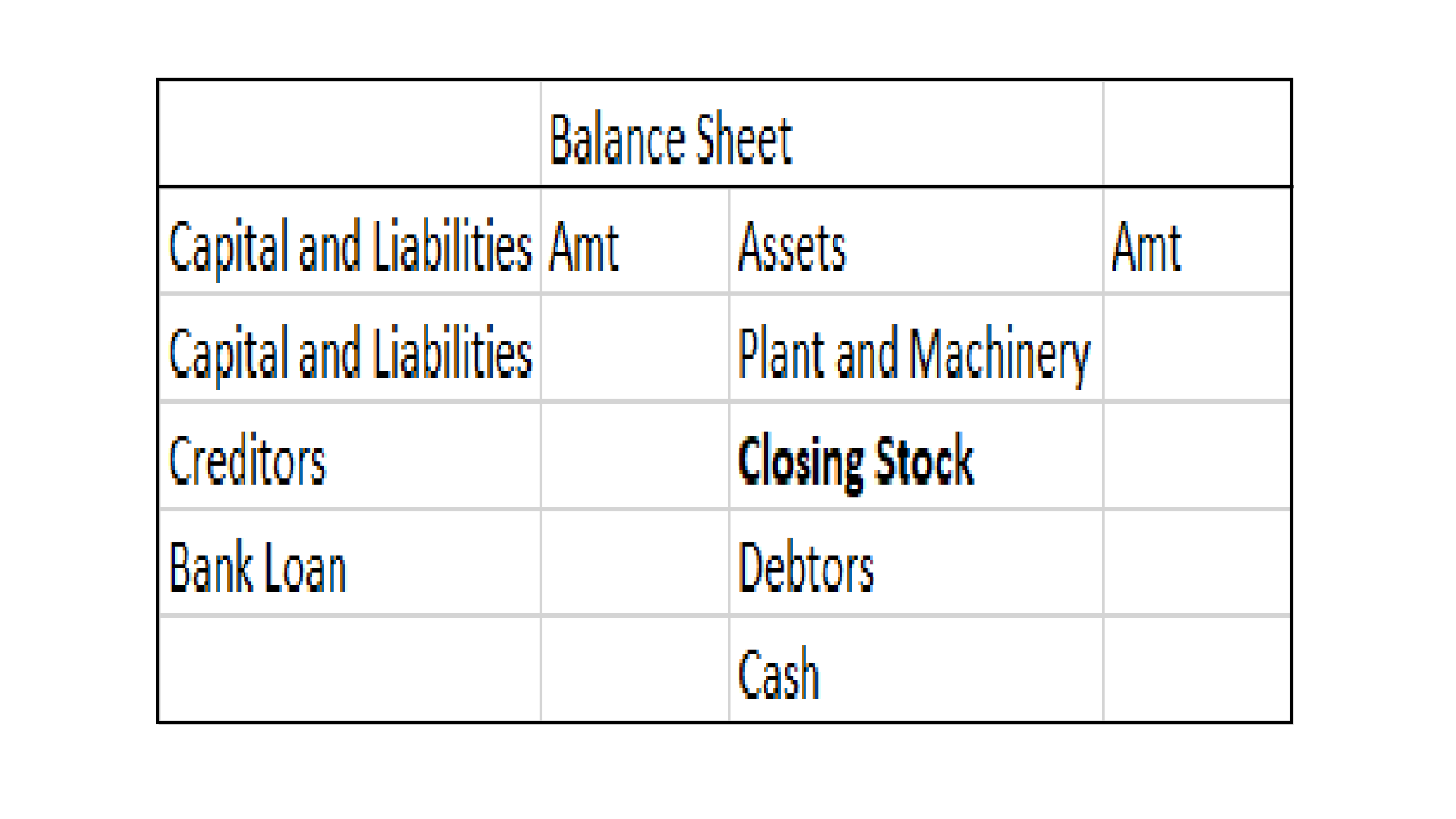
A balance sheet of a company is a financial statement that depicts the assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity of the company at a point of time, usually at the end of the accounting year. A balance sheet of a company is reported in a vertical format which is different from that of a partnershiRead more
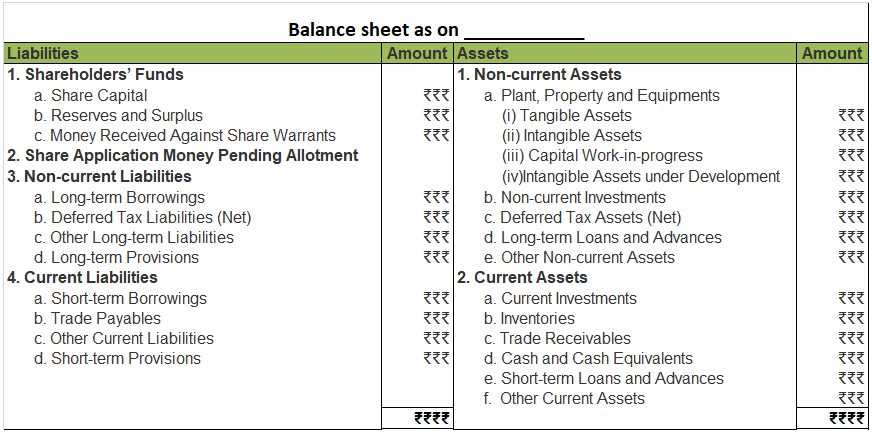
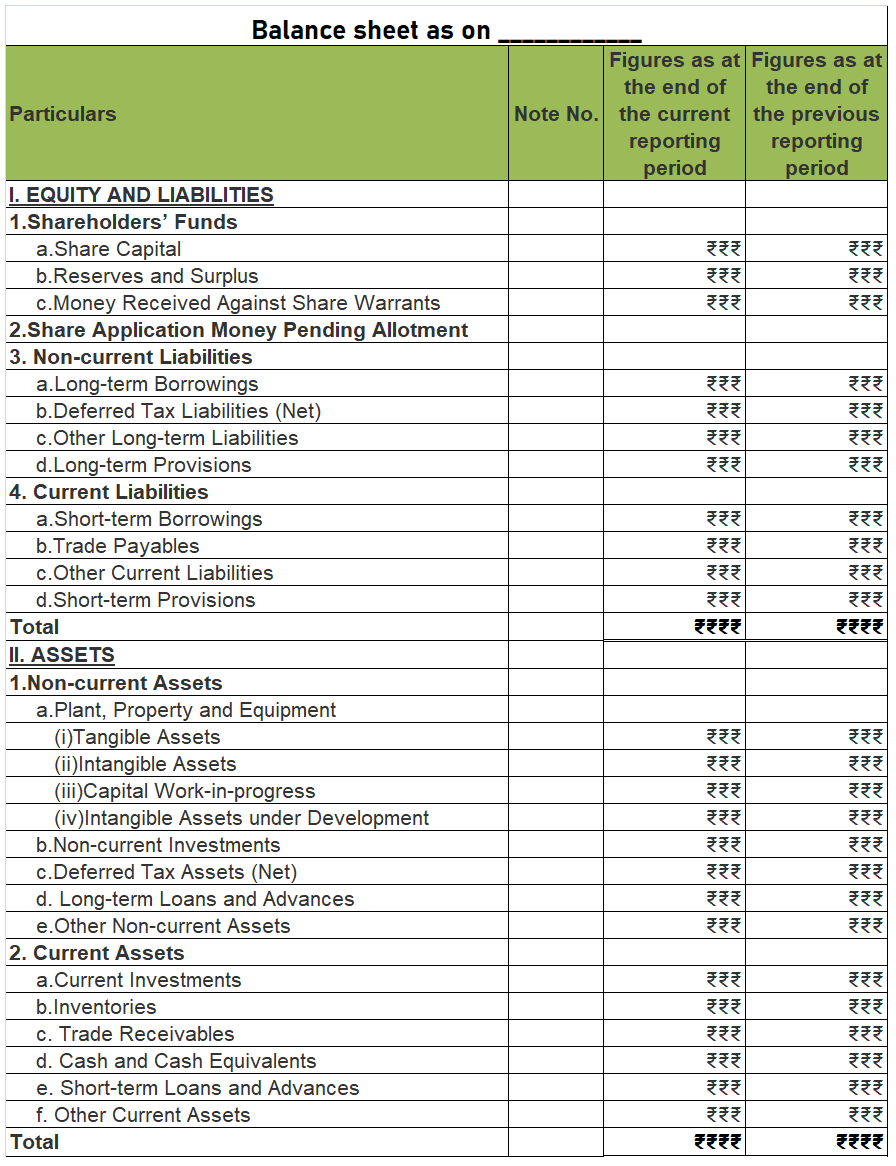
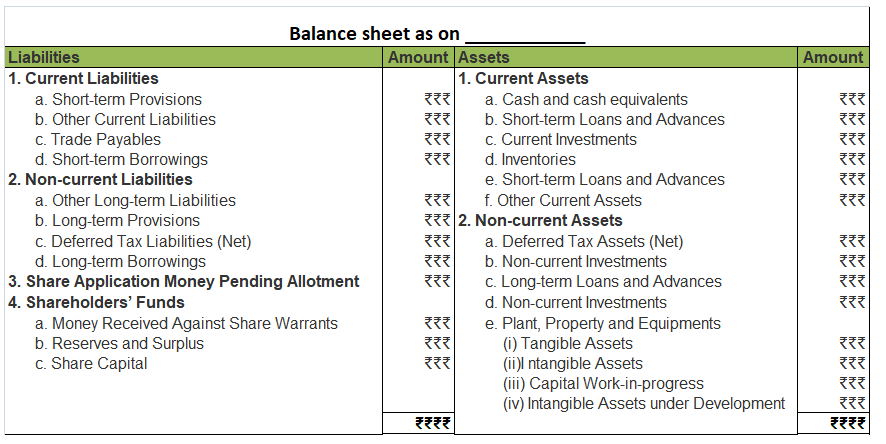
A balance sheet of a company is a financial statement that depicts the assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity of the company at a point of time, usually at the end of the accounting year. A balance sheet of a company is reported in a vertical format which is different from that of a partnership where the horizontal format is used.
COMPONENTS OF A BALANCE SHEET
The three main components of a balance sheet are Assets, Liabilities and Shareholders’ equity.
FORMAT OF BALANCE SHEET
As per the Companies Act 2013, the following format should be used for preparing a balance sheet.
From the above Balance sheet, we should get:
Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity
Relevant notes for each component should also be prepared when necessary.
See less