Introduction First, we should know what Earnings per share is. Earnings per share or EPS is the earnings available to each equity share of a company. The general formula of Earning per share is as follows: Earnings per share indicate the profit-generating capability of an enterprise and potential inRead more
Introduction
First, we should know what Earnings per share is.
Earnings per share or EPS is the earnings available to each equity share of a company. The general formula of Earning per share is as follows:
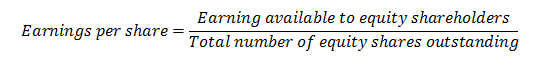 Earnings per share indicate the profit-generating capability of an enterprise and potential investors often compare the EPS of different companies to choose the best investment alternative.
Earnings per share indicate the profit-generating capability of an enterprise and potential investors often compare the EPS of different companies to choose the best investment alternative.
It is shown at the bottom of the Statement of profit and loss of a company.
Basic Earnings per share
As per AS-20, there are two types of EPS.
- Basic EPS
- Diluted EPS
Basic Earnings per share has the same meaning as given above. But the formula of basic earnings per share as per AS-20 is as follows:
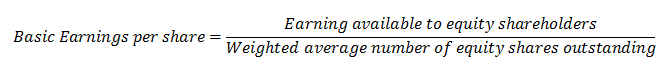
The formula of basic earnings per share is slightly different from the general formula of EPS. Here the numerator is the same as discussed above. But the denominator is different.
Here it is ‘Weight average number of equity shares outstanding’ instead of ‘Total number of equity shares outstanding.
The two components of the formula are discussed below:
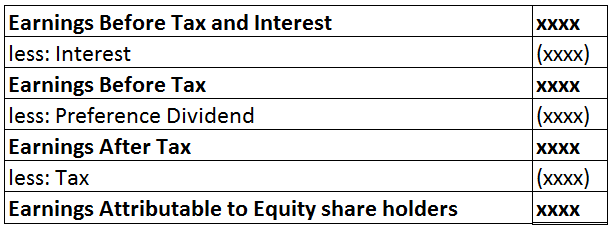
Meaning of earnings available to equity shareholders
The earnings or net profit which remains after deduction of interest payable, preference dividend, if any, and tax is known as earnings available to equity shareholders. It is calculated as shown below:
Weighted average number of equity shares outstanding
The weighted average will be calculated by applying the weight of the time period for which the numbers of shares were outstanding. Let’s see a simple case to understand the calculation of the weighted average number of equity shares outstanding:
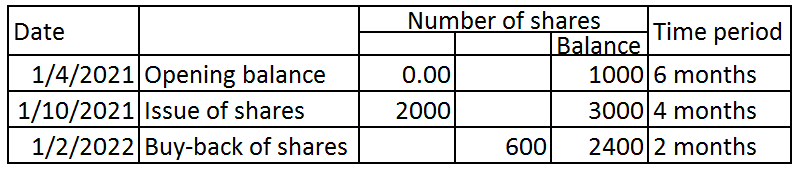
Solution:
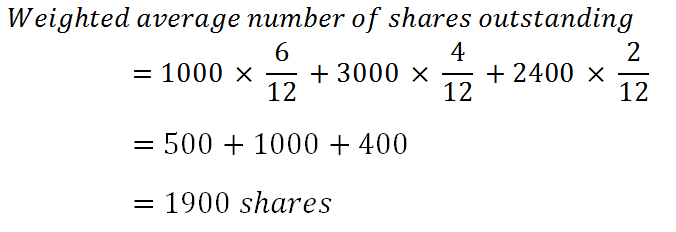
Alternative way:
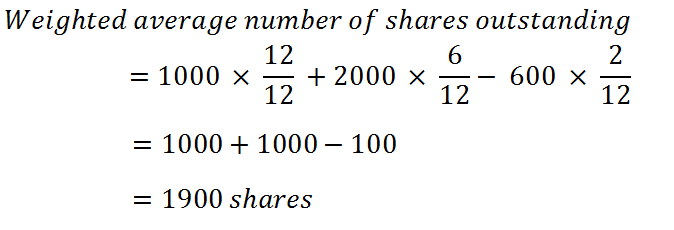
The calculation of the weighted average number of equity shares is different in special cases like:
- party paid-up shares
- bonus shares and
- right issue shares
Partly paid-up shares
Partly paid-up shares are not considered in the above calculation unless they are eligible to take part in dividends. In that case, such partly paid-up shares are included in the calculation as fractional shares.
For example, 300 equity shares of Rs. 10 each and Rs. 5 paid up will be considered as 150 shares. (300 x 5/10)
Bonus shares
We know bonus shares are issued at no cost to the shareholders. Issue of bonus shares leads to an increase in the number of equity shares without an increase in the resources.
AS-20 tells us to make adjustments to the number of shares outstanding before the issue of bonus shares as if the bonus shares were issued at the beginning of the earliest reported period. The effect will be retrospective.
Take the following example:
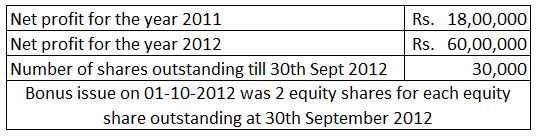
Here, number of bonus shares = 30,000 x 2 = 60,000
Therefore, EPS for 2012 = 60,00,000 /(30,000 + 60,000)= Rs. 6.67
As the earliest report period is 2011, its EPS will also have to be adjusted. Bonus issue will be treated as if it had occurred at the beginning of the earliest reported period.
Adjusted EPS for 2011= 18,00,000 / (30,000 + 60,000) = Rs. 20
Right issue
The right issue generally has an exercise price that is less than the fair value of the shares. Hence, we can say that the right issue has an element of bonus in them.
So, just like in the case of a bonus issue, we will have to adjust the number of shares outstanding before the right issue up to the earliest reported period by an adjustment factor.
The number of shares outstanding before the right issue is to be multiplied by the adjustment factor given below:
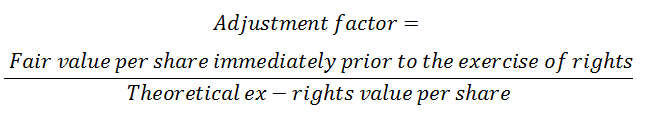
Theoretical ex-right value per share is calculated in the following way:

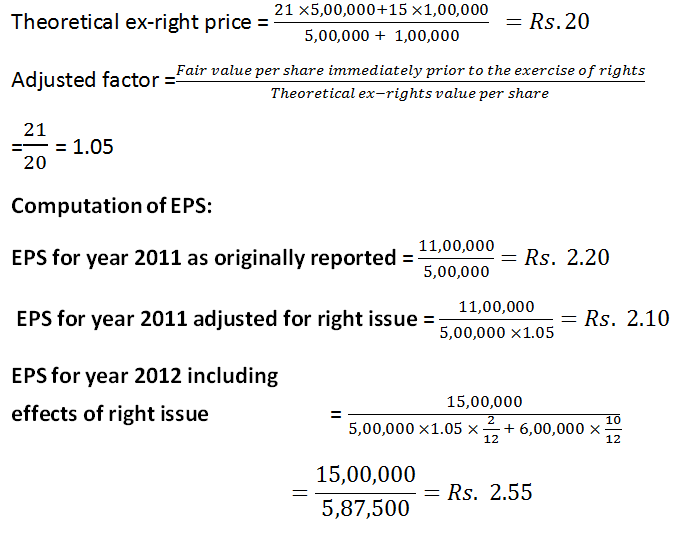
Let’s see an example:
Net profit for 2011 Rs. 11,00,000
Net profit for 2012 Rs. 15,00,000
No. of shares outstanding prior to rights issue 5,00,000 shares
Rights issue price Rs. 15
Last date to exercise rights 1st March 2012
The right issue is one new share for every 5 shares outstanding (i.e. 1,00,000 new shares)
The fair value of shares immediately prior to 1st March 2012 = Rs. 21
Solution:
See less


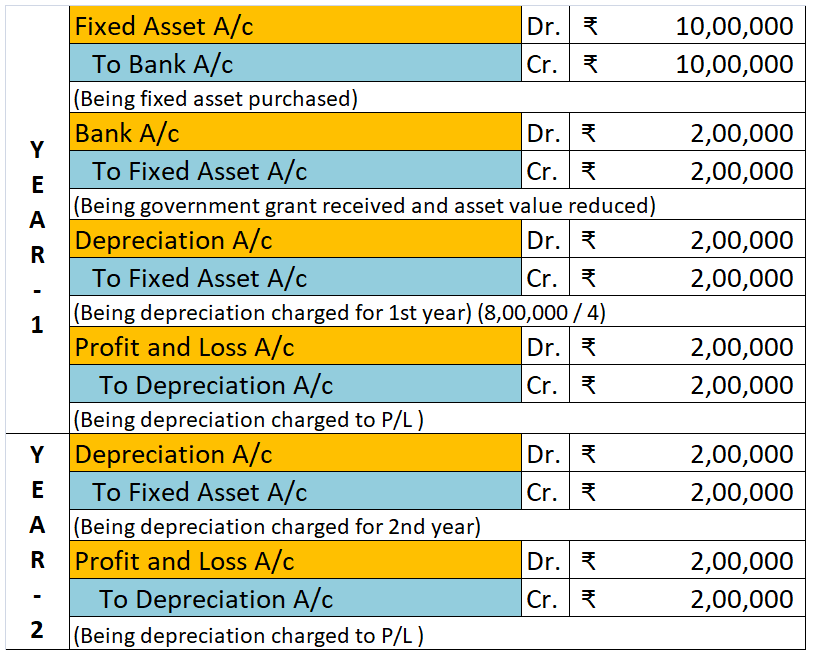
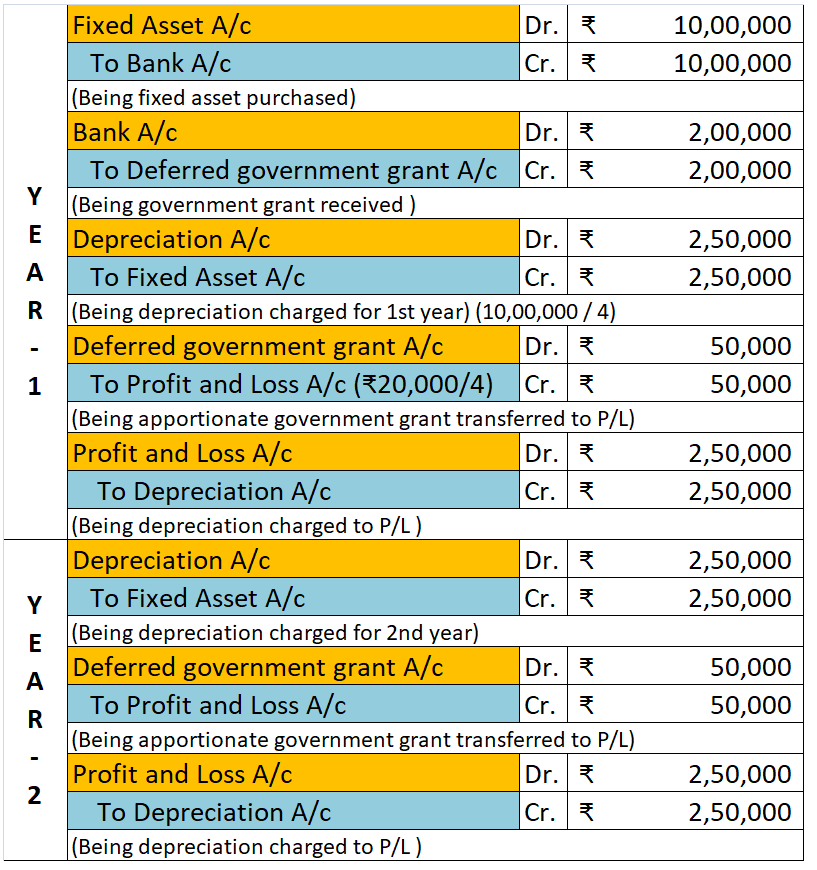
Introduction Ind AS 110 stands for Indian Accounting Standard 110. It deals with principles of preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements when an entity controls one or more other entities. It is often seen that an entity owns and controls one or more entities. Like a parent cRead more
Introduction
Ind AS 110 stands for Indian Accounting Standard 110. It deals with principles of preparation and presentation of consolidated financial statements when an entity controls one or more other entities.
It is often seen that an entity owns and controls one or more entities. Like a parent company have many subsidiaries. For example, Alphabet is the parent company of Google. The parent and its subsidiaries prepare their financial statements separately to present to the true and fair view of their business.
Consolidated financial statements are the financial statements of the whole group i.e. taking the parent and its subsidiaries together. It reports the assets, liabilities, equity, income and expenses of the whole group as a single economic entity.
It helps the stakeholders to know the overall performance and positions of assets and liabilities of the whole group.
When to prepare Consolidated Financial Statements(CFS)
The requirement for the preparation of CFS depends on the control model provided by Ind AS 110. As per this model, an investor controls an investee when:
If both the conditions are fulfilled, then it can be said that the investor controls the investee and the investor has to prepare the consolidated financial statements with its investee. Every type of investor-investee relationship is judged as per Ind AS 110.
Exposure or right to variable returns
Variable returns mean no fixed returns and can vary as per the performance of the investee. Such returns can be both positive and negative. These returns include not only return on investment but also the benefits or expenses to which the investor is entitled to or has to bear respectively. Such returns are:
It is not required by Ind AS 110 for an investor to be exposed or have the right to all such variable returns, but there should be significant exposure or right.
Power to affect the variable returns from investee
An investor has power over an investee if it has existing rights that give it direct ability to affect the relevant activities of the investee
An investor generally has many rights over the investee. These rights are of two types:
However, the investor may other substantive rights like power to appoint or remove the board of directors etc.
These rights should not only exist with investors but the investor should also have the ability to exercise such rights.
Scope of Ind AS 110
The investee can be any type of entity, the structure of the investee does not matter whether it is a partnership firm, LLP, company or any Special Purpose Entity (SPE).
If any investor control one or more other entities it will be called parent entity and it will present the consolidated financial statements.
Exemptions
If any parent entity fulfils any of these conditions, then the presentation of consolidated financial statements is not necessary:
- It is an investment entity.
- Its debt or equity securities are not listed on any recognized stock exchange or any other public market.
- It is a wholly-owned or partially owned subsidiary of another entity and all of its owners have been informed about and do not have any objections to the parent not preparing the consolidated financial statements.
- Its ultimate or any intermediate parent entity has prepared consolidated financial statements for the whole group.
- It did not file or is in process of filing its financial statement with the concerned securities commission or any other regulatory body for issuing its securities in the public market.
See less