To begin with, let me give you a brief explanation of both the terms i.e. Accounting policies and accounting principles- In order to maintain the financial statements, the company’s management adopts various Accounting Policies of its own. This generally includes the rules, the directions as to howRead more
To begin with, let me give you a brief explanation of both the terms i.e. Accounting policies and accounting principles-
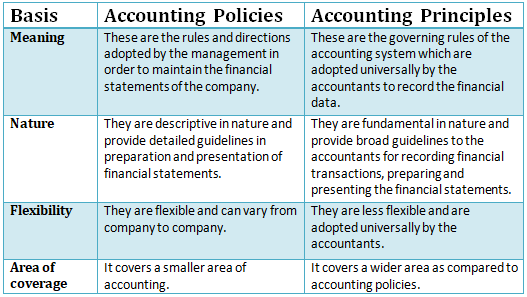
In order to maintain the financial statements, the company’s management adopts various Accounting Policies of its own. This generally includes the rules, the directions as to how the financial statements will be prepared or how the valuation of depreciation would be done, and so on. These are flexible in nature and vary from company to company.
For Example 1, Johnson Co. uses FIFO (first in first out) method to value the inventory. That is to say that, while selling its product, it sells those goods or products which it has acquired or produced first.
It does not consider the LIFO or weighted average cost. The other company may adopt the other method as per its wish.
Example 2, Johnson Co. uses the straight-line method of depreciating an asset, whereas the other company can opt for a written down value method depending upon the need of the company.
So what I am trying to explain from this is that the accounting policies are flexible and can be adopted as per the needs of the company.
Accounting Principles are the rules which the accountants adopt universally for recording and reporting the financial data. It brings uniformity in accounting throughout the practice of accounting. These are generally less flexible in nature.
For Example, “Cost” is a principle. According to this accounting principle, an asset is recorded in the books at the price paid to acquire it and this cost will be the basis for all the subsequent accounting for the asset. However, asset market value may change over time, but for the accounting purpose, it continues to be shown at its book value i.e. at which it is acquired.
Some more examples would be of Matching principle, Consistency principle, Money measurement principle, etc.
Differences
Conclusion
The point is Accounting Principles are the broad direction to reach a goal and to reach that goal helps the accounting policies.
See less
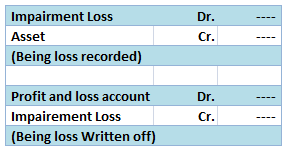
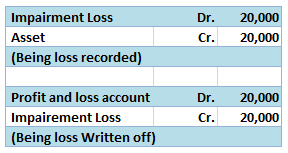
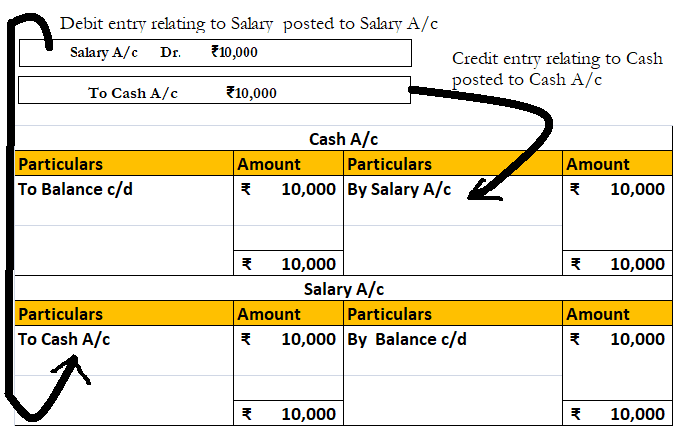
The terms outstanding expenses and accrued expenses are two accounting terms which are often used interchangeably. However, these two terms are not the same and have different meanings. The difference between these two terms is given below: What are Outstanding expenses? As the name suggests, outstaRead more
The terms outstanding expenses and accrued expenses are two accounting terms which are often used interchangeably. However, these two terms are not the same and have different meanings. The difference between these two terms is given below:
What are Outstanding expenses?
As the name suggests, outstanding expenses are the expenses that are due but have not been paid yet. It means that the business is supposed to pay the amount due but it has not paid the same at the end of the accounting period.
Outstanding expenses are recognized as a current liability because the business is liable to pay such expenses. These expenses are recorded in the books of accounts but the payment is still pending.
Some examples of outstanding expenses are:
What are Accrued expenses?
Accrued expenses are the expenses that a business has incurred during the accounting period but they have not yet been recorded in the books of accounts because the bill has not yet been received or the payment is not due yet.
The concept of Accrued expenses helps in complying with the accrual basis of accounting which says that the expense shall be recognised at the time it occurs regardless of the fact that payment is received or not.
Examples of accrued expenses are:
Key differences between outstanding expenses and accrued expenses
To summarise the above discussion, the key differences between outstanding expenses and accrued expenses are given in the table below:
See less